|
Tommotiids
Tommotiids are an extinct group of Cambrian invertebrates thought to be early lophophorates (the group containing Bryozoa, Brachiopoda, and Phoronida). The majority of tommotiids are mineralised with calcium phosphate rather than calcium carbonate. although silicified examples hint that some species bore carbonate or carbonaceous sclerites. ''Micrina'' and '' Paterimitra'' possess bivalved shells in their larval phases, which preserve characters that might position them in the Linguliformea and Rhynchonelliformea stem lineages respectively. This would indicate that the brachiopod shell represents the retention of a larval character. For a long part of their history, the tommotiids were only known from disarticulated shells - a complete organism had not been found. The 2008 discovery of ''Eccentrotheca'' offered the first insight into a complete organism, and permitted a reconstruction of the animal as a sessile, tube-like animal made up of a spiral of overlapping plates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brachiopod
Brachiopods (), phylum Brachiopoda, are a phylum of trochozoan animals that have hard "valves" (shells) on the upper and lower surfaces, unlike the left and right arrangement in bivalve molluscs. Brachiopod valves are hinged at the rear end, while the front can be opened for feeding or closed for protection. Two major categories are traditionally recognized, articulate and inarticulate brachiopods. The word "articulate" is used to describe the tooth-and-groove structures of the valve-hinge which is present in the articulate group, and absent from the inarticulate group. This is the leading diagnostic skeletal feature, by which the two main groups can be readily distinguished as fossils. Articulate brachiopods have toothed hinges and simple, vertically-oriented opening and closing muscles. Conversely, inarticulate brachiopods have weak, untoothed hinges and a more complex system of vertical and oblique (diagonal) muscles used to keep the two valves aligned. In many brachiopods, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micrina
''Micrina'' is an extinct genus of tommotiids with affinities to brachiopods. ''Micrina'' can be considered a stem group brachiopod based on its larval shell Its microstructure is very brachiopod like and its adult morphology is similarly bivalved, even though it was once thought to be halkieriid-like. ''Micrina'' is quite similar to'' Mickwitzia Mickwitziids are a Cambrian group of shelly fossils with originally phosphatic valves, belonging to the Brachiopod stem group, and exemplified by the genus ''Mickwitzia'' – the other genera are ''Heliomedusa'' (a possible junior synonym of ''Mi ...'' in terms of shell microstructure. The two genera are evidently closely related. Species *''M. etheridgei'' (Tate, 1892) *''M. pusilla'' Gravestock ''et al.'', 2001 *''M. ridicula'' (Barskova, 1988) *''M. xiaotanensis'' Li & Xiao, 2004 References Prehistoric brachiopod genera Cambrian brachiopods {{Palaeo-protostome-stub Cambrian genus extinctions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
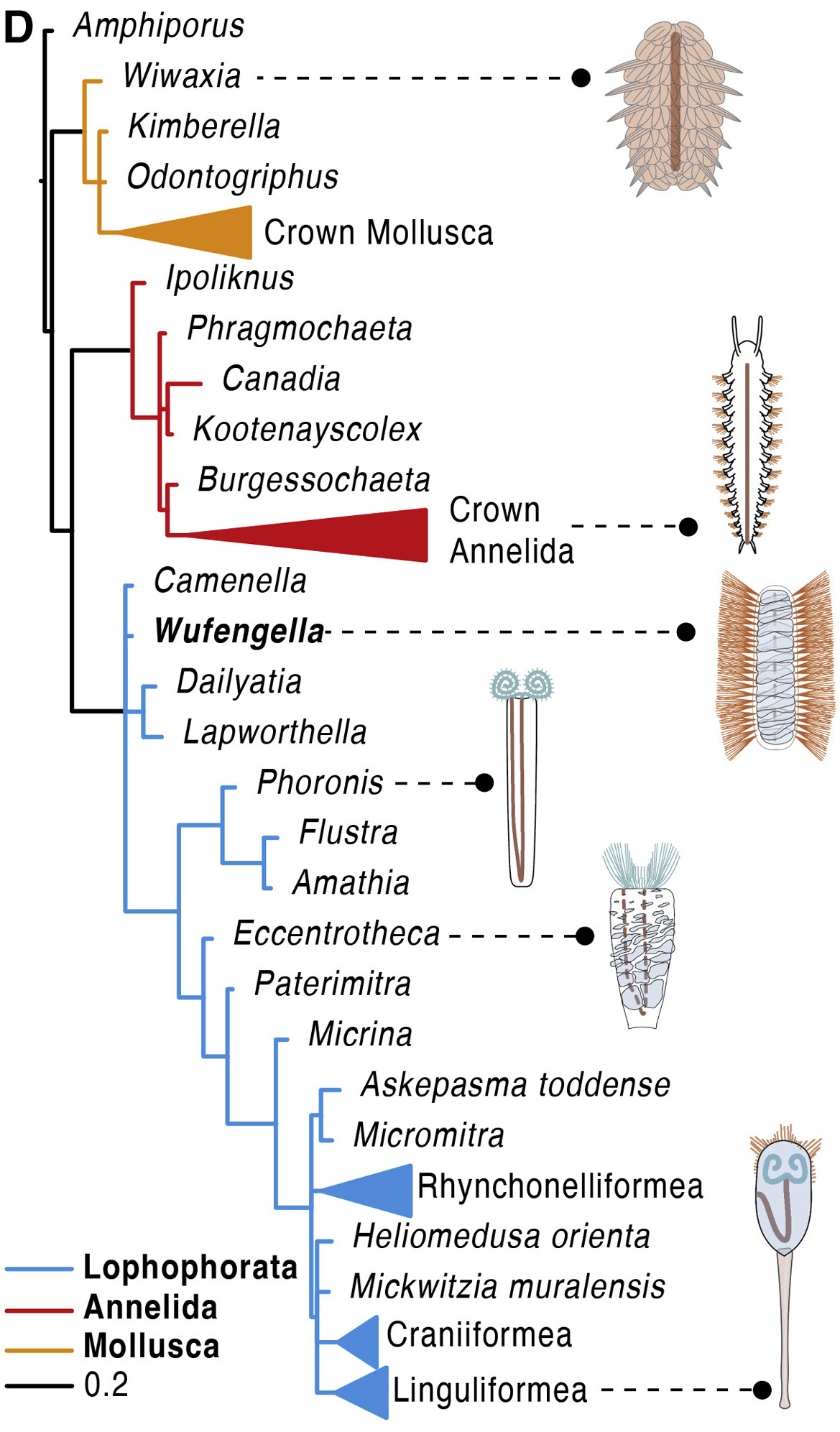
Wufengella
''Wufengella'' is a genus of extinct camenellan " tommotiid" that lived during the Early Cambrian ( Stage 3). Described in 2022, the only species ''Wufengella bengtsonii'' was discovered from the Maotianshan Shales of Chiungchussu (Qiongzhusi) Formation in Yunnan, China. The fossil indicates that the animal was an armoured worm that close to the common ancestry of the phyla Phonorida, Brachiozoa and Bryozoa, which are collectively grouped into a clade called Lophophorata. Discovery ''Wufengella'' is known from a single specimen. The fossil was discovered by Chinese palaeontologists Jin Guo and Peiyun Cong at the Yunnan University. An almost complete fossil, parts of the anterior end are missing. The location of the specimen, Chiungchussu Formation at Haikou, Kunming, Southwest China, is member of the Chengjian Lagerstätte that is established to belong to Cambrian Stage 3 (between 521 and 514 million year ago). The same fossil deposit had yielded worm-like lobopod ''Facive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wufengella Phlyogeny
''Wufengella'' is a genus of extinct camenellan "tommotiid" that lived during the Early Cambrian (Stage 3). Described in 2022, the only species ''Wufengella bengtsonii'' was discovered from the Maotianshan Shales of Chiungchussu (Qiongzhusi) Formation in Yunnan, China. The fossil indicates that the animal was an armoured worm that close to the common ancestry of the phyla Phonorida, Brachiozoa and Bryozoa, which are collectively grouped into a clade called Lophophorata. Discovery ''Wufengella'' is known from a single specimen. The fossil was discovered by Chinese palaeontologists Jin Guo and Peiyun Cong at the Yunnan University. An almost complete fossil, parts of the anterior end are missing. The location of the specimen, Chiungchussu Formation at Haikou, Kunming, Southwest China, is member of the Chengjian Lagerstätte that is established to belong to Cambrian Stage 3 (between 521 and 514 million year ago). The same fossil deposit had yielded worm-like lobopod ''Facivermis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brachiopod Fold Hypothesis
The origin of the brachiopods is uncertain; they either arose from reduction of a multi-plated tubular organism, or from the folding of a slug-like organism with a protective shell on either end. Since their Cambrian origin, the phylum rose to a Palaeozoic dominance, but dwindled during the Mesozoic. Origins Brachiopod fold hypothesis The long-standing hypothesis of brachiopod origins, which has recently come under fire, suggests that the brachiopods arose by the folding of a ''Halkieria''-like organism, which bore two protective shells at either end of a scaled body. For a summary, see The tannuolinids were thought to represent an intermediate form, although the fact that they do not, as thought, possess a scleritome means that this is now considered unlikely. Under this hypothesis, the Phoronid worms share a similar evolutionary history; molecular data also appear to indicate their membership of Brachiopoda. Under the Brachiopod Fold Hypothesis, the "dorsal" and "ventr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraphyletic
In taxonomy (general), taxonomy, a group is paraphyletic if it consists of the group's most recent common ancestor, last common ancestor and most of its descendants, excluding a few Monophyly, monophyletic subgroups. The group is said to be paraphyletic ''with respect to'' the excluded subgroups. In contrast, a monophyletic group (a clade) includes a common ancestor and ''all'' of its descendants. The terms are commonly used in phylogenetics (a subfield of biology) and in the tree model of historical linguistics. Paraphyletic groups are identified by a combination of Synapomorphy and apomorphy, synapomorphies and symplesiomorphy, symplesiomorphies. If many subgroups are missing from the named group, it is said to be polyparaphyletic. The term was coined by Willi Hennig to apply to well-known taxa like Reptilia (reptiles) which, as commonly named and traditionally defined, is paraphyletic with respect to mammals and birds. Reptilia contains the last common ancestor of reptiles a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mickwitzia
Mickwitziids are a Cambrian group of shelly fossils with originally phosphatic valves, belonging to the Brachiopod stem group, and exemplified by the genus ''Mickwitzia'' – the other genera are ''Heliomedusa'' (a possible junior synonym of ''Mickwitzia''?) and ''Setatella''. The family Mickwitziidae is conceivably paraphyletic with respect to certain crown-group brachiopods. Shell microstructure Punctae or tubes penetrate through multiple shell wall layers, and individual punctae often develop a single, axial phosphatic tube. The shell comprises multiple phosphatic laminae; the region closest to the edge of the shell was presumably more organic-walled than phosphatized as it tends to be more flimsily preserved. Members of the genus appear to share characteristic shell microstructure in common with Tommotiids such as ''Micrina'', and like this taxon, mickwitziids may not have been able to enclose their entire body within a bivalved shell. The shells are punctuated with in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tannuolina
''Tannuolina'' is a genus of tommotiid, belonging to the brachiopod stem lineage. Its phosphatic shells exhibit a complex series of open pores/chambers/channels in outer shell layer.Kouchinsky, A., Bengtson, S. & Murdock, D. J. E. A new tannuolinid problematic from the lower Cambrian of the Sukharikha River in northern Siberia. Acta Pal. Pol. 55, 321–331 (2010). It is conventionally interpreted as an essentially bivalved organism, similar to '' Micrina'', though some use the unequal ratio of stellate to mitrate sclerites to argue for a halkieriid The halkieriids are a group of fossil organisms from the Lower to Middle Cambrian. Their eponymous genus is ''Halkieria'' , which has been found on almost every continent in Lower to Mid Cambrian deposits, forming a large component of the smal ...-like anatomy.Li, G.-X. & Xiao, S.-H. ''Tannuolina'' and ''Micrina'' (Tannuolinidae) from the Lower Cambrian of Eastern Yunnan, South China, and Their Scleritome Reconstruction. J. Paleo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Askepasma
''Askepasma'' is an extinct genus of brachiopods which existed in what is now Australia and southern China during the Lower Cambrian. The type species is ''A. toddense''. ''A. transversalis'' occurs in Guizhou, and ''A. saproconcha'' is the oldest known southern Australian brachiopod from the lower Cambrian. References External links ''Askepasma''at the Paleobiology Database The Paleobiology Database is an online resource for information on the distribution and classification of fossil animals, plants, and microorganisms. History The Paleobiology Database (PBDB) originated in the NCEAS-funded Phanerozoic Marine Pale ... {{Taxonbar, from=Q4807170 Prehistoric brachiopod genera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |