|
Toxoplasmic Chorioretinitis
Toxoplasma chorioretinitis, more simply known as ocular toxoplasmosis, is possibly the most common cause of infections in the back of the eye (posterior segment) worldwide. The causitive agent is ''Toxoplasma gondii'', and in the United States, most cases are acquired congenitally. The most common symptom is decreased visual acuity in one eye. The diagnosis is made by examination of the eye, using ophthalmoscopy. Sometimes serologic testing is used to rule out the disease, but due to high rates of false positives, serologies are not diagnostic of toxoplasmic retinitis. If vision is not compromised, treatment may not be necessary. When vision is affected or threatened, treatment consists of pyrimethamine, sulfadiazine, and folinic acid for 4–6 weeks. Prednisone is sometimes used to decrease inflammation. Signs and symptoms A unilateral decrease in visual acuity is the most common symptom of toxoplasmic retinitis. Under ophthalmic examination, toxoplasmic chorioretinitis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chorioretinitis
Chorioretinitis is an inflammation of the choroid (thin pigmented vascular coat of the eye) and retina of the eye. It is a form of posterior uveitis. If only the choroid is inflamed, not the retina, the condition is termed choroiditis. The ophthalmologist's goal in treating these potentially blinding conditions is to eliminate the inflammation and minimize the potential risk of therapy to the patient. Symptoms Symptoms may include the presence of floating black spots, blurred vision, pain or redness in the eye, sensitivity to light, or excessive tearing. Causes Chorioretinitis is often caused by toxoplasmosis and cytomegalovirus infections (mostly seen in immunodeficient subjects such as people with HIV/AIDS or on immunosuppressant drugs). Congenital toxoplasmosis via transplacental transmission can also lead to sequelae such as chorioretinitis along with hydrocephalus and cerebral calcifications. Other possible causes of chorioretinitis are syphilis, sarcoidosis, tuberculosis, Be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Platelet Count
Platelets, also called thrombocytes (from Greek θρόμβος, "clot" and κύτος, "cell"), are a component of blood whose function (along with the coagulation factors) is to react to bleeding from blood vessel injury by clumping, thereby initiating a blood clot. Platelets have no cell nucleus; they are fragments of cytoplasm that are derived from the megakaryocytes of the bone marrow or lung, which then enter the circulation. Platelets are found only in mammals, whereas in other vertebrates (e.g. birds, amphibians), thrombocytes circulate as intact mononuclear cells. One major function of platelets is to contribute to hemostasis: the process of stopping bleeding at the site of interrupted endothelium. They gather at the site and, unless the interruption is physically too large, they plug the hole. First, platelets attach to substances outside the interrupted endothelium: ''adhesion''. Second, they change shape, turn on receptors and secrete chemical messengers: ''activation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AIDS
Human immunodeficiency virus infection and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (HIV/AIDS) is a spectrum of conditions caused by infection with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), a retrovirus. Following initial infection an individual may not notice any symptoms, or may experience a brief period of influenza-like illness. Typically, this is followed by a prolonged incubation period with no symptoms. If the infection progresses, it interferes more with the immune system, increasing the risk of developing common infections such as tuberculosis, as well as other opportunistic infections, and tumors which are rare in people who have normal immune function. These late symptoms of infection are referred to as acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). This stage is often also associated with unintended weight loss. HIV is spread primarily by unprotected sex (including anal and vaginal sex), contaminated blood transfusions, hypodermic needles, and from mother to child duri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spiramycin
Spiramycin is a macrolide antibiotic and antiparasitic. It is used to treat toxoplasmosis and various other infections of soft tissues. Although used in Europe, Canada and Mexico, spiramycin is still considered an experimental drug in the United States, but can sometimes be obtained by special permission from the FDA for toxoplasmosis in the first trimester of pregnancy. Another treatment option (typically used after 16w gestation) are a combination of pyrimethamine and sulfadiazine (given with leucovorin). Spiramycin has been used in Europe since the year 2000 under the trade name A trade name, trading name, or business name, is a pseudonym used by companies that do not operate under their registered company name. The term for this type of alternative name is a "fictitious" business name. Registering the fictitious name w ... "Rovamycine", produced by Rhone-Poulenc Rorer, Sanofi and Famar Lyon, France and Eczacıbaşı İlaç, Turkey. It also goes under the name Rovamycine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azithromycin
Azithromycin, sold under the brand names Zithromax (in oral form) and Azasite (as an eye drop), is an antibiotic medication used for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. This includes middle ear infections, strep throat, pneumonia, traveler's diarrhea, and certain other intestinal infections. Along with other medications, it may also be used for malaria. It can be taken by mouth or intravenously. Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea and upset stomach. An allergic reaction, such as anaphylaxis, QT prolongation, or a type of diarrhea caused by ''Clostridium difficile'' is possible. No harm has been found with its use during pregnancy. Its safety during breastfeeding is not confirmed, but it is likely safe. Azithromycin is an azalide, a type of macrolide antibiotic. It works by decreasing the production of protein, thereby stopping bacterial growth. Azithromycin was discovered in 1980 by the Yugoslav pharmaceutical company Pliva and approved f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clindamycin
Clindamycin is an antibiotic medication used for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections, including osteomyelitis (bone) or joint infections, pelvic inflammatory disease, strep throat, pneumonia, acute otitis media (middle ear infections), and endocarditis. It can also be used to treat acne, and some cases of methicillin-resistant ''Staphylococcus aureus'' (MRSA). In combination with quinine, it can be used to treat malaria. It is available by mouth, by injection into a vein, and as a cream or a gel to be applied to the skin or in the vagina. Common side effects include nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, rashes, and pain at the site of injection. It increases the risk of hospital-acquired ''Clostridium difficile'' colitis about fourfold and thus is only recommended when other antibiotics are not appropriate. Alternative antibiotics may be recommended as a result. It appears to be generally safe in pregnancy. It is of the lincosamide class and works by blocking bacter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bactrim
Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole, sold under the brand name Bactrim among others, is a fixed-dose combination antibiotic medication used to treat a variety of bacterial infections. It consists of one part trimethoprim to five parts sulfamethoxazole. It is used to treat urinary tract infections, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) skin infections, travelers' diarrhea, respiratory tract infections, and cholera, among others. It is used both to treat and prevent pneumocystis pneumonia and toxoplasmosis in people with HIV/AIDS and other causes of immunosuppression. It can be given by mouth or intravenously. Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines and is also available as a generic medication. In 2020, it was the 121st most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 5million prescriptions. Medical uses ''Pneumocystis jirovecii'' pneumonia Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (TMP/SMX) is t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
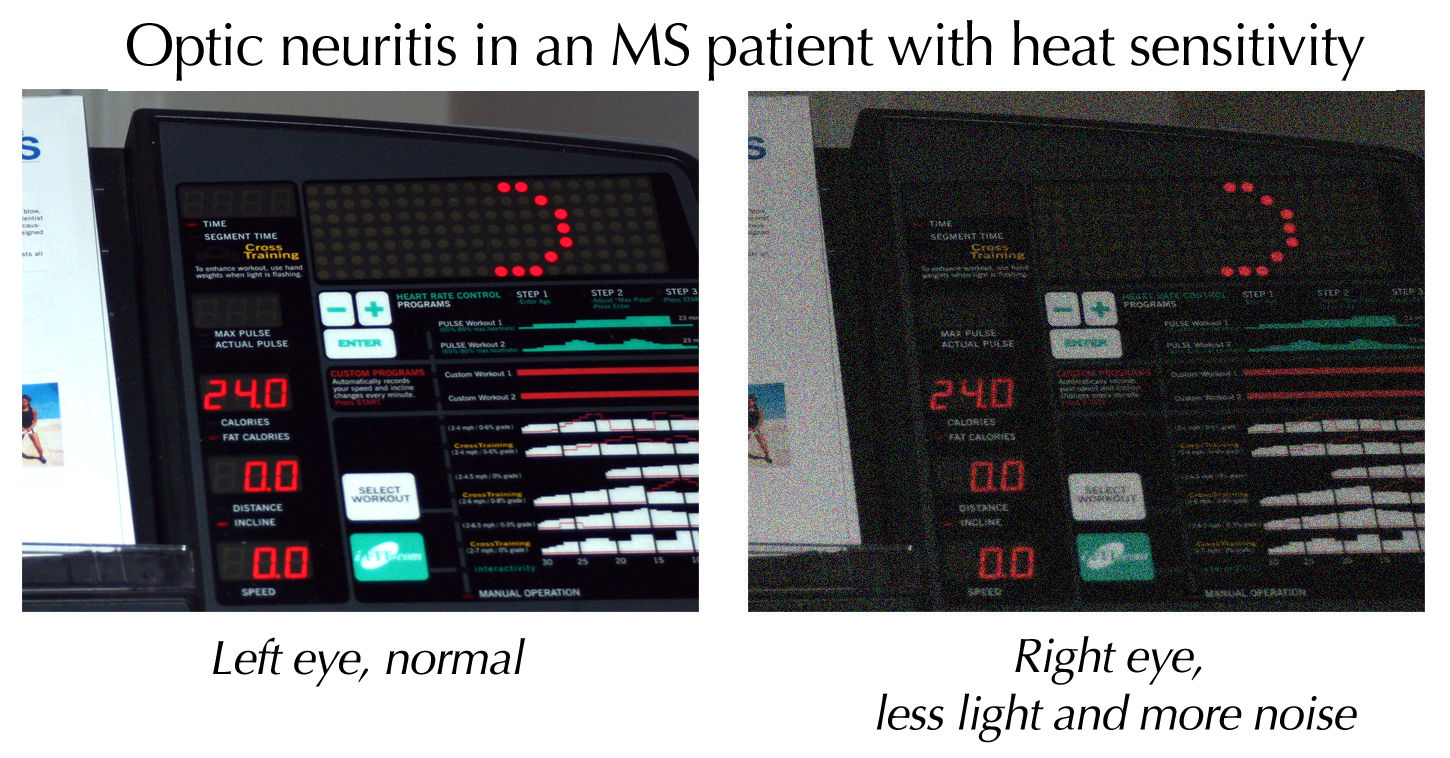
Optic Neuritis
Optic neuritis describes any condition that causes inflammation of the optic nerve; it may be associated with demyelinating diseases, or infectious or inflammatory processes. It is also known as optic papillitis (when the head of the optic nerve is involved), neuroretinitis (when there is a combined involvement of the optic disc and surrounding retina in the macular area) and retrobulbar neuritis (when the posterior part of the nerve is involved). Prelaminar optic neuritis describes involvement of the non-myelinated axons in the retina. It is most often associated with multiple sclerosis, and it may lead to complete or partial loss of vision in one or both eyes. Other causes include: # Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy # Parainfectious optic neuritis (associated with viral infections such as measles, mumps, chickenpox, whooping cough and glandular fever) # Infectious optic neuritis (sinus related or associated with cat-scratch fever, tuberculosis, Lyme disease and crypt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prednisone
Prednisone is a glucocorticoid medication mostly used to immunosuppressive drug, suppress the immune system and decrease inflammation in conditions such as asthma, COPD, and rheumatologic diseases. It is also used to treat high blood calcium due to cancer and adrenal insufficiency along with other steroids. It is taken Oral administration, by mouth. Common side effects with long-term use include cataracts, Osteoporosis, bone loss, easy bruising, muscle weakness, and oral candidiasis, thrush. Other side effects include weight gain, swelling, high blood sugar, increased risk of infection, and psychosis. It is generally considered safe in pregnancy and low doses appear to be safe when breastfeeding. After prolonged use, prednisone needs to be stopped gradually. Prednisone is a prodrug and must be converted to prednisolone by the liver before it becomes active. Prednisolone then binds to glucocorticoid receptors, activating them and triggering changes in gene expression. Pred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Folinic Acid
Folinic acid, also known as leucovorin, is a medication used to decrease the toxic effects of methotrexate and pyrimethamine. It is also used in combination with 5-fluorouracil to treat colorectal cancer and pancreatic cancer, may be used to treat folate deficiency that results in anemia, and methanol poisoning. It is taken by mouth, injection into a muscle, or injection into a vein. Side effects may include trouble sleeping, allergic reactions, or fever. Use in pregnancy or breastfeeding is generally regarded as safe. When used for anemia it is recommended that pernicious anemia as a cause be ruled out first. Folinic acid is a form of folic acid that does not require activation by dihydrofolate reductase to be useful to the body. Folinic acid was first made in 1945. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Medical use Folinic acid is given following methotrexate as part of a total chemotherapeutic plan, where it may protect against bone marro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leukocyte Count
White blood cells, also called leukocytes or leucocytes, are the cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign invaders. All white blood cells are produced and derived from multipotent cells in the bone marrow known as hematopoietic stem cells. Leukocytes are found throughout the body, including the blood and lymphatic system. All white blood cells have nuclei, which distinguishes them from the other blood cells, the anucleated red blood cells (RBCs) and platelets. The different white blood cells are usually classified by cell lineage (myeloid cells or lymphoid cells). White blood cells are part of the body's immune system. They help the body fight infection and other diseases. Types of white blood cells are granulocytes (neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils), and agranulocytes (monocytes, and lymphocytes (T cells and B cells)). Myeloid cells (myelocytes) include neutrophils, eosinophils, mast cells, basophi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toxoplasma Gondii
''Toxoplasma gondii'' () is an obligate intracellular parasitic protozoan (specifically an apicomplexan) that causes toxoplasmosis. Found worldwide, ''T. gondii'' is capable of infecting virtually all warm-blooded animals, but felids, such as domestic cats, are the only known definitive hosts in which the parasite may undergo sexual reproduction. ''T. gondii'' has been shown to alter the behavior of infected rodents in ways that increase the rodents' chances of being preyed upon by felids. Support for this "manipulation hypothesis" stems from studies showing that ''T. gondii''-infected rats have a decreased aversion to cat urine. Because cats are the only hosts within which ''T. gondii'' can sexually reproduce to complete and begin its lifecycle, such behavioral manipulations are thought to be evolutionary adaptations that increase the parasite's reproductive success. Rats that do not avoid cat habitations will more likely become cat prey. ''Toxoplasma gondii'' infection i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |