|
Total Factor Productivity
In economics, total-factor productivity (TFP), also called multi-factor productivity, is usually measured as the ratio of aggregate output (e.g., GDP) to aggregate inputs. Under some simplifying assumptions about the production technology, growth in TFP becomes the portion of growth in output not explained by growth in traditionally measured inputs of labour and capital used in production. TFP is calculated by dividing output by the weighted geometric average of labour and capital input, with the standard weighting of 0.7 for labour and 0.3 for capital. Total factor productivity is a measure of productive efficiency in that it measures how much output can be produced from a certain amount of inputs. It accounts for part of the differences in cross-country per-capita income. For relatively small percentage changes, the rate of ''TFP'' growth can be estimated by subtracting growth rates of labor and capital inputs from the growth rate of output. Background Technology growth and e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economics
Economics () is the social science that studies the Production (economics), production, distribution (economics), distribution, and Consumption (economics), consumption of goods and services. Economics focuses on the behaviour and interactions of Agent (economics), economic agents and how economy, economies work. Microeconomics analyzes what's viewed as basic elements in the economy, including individual agents and market (economics), markets, their interactions, and the outcomes of interactions. Individual agents may include, for example, households, firms, buyers, and sellers. Macroeconomics analyzes the economy as a system where production, consumption, saving, and investment interact, and factors affecting it: employment of the resources of labour, capital, and land, currency inflation, economic growth, and public policies that have impact on glossary of economics, these elements. Other broad distinctions within economics include those between positive economics, desc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy Conversion Efficiency
Energy conversion efficiency (''η'') is the ratio between the useful output of an energy conversion machine and the input, in energy terms. The input, as well as the useful output may be chemical, electric power, mechanical work, light (radiation), or heat. The resulting value, ''η'' (eta), ranges between 0 and 1. Overview Energy conversion efficiency depends on the usefulness of the output. All or part of the heat produced from burning a fuel may become rejected waste heat if, for example, work is the desired output from a thermodynamic cycle. Energy converter is an example of an energy transformation. For example, a light bulb falls into the categories energy converter. \eta = \frac Even though the definition includes the notion of usefulness, efficiency is considered a technical or physical term. Goal or mission oriented terms include effectiveness and efficacy. Generally, energy conversion efficiency is a dimensionless number between 0 and 1.0, or 0% to 100%. Ef ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Easterly
William Russell Easterly (born September 7, 1957) is an American economist, specializing in economic development. He is a professor of economics at New York University, joint with Africa House, and co-director of NYU’s Development Research Institute. He is a Research Associate of NBER, senior fellow at the Bureau for Research and Economic Analysis of Development (BREAD) of Duke University, and a nonresident senior fellow at the Brookings Institution in Washington DC. Easterly is an associate editor of the ''Journal of Economic Growth''. Easterly is the author of three books: '' The Elusive Quest for Growth: Economists’ Adventures and Misadventures in the Tropics'' (2001); ''The White Man’s Burden: Why the West’s Efforts to Aid the Rest Have Done So Much Ill and So Little Good'' (2006), which won the 2008 Hayek Prize; and ''The Tyranny of Experts: Economists, Dictators, and the Forgotten Rights of the Poor'' (2014), which was a finalist for the 2015 Hayek Prize. Biography ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ross Levine
Ross Levine (born April 16, 1960) is an American economist who currently holds the Willis H. Booth Chair in Banking and Finance at the University of California at Berkeley. He is also a senior fellow at the Milken Institute, a member of the Council on Foreign Relations, and an advisor to the World Economic Forum. As of 2018, he is the 12th most cited economist in the world. Education He received his B.A. in economics from Cornell University in 1982, graduating Phi Beta Kappa. He completed his Ph.D. at UCLA in 1987. Career Upon completion of his doctorate, he began work as an economist for the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System. From 1990 to 1997, he was a principal economist at The World Bank. He became an associate professor at the University of Virginia in 1997 and was granted tenure two years later. From 1999 to 2005, he was the Curtis L. Carlson Professor of Finance at the University of Minnesota. In 2005, he was hired by the department of economics at Brown ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
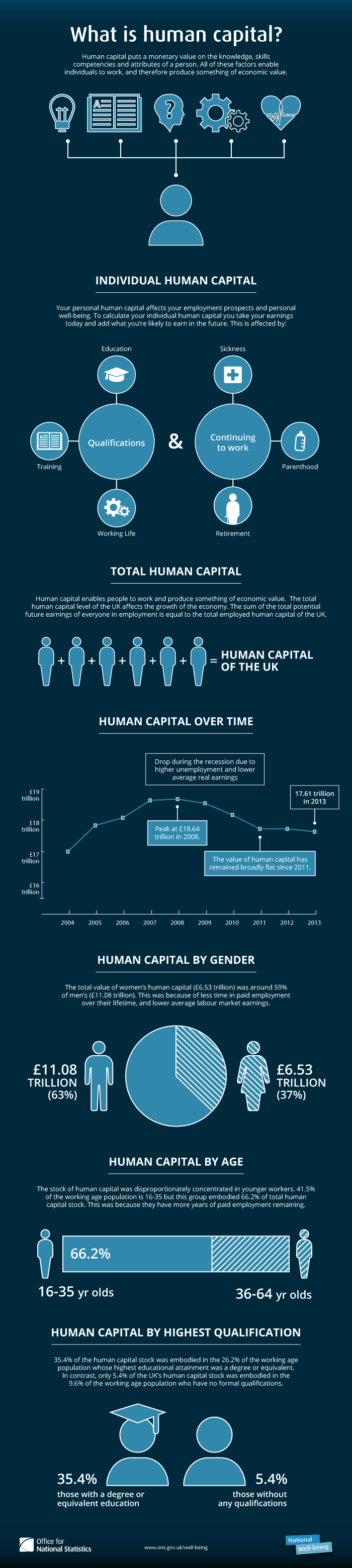
Human Capital
Human capital is a concept used by social scientists to designate personal attributes considered useful in the production process. It encompasses employee knowledge, skills, know-how, good health, and education. Human capital has a substantial impact on individual earnings. Research indicates that human capital investments have high economic returns throughout childhood and young adulthood. Companies can invest in human capital, for example, through education and training, enabling improved levels of quality and production. As a result of his conceptualization and modeling work using Human Capital as a key factor, the 2018 Nobel Prize for Economics was jointly awarded to Paul Romer, who founded the modern innovation-driven approach to understanding economic growth. In the recent literature, the new concept of task-specific human capital was coined in 2004 by Robert Gibbons, an economist at MIT, and Michael Waldman, an economist at Cornell University. The concept emphasizes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Growth Accounting
Growth accounting is a procedure used in economics to measure the contribution of different factors to economic growth and to indirectly compute the rate of technological progress, measured as a residual, in an economy. Growth accounting decomposes the growth rate of an economy's total output into that which is due to increases in the contributing amount of the factors used—usually the increase in the amount of capital and labor—and that which cannot be accounted for by observable changes in factor utilization. The unexplained part of growth in GDP is then taken to represent increases in productivity (getting more output with the same amounts of inputs) or a measure of broadly defined technological progress. The technique has been applied to virtually every economy in the world and a common finding is that observed levels of economic growth cannot be explained simply by changes in the stock of capital in the economy or population and labor force growth rates. Hence, technologica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capital Controversy
The Cambridge capital controversy, sometimes called "the capital controversy"Brems (1975) pp. 369-384 or "the two Cambridges debate", was a dispute between proponents of two differing theoretical and mathematical positions in economics that started in the 1950s and lasted well into the 1960s. The debate concerned the nature and role of capital goods and a critique of the neoclassical vision of aggregate production and distribution.Tcherneva (2011) The name arises from the location of the principals involved in the controversy: the debate was largely between economists such as Joan Robinson and Piero Sraffa at the University of Cambridge in England and economists such as Paul Samuelson and Robert Solow at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. The English side is most often labeled "post-Keynesian", while some call it " neo-Ricardian", and the Massachusetts side " neoclassical". Most of the debate is mathematical, while some major ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimensional Analysis
In engineering and science, dimensional analysis is the analysis of the relationships between different physical quantities by identifying their base quantities (such as length, mass, time, and electric current) and units of measure (such as miles vs. kilometres, or pounds vs. kilograms) and tracking these dimensions as calculations or comparisons are performed. The conversion of units from one dimensional unit to another is often easier within the metric or the SI than in others, due to the regular 10-base in all units. ''Commensurable'' physical quantities are of the same kind and have the same dimension, and can be directly compared to each other, even if they are expressed in differing units of measure, e.g. yards and metres, pounds (mass) and kilograms, seconds and years. ''Incommensurable'' physical quantities are of different kinds and have different dimensions, and can not be directly compared to each other, no matter what units they are expressed in, e.g. metres and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Units Of Measurement
A unit of measurement is a definite magnitude (mathematics), magnitude of a quantity, defined and adopted by convention or by law, that is used as a standard for measurement of the same kind of quantity. Any other quantity of that kind can be expressed as a multiple of the unit of measurement. For example, a length is a physical quantity. The metre (symbol m) is a unit of length that represents a definite predetermined length. For instance, when referencing "10 metres" (or 10 m), what is actually meant is 10 times the definite predetermined length called "metre". The definition, agreement, and practical use of units of measurement have played a crucial role in human endeavour from early ages up to the present. A multitude of System of measurement, systems of units used to be very common. Now there is a global standard, the International System of Units (SI), the modern form of the metric system. In trade, weights and measures is often a subject of governmental r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Widget (economics)
Placeholder names are words that can refer to things or people whose names do not exist, are temporarily forgotten, are not relevant to the salient point at hand, are to avoid stigmatization, are unknowable/unpredictable in the context in which they are being discussed, or are otherwise de-emphasized whenever the speaker or writer is unable to, or chooses not to, specify precisely. Placeholder names for people are often terms referring to an average person or a predicted persona of a typical user. Linguistic role These placeholders typically function grammatically as nouns and can be used for people (e.g. '' John Doe, Jane Doe''), objects (e.g. '' widget''), locations ("Main Street"), or places (e.g. ''Anytown, USA''). They share a property with pronouns, because their referents must be supplied by context; but, unlike a pronoun, they may be used with no referent—the important part of the communication is not the thing nominally referred to by the placeholder, but t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Productivity Model
Productivity in economics is usually measured as the ratio of what is produced (an aggregate output) to what is used in producing it (an aggregate input). Productivity is closely related to the measure of production efficiency. A productivity model is a measurement method which is used in practice for measuring productivity. A productivity model must be able to compute ''Output / Input'' when there are many different outputs and inputs. Comparison of the productivity models The principle of comparing productivity models is to identify the characteristics that are present in the models and to understand their differences. This task is alleviated by the fact that such characteristics can unmistakably be identified by their measurement formula. Bases on the model comparison, it is possible to identify the models that are suited for measuring productivity. A criterion of this solution is the production theory and the production function. It is essential that the model is able to descr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |