|
Trachyandesite
Trachyandesite is an extrusive igneous rock with a composition between trachyte and andesite. It has little or no free quartz, but is dominated by sodic plagioclase and alkali feldspar. It is formed from the cooling of lava enriched in alkali metals and with an intermediate content of silica. The term ''trachyandesite'' had begun to fall into disfavor by 1985 but was revived to describe extrusive igneous rocks falling into the S3 field of the TAS classification. These are divided into sodium-rich benmoreite and potassium-rich latite. Trachyandesitic magma can produce explosive Plinian eruptions, such as happened at Tambora in 1815. The Eyjafjallajökull 2010 eruption (VEI4), which disrupted European and transatlantic air travel from 14–18 October 2010, for some time was dominated by trachyandesite. Petrology Trachyandesite is characterized by a silica content near 58% and a total alkali oxide content near 9%. This places trachyandesite in the S3 field of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trachyandesite At Clermont-Ferrand In France
Trachyandesite is an extrusive igneous rock with a composition between trachyte and andesite. It has little or no free quartz, but is dominated by sodic plagioclase and alkali feldspar. It is formed from the cooling of lava enriched in alkali metals and with an intermediate content of silica. The term ''trachyandesite'' had begun to fall into disfavor by 1985 but was revived to describe extrusive igneous rocks falling into the S3 field of the TAS classification. These are divided into sodium-rich benmoreite and potassium-rich latite. Trachyandesitic magma can produce explosive Plinian eruptions, such as happened at Tambora in 1815. The Eyjafjallajökull 2010 eruption (VEI4), which disrupted European and transatlantic air travel from 14–18 October 2010, for some time was dominated by trachyandesite. Petrology Trachyandesite is characterized by a silica content near 58% and a total alkali oxide content near 9%. This places trachyandesite in the S3 field of the TAS di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
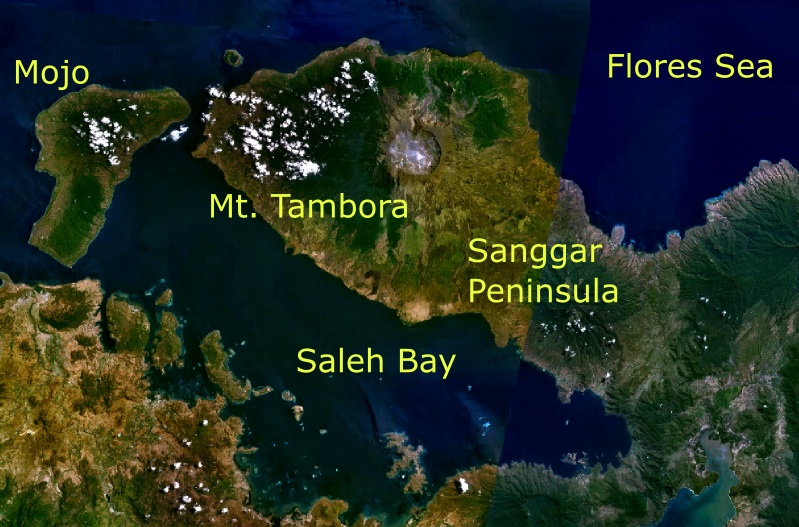
Mount Tambora
Mount Tambora, or Tomboro, is an active stratovolcano in West Nusa Tenggara, Indonesia. Located on Sumbawa in the Lesser Sunda Islands, it was formed by the active subduction zones beneath it. Before 1815, its elevation reached more than high, making it one of the tallest peaks in the Indonesian archipelago. Tambora violently erupted in a series of eruptions beginning 5 April, 1815, culminating in the largest eruption in recorded human history and the largest of the Holocene (10,000 years ago to present). The magma chamber under Tambora had been drained by previous eruptions and underwent several centuries of dormancy as it refilled. Volcanic activity reached a peak that year, culminating in an explosive eruption. The explosion was heard on Sumatra island, more than away. Heavy volcanic ash rains were observed as far away as Borneo, Sulawesi, Java, and Maluku islands, and the maximum elevation of Tambora was reduced from about to . Although estimates vary, the d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Igneous
Igneous rock (derived from the Latin word ''ignis'' meaning fire), or magmatic rock, is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic. Igneous rock is formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or lava. The magma can be derived from partial melts of existing rocks in either a planet's mantle or crust. Typically, the melting is caused by one or more of three processes: an increase in temperature, a decrease in pressure, or a change in composition. Solidification into rock occurs either below the surface as intrusive rocks or on the surface as extrusive rocks. Igneous rock may form with crystallization to form granular, crystalline rocks, or without crystallization to form natural glasses. Igneous rocks occur in a wide range of geological settings: shields, platforms, orogens, basins, large igneous provinces, extended crust and oceanic crust. Geological significance Igneous and metamorphic rocks make up 90–95% of the to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TAS Classification
The TAS classification can be used to assign names to many common types of volcanic rocks based upon the relationships between the combined alkali content and the silica content. These chemical parameters are useful, because the relative proportions of alkalis and silica play an important role in determining actual mineralogy and normative mineralogy. The classification appears to be and can be simple to use for rocks that have been chemically analyzed. Except for the following quotation from Johannsen (1937), this entry is based upon Le Maitre and others (2002). Use of the TAS classification TAS stands for Total Alkali Silica. Before using the TAS or any other classification, however, the following words of Johannsen (1937) should be kept in mind. :''Many and peculiar are the classifications that have been proposed for igneous rocks. Their variability depends in part upon the purpose for which each was intended, and in part upon the difficulties arising from the characters of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2010 Eruptions Of Eyjafjallajökull
Between March and June 2010 a series of volcanic events at Eyjafjallajökull in Iceland caused enormous disruption to air travel across Western Europe. The disruptions started over an initial period of six days in April 2010. Additional localised disruption continued into May 2010, and eruptive activity persisted until June 2010. The eruption was declared officially over in October 2010, after 3 months of inactivity, when snow on the glacier did not melt. From 14 to 20 April, ash from the volcanic eruption covered large areas of Northern Europe. About 20 countries closed their airspace to commercial jet traffic and it affected approximately 10 million travellers. Seismic activity started at the end of 2009 and gradually increased in intensity until on 20 March 2010, a small eruption began, rated as a 1 on the Volcanic Explosivity Index. Beginning on 14 April 2010, the eruption entered a second phase and created an ash cloud that led to the closure of most of the European ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benmoreite
Benmoreite is a silica-undersaturated volcanic rock of intermediate composition. It is a sodium-rich variety of trachyandesite and belongs to the alkalic suite of igneous rocks. Nepheline benmoreite An origin by fractionation from basanite through nepheline hawaiite to nepheline benmoreite has been demonstrated for a volcanic suite in the McMurdo Volcanic Group of late Cenozoic age in McMurdo Sound area of Antarctica. Nepheline benmoreite magmas derived from mantle sources, containing lherzolite xenoliths, display similarities to some plutonic nepheline syenite Nepheline syenite is a holocrystalline plutonic rock that consists largely of nepheline and alkali feldspar. The rocks are mostly pale colored, grey or pink, and in general appearance they are not unlike granites, but dark green varieties are a ...s. See also * References Petrology Intermediate rocks Volcanic rocks {{petrology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andesite
Andesite () is a volcanic rock of intermediate composition. In a general sense, it is the intermediate type between silica-poor basalt and silica-rich rhyolite. It is fine-grained (aphanitic) to porphyritic in texture, and is composed predominantly of sodium-rich plagioclase plus pyroxene or hornblende. Andesite is the extrusive equivalent of plutonic diorite. Characteristic of subduction zones, andesite represents the dominant rock type in island arcs. The average composition of the continental crust is andesitic. Along with basalts, andesites are a component of the Martian crust. The name ''andesite'' is derived from the Andes mountain range, where this rock type is found in abundance. It was first applied by Christian Leopold von Buch in 1826. Description Andesite is an aphanitic (fine-grained) igneous rock that is intermediate in its content of silica and low in alkali metals. It has less than 20% quartz and 10% feldspathoid by volume, with at least 65% of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nepheline
Nepheline, also called nephelite (), is a rock-forming mineral in the feldspathoid groupa silica-undersaturated aluminosilicate, Na3 K Al4 Si4 O16, that occurs in intrusive and volcanic rocks with low silica, and in their associated pegmatites. It is used in glass and ceramic manufacturing and other industries, and has been investigated as an ore of aluminium. Description and properties Nepheline crystals are rare and belong to the hexagonal system, usually having the form of a short, six-sided prism terminated by the basal plane. The crystals appear to have more symmetry than they actually possess, but unsymmetrical etched figures produced artificially on the prism faces indicate that the crystals are hemimorphic and tetartohedral, the only element of symmetry being a polar hexad axis. Nepheline is found in compact, granular aggregates, and can be white, yellow, gray, green, or reddish. Its hardness on the Mohs scale is 5.5–6, and its specific gravity 2.60–2.65. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyroxene
The pyroxenes (commonly abbreviated to ''Px'') are a group of important rock-forming inosilicate minerals found in many igneous and metamorphic rocks. Pyroxenes have the general formula , where X represents calcium (Ca), sodium (Na), iron (Fe II) or magnesium (Mg) and more rarely zinc, manganese or lithium, and Y represents ions of smaller size, such as chromium (Cr), aluminium (Al), magnesium (Mg), cobalt (Co), manganese (Mn), scandium (Sc), titanium (Ti), vanadium (V) or even iron (Fe II) or (Fe III). Although aluminium substitutes extensively for silicon in silicates such as feldspars and amphiboles, the substitution occurs only to a limited extent in most pyroxenes. They share a common structure consisting of single chains of silica tetrahedra. Pyroxenes that crystallize in the monoclinic system are known as clinopyroxenes and those that crystallize in the orthorhombic system are known as orthopyroxenes. The name ''pyroxene'' is derived from the Ancient Greek words for 'f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biotite
Biotite is a common group of phyllosilicate minerals within the mica group, with the approximate chemical formula . It is primarily a solid-solution series between the iron- endmember annite, and the magnesium-endmember phlogopite; more aluminous end-members include siderophyllite and eastonite. Biotite was regarded as a mineral ''species'' by the International Mineralogical Association until 1998, when its status was changed to a mineral ''group''. The term ''biotite'' is still used to describe unanalysed dark micas in the field. Biotite was named by J.F.L. Hausmann in 1847 in honor of the French physicist Jean-Baptiste Biot, who performed early research into the many optical properties of mica. Members of the biotite group are sheet silicates. Iron, magnesium, aluminium, silicon, oxygen, and hydrogen form sheets that are weakly bound together by potassium ions. The term "iron mica" is sometimes used for iron-rich biotite, but the term also refers to a flaky mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphibole
Amphibole () is a group of inosilicate minerals, forming prism or needlelike crystals, composed of double chain tetrahedra, linked at the vertices and generally containing ions of iron and/or magnesium in their structures. Its IMA symbol is Amp. Amphiboles can be green, black, colorless, white, yellow, blue, or brown. The International Mineralogical Association currently classifies amphiboles as a mineral supergroup, within which are two groups and several subgroups. Mineralogy Amphiboles crystallize into two crystal systems, monoclinic and orthorhombic. In chemical composition and general characteristics they are similar to the pyroxenes. The chief differences from pyroxenes are that (i) amphiboles contain essential hydroxyl (OH) or halogen (F, Cl) and (ii) the basic structure is a double chain of tetrahedra (as opposed to the single chain structure of pyroxene). Most apparent, in hand specimens, is that amphiboles form oblique cleavage planes (at around 120 degrees), wher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)



