|
Topological Fluid Dynamics
Topological ideas are relevant to fluid dynamics (including magnetohydrodynamics) at the kinematic level, since any fluid flow involves continuous deformation of any transported scalar or vector field. Problems of stirring and mixing are particularly susceptible to topological techniques. Thus, for example, the Thurston–Nielsen classification has been fruitfully applied to the problem of stirring in two-dimensions by any number of stirrers following a time-periodic 'stirring protocol' (Boyland, Aref & Stremler 2000). Other studies are concerned with flows having chaotic particle paths, and associated exponential rates of mixing (Ottino 1989). At the dynamic level, the fact that vortex lines are transported by any flow governed by the classical Euler equations implies conservation of any vortical structure within the flow. Such structures are characterised at least in part by the helicity of certain sub-regions of the flow field, a topological invariant of the equations. Helicit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluid Dynamics
In physics and engineering, fluid dynamics is a subdiscipline of fluid mechanics that describes the flow of fluids— liquids and gases. It has several subdisciplines, including ''aerodynamics'' (the study of air and other gases in motion) and hydrodynamics (the study of liquids in motion). Fluid dynamics has a wide range of applications, including calculating forces and moments on aircraft, determining the mass flow rate of petroleum through pipelines, predicting weather patterns, understanding nebulae in interstellar space and modelling fission weapon detonation. Fluid dynamics offers a systematic structure—which underlies these practical disciplines—that embraces empirical and semi-empirical laws derived from flow measurement and used to solve practical problems. The solution to a fluid dynamics problem typically involves the calculation of various properties of the fluid, such as flow velocity, pressure, density, and temperature, as functions of space and time. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
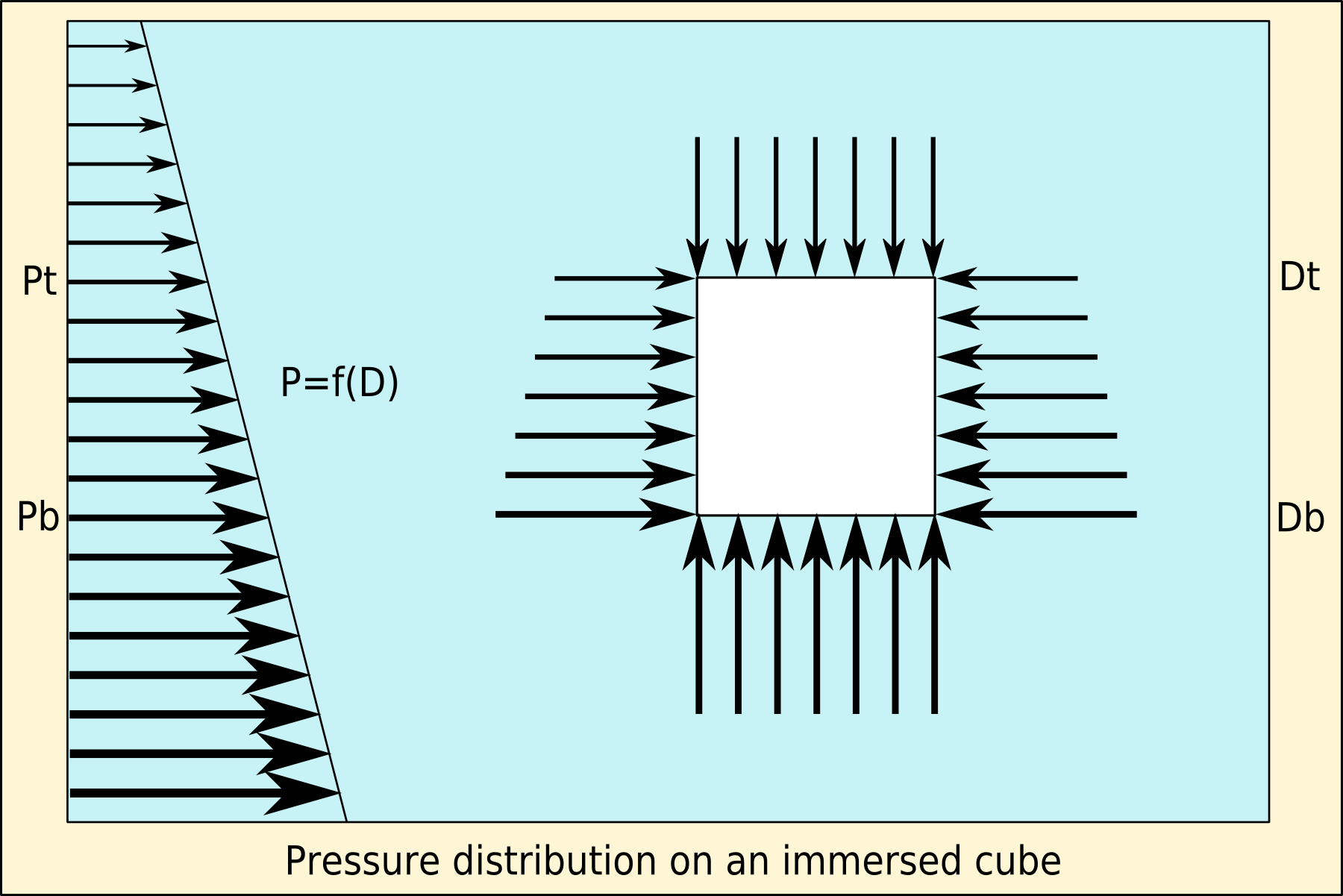
Buoyancy
Buoyancy (), or upthrust, is an upward force exerted by a fluid that opposes the weight of a partially or fully immersed object. In a column of fluid, pressure increases with depth as a result of the weight of the overlying fluid. Thus the pressure at the bottom of a column of fluid is greater than at the top of the column. Similarly, the pressure at the bottom of an object submerged in a fluid is greater than at the top of the object. The pressure difference results in a net upward force on the object. The magnitude of the force is proportional to the pressure difference, and (as explained by Archimedes' principle) is equivalent to the weight of the fluid that would otherwise occupy the submerged volume of the object, i.e. the displaced fluid. For this reason, an object whose average density is greater than that of the fluid in which it is submerged tends to sink. If the object is less dense than the liquid, the force can keep the object afloat. This can occur only in a no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renzo L
Renzo, the diminutive of Lorenzo, is an Italian masculine given name and a surname. Given name Notable people named Renzo include the following: *Renzo Alverà (1933–2005), Italian bobsledder *Renzo Arbore (born 1937), Italian TV host, showman, singer, musician, film actor, and film director *Renzo Barbieri (1940–2007), Italian author and editor of Italian comics *Renzo Caldara (born 1943), Italian bobsledder *Renzo Cesana (1907–1970), Italian-American actor, writer, composer, and songwriter *Renzo Cramerotti (born 1947), Italian male javelin thrower *Renzo Dalmazzo (1886–?), Italian lieutenant general *Renzo De Felice (1929–1996), Italian historian *Renzo De Vecchi (1894–1967), Italian football player and coach * Renzo Fenci (1914–1999), Italian-American sculptor based in Southern California. *Renzo Furlan (born 1970), Italian tennis player * Renzo Fujiwara (born 1973), A minor character in the movie The End of Cygnus *Renzo Gobbo (born 1961), Italian associat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eugene Parker
Eugene Newman Parker (June 10, 1927 – March 15, 2022) was an American solar and plasma physicist. In the 1950s he proposed the existence of the solar wind and that the magnetic field in the outer Solar System would be in the shape of a Parker spiral, predictions that were later confirmed by spacecraft measurements. In 1987, Parker proposed the existence of nanoflares, a leading candidate to explain the coronal heating problem. Parker obtained his PhD from Caltech and spent four years as a postdoctoral researcher at the University of Utah. He joined University of Chicago in 1955 and spent the rest of his career there, holding positions in the physics department, the astronomy and astrophysics department, and the Enrico Fermi Institute. Parker was elected to the National Academy of Sciences in 1967. In 2017, NASA named its Parker Solar Probe in his honor, the first NASA spacecraft named after a living person. Biography Parker was born in Houghton, Michigan to Glenn and Hele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keith Moffatt
Henry Keith Moffatt, FRS FRSE (born 12 April 1935) is a Scottish mathematician with research interests in the field of fluid dynamics, particularly magnetohydrodynamics and the theory of turbulence. He was Professor of Mathematical Physics at the University of Cambridge from 1980 to 2002. Early life and education Moffatt was born on 12 April 1935 to Emmeline Marchant and Frederick Henry Moffatt''.'' He was schooled at George Watson's College, Edinburgh, going on to study Mathematical Sciences at the University of Edinburgh, graduating in 1957. He then went to Trinity College, Cambridge, where he studied mathematics and, 1959, he was a Wrangler. In 1960, he was awarded a Smith's Prize while preparing his PhD. He received his PhD in 1962, the title of his dissertation was ''Magnetohydrodynamic Turbulence.'' Career After completing his PhD, Moffatt joined the staff of the Mathematics Faculty in Cambridge as an Assistant Lecturer and became a Fellow of Trinity College. He was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hassan Aref
Hassan Aref (Arabic: حسن عارف), (28 September 1950 – 9 September 2011) was the Reynolds Metals Professor in the Department of Engineering Science and Mechanics at Virginia Tech, and the Niels Bohr Visiting Professor at the Technical University of Denmark. Education He was educated at the University of Copenhagen Niels Bohr Institute, graduating in 1975 with a cand. scient degree in Physics and Mathematics. Subsequently he received a PhD degree in Physics from Cornell University in 1980. Career Academia and research Prior to joining Virginia Tech as Dean of Engineering in 2003-2005 Aref was Head of the Department of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics at University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign for a decade from 1992-2003. Before that he was on the faculty of University of California, San Diego, split between the Department of Applied Mechanics and Engineering Science and the Institute of Geophysics and Planetary Physics 1985-1992. Simultaneously, he was Chief Scien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boris Khesin
Boris Aronovich Khesin (in Russian: Борис Аронович Хесин, born in 1964) is a Russian and Canadian mathematician working on infinite-dimensional Lie groups, Poisson geometry and hydrodynamics. He is a professor at the University of Toronto. Khesin obtained his Ph.D. from Moscow State University in 1990 under the supervision of Vladimir Arnold Vladimir Igorevich Arnold (alternative spelling Arnol'd, russian: link=no, Влади́мир И́горевич Арно́льд, 12 June 1937 – 3 June 2010) was a Soviet and Russian mathematician. While he is best known for the Kolmogorov– ... (Thesis: ''Normal forms and versal deformations of evolution differential equations''). In 1997 he was awarded the Aisenstadt Prize. References Russian mathematicians 1964 births Living people Moscow State University alumni Soviet mathematicians Canadian mathematicians {{Russia-mathematician-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vladimir Arnold
Vladimir Igorevich Arnold (alternative spelling Arnol'd, russian: link=no, Влади́мир И́горевич Арно́льд, 12 June 1937 – 3 June 2010) was a Soviet and Russian mathematician. While he is best known for the Kolmogorov–Arnold–Moser theorem regarding the stability of integrable systems, he made important contributions in several areas including dynamical systems theory, algebra, catastrophe theory, topology, algebraic geometry, symplectic geometry, differential equations, classical mechanics, hydrodynamics and singularity theory, including posing the ADE classification problem, since his first main result—the solution of Hilbert's thirteenth problem in 1957 at the age of 19. He co-founded two new branches of mathematics— KAM theory, and topological Galois theory (this, with his student Askold Khovanskii). Arnold was also known as a popularizer of mathematics. Through his lectures, seminars, and as the author of several textbooks (such as the famous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reeb Graph
A Reeb graphY. Shinagawa, T.L. Kunii, and Y.L. Kergosien, 1991. Surface coding based on Morse theory. IEEE Computer Graphics and Applications, 11(5), pp.66-78 (named after Georges Reeb by René Thom) is a mathematical object reflecting the evolution of the level sets of a real-valued function on a manifold. According to a similar concept was introduced by G.M. Adelson-Velskii and A.S. Kronrod and applied to analysis of Hilbert's thirteenth problem. Proposed by G. Reeb as a tool in Morse theory, Reeb graphs are the natural tool to study multivalued functional relationships between 2D scalar fields \psi, \lambda, and \phi arising from the conditions \nabla \psi = \lambda \nabla \phi and \lambda \neq 0, because these relationships are single-valued when restricted to a region associated with an individual edge of the Reeb graph. This general principle was first used to study neutral surfaces in oceanography. Reeb graphs have also found a wide variety of applications in comput ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contour Line
A contour line (also isoline, isopleth, or isarithm) of a function of two variables is a curve along which the function has a constant value, so that the curve joins points of equal value. It is a plane section of the three-dimensional graph of the function f(x,y) parallel to the (x,y)-plane. More generally, a contour line for a function of two variables is a curve connecting points where the function has the same particular value. In cartography, a contour line (often just called a "contour") joins points of equal elevation (height) above a given level, such as mean sea level. A contour map is a map illustrated with contour lines, for example a topographic map, which thus shows valleys and hills, and the steepness or gentleness of slopes. The contour interval of a contour map is the difference in elevation between successive contour lines. The gradient of the function is always perpendicular to the contour lines. When the lines are close together the magnitude of the grad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multivalued Function
In mathematics, a multivalued function, also called multifunction, many-valued function, set-valued function, is similar to a function, but may associate several values to each input. More precisely, a multivalued function from a domain to a codomain associates each in to one or more values in ; it is thus a serial binary relation. Some authors allow a multivalued function to have no value for some inputs (in this case a multivalued function is simply a binary relation). However, in some contexts such as in complex analysis (''X'' = ''Y'' = C), authors prefer to mimic function theory as they extend concepts of the ordinary (single-valued) functions. In this context, an ordinary function is often called a single-valued function to avoid confusion. The term ''multivalued function'' originated in complex analysis, from analytic continuation. It often occurs that one knows the value of a complex analytic function f(z) in some neighbourhood of a point z=a. This is the case fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutral Density
The neutral density ( \gamma^n\, ) or empirical neutral density is a density variable used in oceanography, introduced in 1997 by David R. Jackett and Trevor McDougall.Jackett, David R., Trevor J. McDougall, 1997: A Neutral Density Variable for the World's Oceans. J. Phys. Oceanogr., 27, 237–263 It is a function of the three state variables (salinity, temperature, and pressure) and the geographical location (longitude and latitude). It has the typical units of density (M/V). Isosurfaces of \gamma^n\, form “neutral density surfaces”, which are closely aligned with the "neutral tangent plane". It is widely believed, although this has yet to be rigorously proven, that the flow in the deep ocean is almost entirely aligned with the neutral tangent plane, and strong lateral mixing occurs along this plane ("epineutral mixing") vs weak mixing across this plane ("dianeutral mixing"). These surfaces are widely used in water mass analyses. Neutral density is a density variable that d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |