|
Tornadic Vortex Signature
A tornadic vortex signature, abbreviated TVS, is a Pulse-Doppler radar weather radar detected rotation algorithm that indicates the likely presence of a strong mesocyclone that is in some stage of tornadogenesis. It may give meteorologists the ability to pinpoint and track the location of tornadic rotation within a larger storm, but it is not an important feature in the National Weather Service's warning operations. The tornadic vortex signature was first identified by Donald W. Burgess, Leslie R. Lemon, and Rodger A. Brown in the 1970s using experimental Doppler radar at the National Severe Storms Laboratory (NSSL) in Norman, Oklahoma. The National Weather Service (NWS) now uses an updated algorithm developed by NSSL, the ''tornado detection algorithm'' (TDA) based on data from its WSR-88D system of radars. NSSL also developed the ''mesocyclone detection algorithm'' (MDA). Display The conditions causing a TVS are often visible on the Doppler weather radar storm relative velocit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
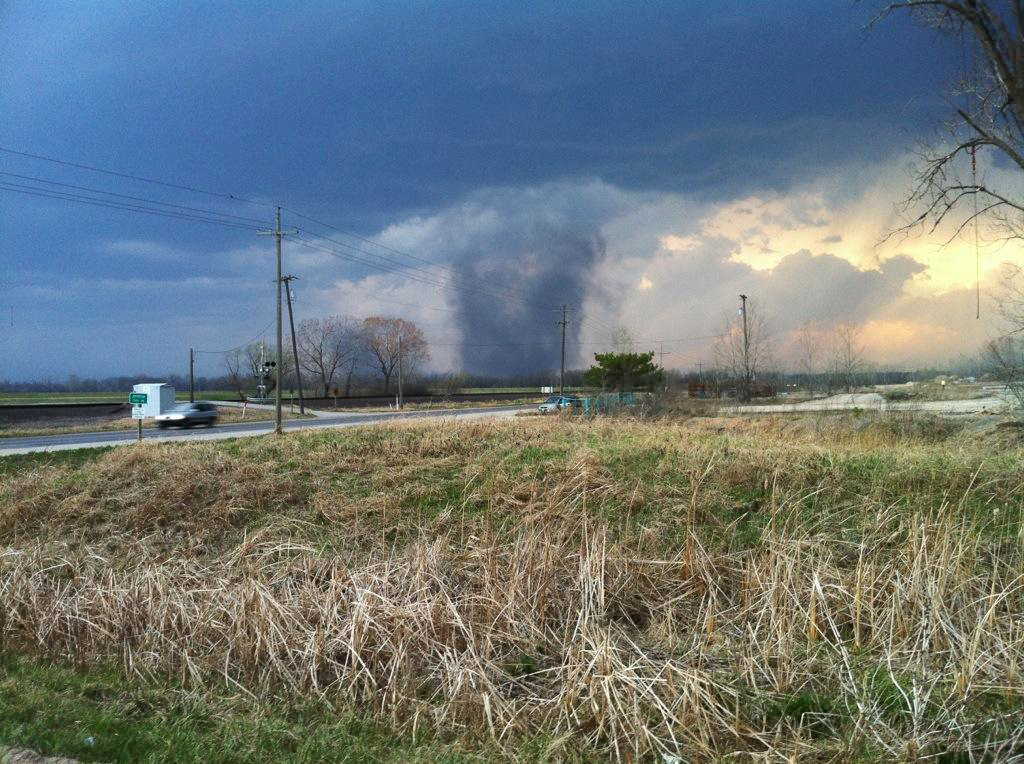
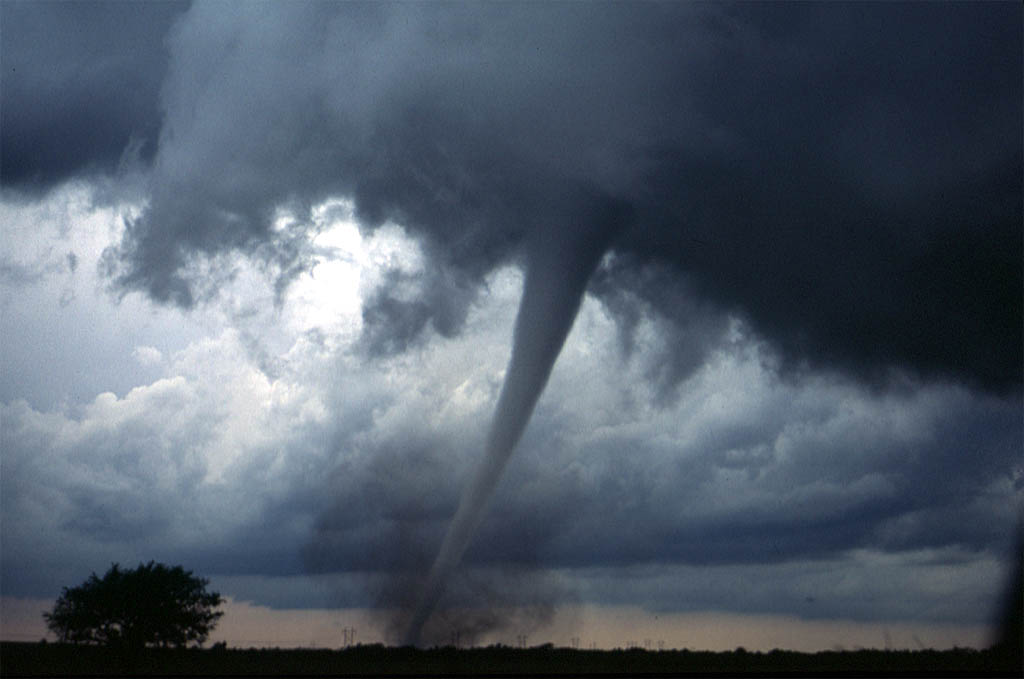
Tornado Vortex Sig, Tuscaloosa
A tornado is a violently rotating column of air that is in contact with both the surface of the Earth and a cumulonimbus cloud or, in rare cases, the base of a cumulus cloud. It is often referred to as a twister, whirlwind or cyclone, although the word cyclone is used in meteorology to name a weather system with a low-pressure area in the center around which, from an observer looking down toward the surface of the Earth, winds blow counterclockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and clockwise in the Southern. Tornadoes come in many shapes and sizes, and they are often visible in the form of a condensation funnel originating from the base of a cumulonimbus cloud, with a cloud of rotating debris and dust beneath it. Most tornadoes have wind speeds less than , are about across, and travel several kilometers (a few miles) before dissipating. The most extreme tornadoes can attain wind speeds of more than , are more than in diameter, and stay on the ground for more than 100 km ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Storm Spotting
Storm spotting is a form of weather spotting in which observers watch for the approach of severe weather, monitor its development and progression, and actively relay their findings to local authorities. History Storm spotting developed in the United States during the early 1940s. A joint project between the military and the weather bureau saw the deployment of trained military and aviation lightning spotters in areas where ammunitions for the war were manufactured. During 1942, a serious tornado struck a key operations center in Oklahoma and another tornado on May 15, 1943 destroyed parts of the Fort Riley military base located in Kansas. After these two events and a string of other tornado outbreaks, spotter networks became commonplace, and it is estimated that there were over 200 networks by 1945. Their mandate had also changed to include reporting all types of active or severe weather; this included giving snow depth and other reports during the winter as well as fire report ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convective Storm Detection
Convective storm detection is the meteorological observation, and short-term prediction, of deep moist convection (DMC). DMC describes atmospheric conditions producing single or clusters of large vertical extension clouds ranging from cumulus congestus to cumulonimbus, the latter producing thunderstorms associated with lightning and thunder. Those two types of clouds can produce severe weather at the surface and aloft. The ability to discern the presence of deep moist convection in a storm significantly improves meteorologists' capacity to predict and monitor associated phenomena such as tornadoes, large hail, strong winds, and heavy rain leading to flash flooding. It relies on direct eyewitness observations, for example from storm spotters; and on remote sensing, especially weather radar. Some in situ measurements are used for direct detection as well, notably, wind speed reports from surface observation stations. It is part of the ''integrated warning system'', cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wind Direction
Wind direction is generally reported by the direction from which it originates. For example, a ''north'' or ''northerly'' wind blows from the north to the south. The exceptions are onshore winds (blowing onto the shore from the water) and offshore winds (blowing off the shore to the water). Wind direction is usually reported in cardinal (or compass) direction, or in degrees. Consequently, a wind blowing from the north has a wind direction referred to as 0° (360°); a wind blowing from the east has a wind direction referred to as 90°, etc. Weather forecasts typically give the direction of the wind along with its speed, for example a "northerly wind at 15 km/h" is a wind blowing ''from'' the north at a speed of 15 km/h. Measurement techniques A variety of instruments can be used to measure wind direction, such as the windsock and wind vane. Both of these instruments work by moving to minimize air resistance. The way a weather vane is pointed by prevailing winds indicates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wind Speed
In meteorology, wind speed, or wind flow speed, is a fundamental atmospheric quantity caused by air moving from high to low pressure, usually due to changes in temperature. Wind speed is now commonly measured with an anemometer. Wind speed affects weather forecasting, aviation and maritime operations, construction projects, growth and metabolism rate of many plant species, and has countless other implications. Note that wind direction is usually almost parallel to isobars (and not perpendicular, as one might expect), due to Earth's rotation. Units Metres per second (m/s) is the SI unit for velocity and the unit recommended by the World Meteorological Organization for reporting wind speeds, and is amongst others used in weather forecasts in the Nordic countries. Since 2010 the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) also recommends meters per second for reporting wind speed when approaching runways, replacing their former recommendation of using kilometres pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wind Shear
Wind shear (or windshear), sometimes referred to as wind gradient, is a difference in wind speed and/or direction over a relatively short distance in the atmosphere. Atmospheric wind shear is normally described as either vertical or horizontal wind shear. Vertical wind shear is a change in wind speed or direction with a change in altitude. Horizontal wind shear is a change in wind speed with a change in lateral position for a given altitude. Wind shear is a microscale meteorological phenomenon occurring over a very small distance, but it can be associated with mesoscale or synoptic scale weather features such as squall lines and cold fronts. It is commonly observed near microbursts and downbursts caused by thunderstorms, fronts, areas of locally higher low-level winds referred to as low-level jets, near mountains, radiation inversions that occur due to clear skies and calm winds, buildings, wind turbines, and sailboats. Wind shear has significant effects on the contro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Straight-line Wind
In meteorology, a downburst is a strong downward and outward gushing wind system that emanates from a point source above and blows radially, that is, in straight lines in all directions from the area of impact at surface level. Capable of producing damaging winds, it may sometimes be confused with a tornado, where high-velocity winds circle a central area, and air moves inward and upward. These usually last for seconds to minutes. Downbursts are particularly strong downdrafts within thunderstorms (or deep, moist convection as sometimes downbursts emanate from cumulonimbus or even cumulus congestus clouds that are not producing lightning). Downbursts are most often created by an area of significantly precipitation-cooled air that, after reaching the surface ( subsiding), spreads out in all directions producing strong winds. Dry downbursts are associated with thunderstorms that exhibit very little rain, while wet downbursts are created by thunderstorms with significant amounts o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesovortex
A mesovortex is a small-scale rotational feature found in a convective storm, such as a quasi-linear convective system (QLCS, i.e. squall line), a supercell, or the eyewall of a tropical cyclone. Mesovortices range in diameter from tens of miles to a mile or less and can be immensely intense. Eyewall mesovortex An ''eyewall mesovortex'' is a small-scale rotational feature found in an eyewall of an intense tropical cyclone. Eyewall mesovortices are similar, in principle, to small "suction vortices" often observed in multiple-vortex tornadoes. In these vortices, wind speed can be up to 10% higher than in the rest of the eyewall. Eyewall mesovortices are most common during periods of intensification in tropical cyclones. Eyewall mesovortices often exhibit unusual behavior in tropical cyclones. They usually revolve around the low pressure center, but sometimes they remain stationary. Eyewall mesovortices have even been documented to cross the eye of a storm. These phenomena have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squall Line
A squall line, or more accurately a quasi-linear convective system (QLCS), is a line of thunderstorms, often forming along or ahead of a cold front. In the early 20th century, the term was used as a synonym for cold front (which often are accompanied by abrupt and gusty wind shifts). Linear thunderstorm structures often contain heavy precipitation, hail, frequent lightning, strong straight-line winds, and occasionally tornadoes or waterspouts. Particularly strong straight-line winds can occur where the linear structure forms into the shape of a bow echo. Tornadoes can occur along waves within a line echo wave pattern (LEWP), where mesoscale low-pressure areas are present. Some bow echoes can grow to become derechos as they move swiftly across a large area. On the back edge of the rainband associated with mature squall lines, a wake low can be present, on very rare occasions associated with a heat burst. Theory Polar front theory was developed by Jacob Bjerknes, derived from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gustnado
A gustnado is a brief, shallow surface-based vortex which forms within the downburst emanating from a thunderstorm. The name is a portmanteau by elision of " gust front tornado", as gustnadoes form due to non-tornadic straight-line wind features in the downdraft ( outflow), specifically within the gust front of strong thunderstorms. Gustnadoes tend to be noticed when the vortices loft sufficient debris or form condensation cloud to be visible although it is the wind that makes the gustnado, similarly to tornadoes. As these eddies very rarely connect from the surface to the cloud base, they are very rarely considered as tornadoes. The gustnado has little in common with tornadoes structurally or dynamically in regard to vertical development, intensity, longevity, or formative process—as classic tornadoes are associated with mesocyclones within the inflow ( updraft) of the storm, not the outflow. The average gustnado lasts a few seconds to a few minutes, although there c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landspout
__NOTOC__ Landspout is a term created by atmospheric scientist Howard B. Bluestein in 1985 for a kind of tornado not associated with a mesocyclone. The ''Glossary of Meteorology'' defines a landspout as : "Colloquial expression describing tornadoes occurring with a parent cloud in its growth stage and with its vorticity originating in the boundary layer. : The parent cloud does not contain a preexisting mid-level mesocyclone. The landspout was so named because it looks like "a weak Florida Keys waterspout over land." Landspouts are typically weaker than mesocyclone associated tornadoes spawned within supercell thunderstorms, in which the strongest tornadoes form. Characteristics Landspouts are a type of tornado that forms during the growth stage of a cumulus congestus or occasionally a cumulonimbus cloud when an updraft stretches boundary layer vorticity upward into a vertical axis and tightens it into a strong vortex. These generally are smaller and weaker than supercell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
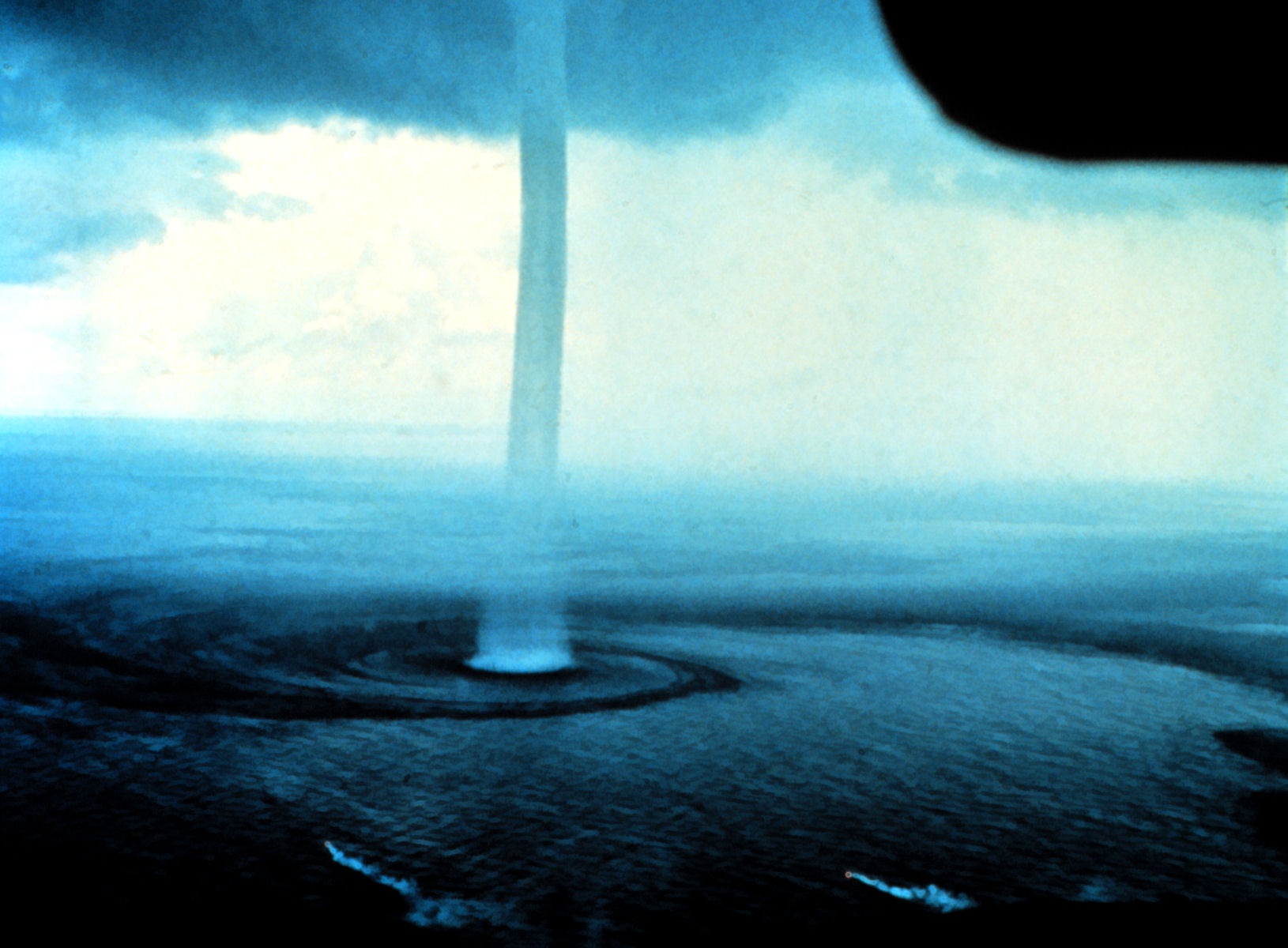
Waterspout
A waterspout is an intense columnar vortex (usually appearing as a funnel-shaped cloud) that occurs over a body of water. Some are connected to a cumulus congestus cloud, some to a cumuliform cloud and some to a cumulonimbus cloud. In the common form, it is a non-supercell tornado over water having a five-part life cycle: formation of a dark spot on the water surface, spiral pattern on the water surface, formation of a spray ring, development of the visible condensation funnel, and ultimately, decay. Most waterspouts do not suck up water; they are small and weak rotating columns of air over water. Although they are most often weaker than their land counterparts, stronger versions spawned by mesocyclones do occur. While waterspouts form mostly in tropical and subtropical areas, other areas also report waterspouts, including Europe, Western Asia (the Middle East), Australia, New Zealand, the Great Lakes, Antarctica, and on rare occasions, the Great Salt Lake, among other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_eye_close-up.jpg)



