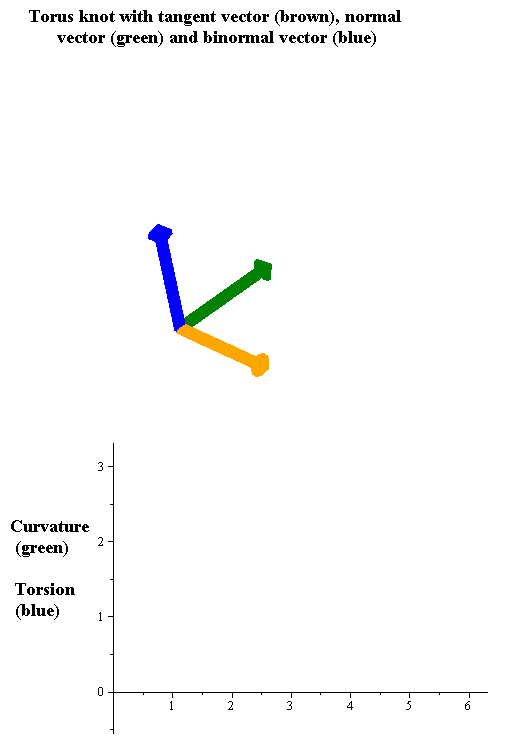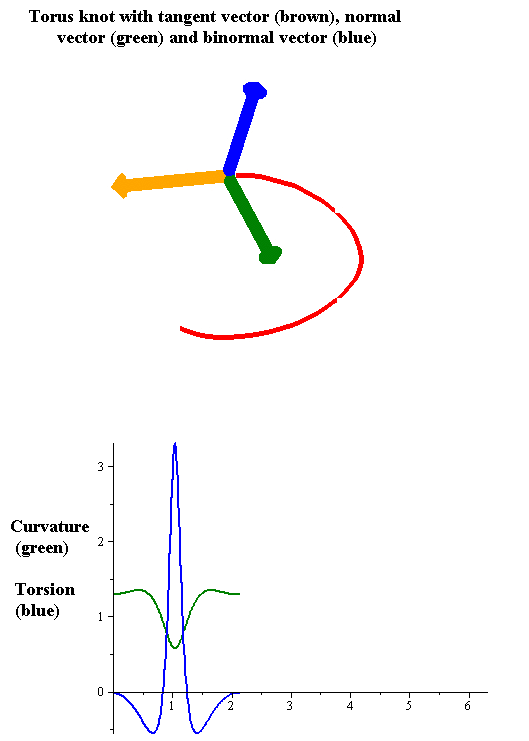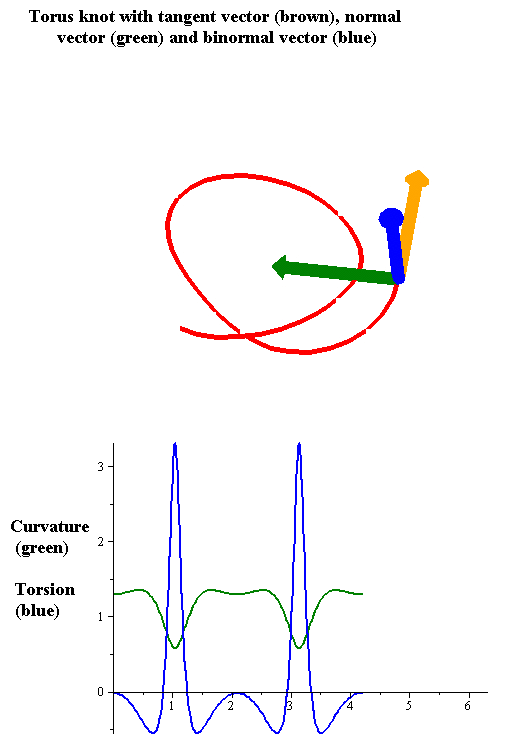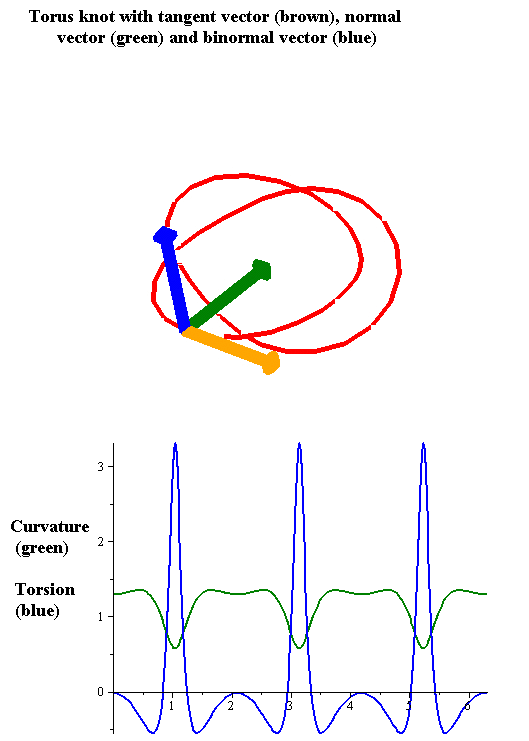
|
Torsion Of A Curve
In the differential geometry of curves in three dimensions, the torsion of a curve measures how sharply it is twisting out of the osculating plane. Taken together, the curvature and the torsion of a space curve are analogous to the curvature of a plane curve. For example, they are coefficients in the system of differential equations for the Frenet frame given by the Frenet–Serret formulas. Definition Let be a space curve parametrized by arc length and with the unit tangent vector . If the curvature of at a certain point is not zero then the principal normal vector and the binormal vector at that point are the unit vectors : \mathbf=\frac, \quad \mathbf=\mathbf\times\mathbf respectively, where the prime denotes the derivative of the vector with respect to the parameter . The torsion measures the speed of rotation of the binormal vector at the given point. It is found from the equation : \mathbf' = -\tau\mathbf. which means : \tau = -\mathbf\cdot\mathbf'. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Differential Geometry Of Curves
Differential geometry of curves is the branch of geometry that deals with smooth curves in the plane and the Euclidean space by methods of differential and integral calculus. Many specific curves have been thoroughly investigated using the synthetic approach. Differential geometry takes another path: curves are represented in a parametrized form, and their geometric properties and various quantities associated with them, such as the curvature and the arc length, are expressed via derivatives and integrals using vector calculus. One of the most important tools used to analyze a curve is the Frenet frame, a moving frame that provides a coordinate system at each point of the curve that is "best adapted" to the curve near that point. The theory of curves is much simpler and narrower in scope than the theory of surfaces and its higher-dimensional generalizations because a regular curve in a Euclidean space has no intrinsic geometry. Any regular curve may be parametrized by the a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Curves
A curve is a geometrical object in mathematics. Curve(s) may also refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media Music * Curve (band), an English alternative rock music group * ''Curve'' (album), a 2012 album by Our Lady Peace * "Curve" (song), a 2017 song by Gucci Mane featuring The Weeknd * ''Curve'', a 2001 album by Doc Walker * "Curve", a song by John Petrucci from ''Suspended Animation'', 2005 * "Curve", a song by Cam'ron from the album '' Crime Pays'', 2009 Periodicals * ''Curve'' (design magazine), an industrial design magazine * ''Curve'' (magazine), a U.S. lesbian magazine Other uses in arts, entertainment, and media * ''Curve'' (film), a 2015 film * BBC Two 'Curve' idents, various animations based around a curve motif Brands and enterprises *Curve (payment card), a payment card that aggregates multiple payment cards * Curve (theatre), a theatre in Leicester, United Kingdom * Curve, fragrance by Liz Claiborne * BlackBerry Curve, a series of phones from Research in Motio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Differential Geometry
Differential geometry is a mathematical discipline that studies the geometry of smooth shapes and smooth spaces, otherwise known as smooth manifolds. It uses the techniques of differential calculus, integral calculus, linear algebra and multilinear algebra. The field has its origins in the study of spherical geometry as far back as antiquity. It also relates to astronomy, the geodesy of the Earth, and later the study of hyperbolic geometry by Lobachevsky. The simplest examples of smooth spaces are the plane and space curves and surfaces in the three-dimensional Euclidean space, and the study of these shapes formed the basis for development of modern differential geometry during the 18th and 19th centuries. Since the late 19th century, differential geometry has grown into a field concerned more generally with geometric structures on differentiable manifolds. A geometric structure is one which defines some notion of size, distance, shape, volume, or other rigidifying structu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Springer-Verlag
Springer Science+Business Media, commonly known as Springer, is a German multinational publishing company of books, e-books and peer-reviewed journals in science, humanities, technical and medical (STM) publishing. Originally founded in 1842 in Berlin, it expanded internationally in the 1960s, and through mergers in the 1990s and a sale to venture capitalists it fused with Wolters Kluwer and eventually became part of Springer Nature in 2015. Springer has major offices in Berlin, Heidelberg, Dordrecht, and New York City. History Julius Springer founded Springer-Verlag in Berlin in 1842 and his son Ferdinand Springer grew it from a small firm of 4 employees into Germany's then second largest academic publisher with 65 staff in 1872.Chronology ". Springer Science+Business Media. In 1964, Springer expanded its business internationally, o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cross Product
In mathematics, the cross product or vector product (occasionally directed area product, to emphasize its geometric significance) is a binary operation on two vectors in a three-dimensional oriented Euclidean vector space (named here E), and is denoted by the symbol \times. Given two linearly independent vectors and , the cross product, (read "a cross b"), is a vector that is perpendicular to both and , and thus normal to the plane containing them. It has many applications in mathematics, physics, engineering, and computer programming. It should not be confused with the dot product (projection product). If two vectors have the same direction or have the exact opposite direction from each other (that is, they are ''not'' linearly independent), or if either one has zero length, then their cross product is zero. More generally, the magnitude of the product equals the area of a parallelogram with the vectors for sides; in particular, the magnitude of the product of two perpendic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Derivative
In mathematics, the derivative of a function of a real variable measures the sensitivity to change of the function value (output value) with respect to a change in its argument (input value). Derivatives are a fundamental tool of calculus. For example, the derivative of the position of a moving object with respect to time is the object's velocity: this measures how quickly the position of the object changes when time advances. The derivative of a function of a single variable at a chosen input value, when it exists, is the slope of the tangent line to the graph of the function at that point. The tangent line is the best linear approximation of the function near that input value. For this reason, the derivative is often described as the "instantaneous rate of change", the ratio of the instantaneous change in the dependent variable to that of the independent variable. Derivatives can be generalized to functions of several real variables. In this generalization, the derivativ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linearly Independent
In the theory of vector spaces, a set of vectors is said to be if there is a nontrivial linear combination of the vectors that equals the zero vector. If no such linear combination exists, then the vectors are said to be . These concepts are central to the definition of dimension. A vector space can be of finite dimension or infinite dimension depending on the maximum number of linearly independent vectors. The definition of linear dependence and the ability to determine whether a subset of vectors in a vector space is linearly dependent are central to determining the dimension of a vector space. Definition A sequence of vectors \mathbf_1, \mathbf_2, \dots, \mathbf_k from a vector space is said to be ''linearly dependent'', if there exist scalars a_1, a_2, \dots, a_k, not all zero, such that :a_1\mathbf_1 + a_2\mathbf_2 + \cdots + a_k\mathbf_k = \mathbf, where \mathbf denotes the zero vector. This implies that at least one of the scalars is nonzero, say a_1\ne 0, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Function (mathematics)
In mathematics, a function from a set to a set assigns to each element of exactly one element of .; the words map, mapping, transformation, correspondence, and operator are often used synonymously. The set is called the domain of the function and the set is called the codomain of the function.Codomain ''Encyclopedia of Mathematics'Codomain. ''Encyclopedia of Mathematics''/ref> The earliest known approach to the notion of function can be traced back to works of Persian mathematicians Al-Biruni and Sharaf al-Din al-Tusi. Functions were originally the idealization of how a varying quantity depends on another quantity. For example, the position of a planet is a ''function'' of time. Historically, the concept was elaborated with the infinitesimal calculus at the end of the 17th century, and, until the 19th century, the functions that were considered were differentiable (that is, they had a high degree of regularity). The concept of a function was formalized at the end of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parametric Equation
In mathematics, a parametric equation defines a group of quantities as functions of one or more independent variables called parameters. Parametric equations are commonly used to express the coordinates of the points that make up a geometric object such as a curve or surface, in which case the equations are collectively called a parametric representation or parameterization (alternatively spelled as parametrisation) of the object. For example, the equations :\begin x &= \cos t \\ y &= \sin t \end form a parametric representation of the unit circle, where ''t'' is the parameter: A point (''x'', ''y'') is on the unit circle if and only if there is a value of ''t'' such that these two equations generate that point. Sometimes the parametric equations for the individual scalar output variables are combined into a single parametric equation in vectors: :(x, y)=(\cos t, \sin t). Parametric representations are generally nonunique (see the "Examples in two dimensions" section belo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helix
A helix () is a shape like a corkscrew or spiral staircase. It is a type of smooth space curve with tangent lines at a constant angle to a fixed axis. Helices are important in biology, as the DNA molecule is formed as two intertwined helices, and many proteins have helical substructures, known as alpha helices. The word ''helix'' comes from the Greek word ''ἕλιξ'', "twisted, curved". A "filled-in" helix – for example, a "spiral" (helical) ramp – is a surface called ''helicoid''. Properties and types The ''pitch'' of a helix is the height of one complete helix turn, measured parallel to the axis of the helix. A double helix consists of two (typically congruent) helices with the same axis, differing by a translation along the axis. A circular helix (i.e. one with constant radius) has constant band curvature and constant torsion. A ''conic helix'', also known as a ''conic spiral'', may be defined as a spiral on a conic surface, with the distance to the apex an expo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |