|
Tomato (firmware)
Tomato is a family of community-developed, custom firmware for consumer-grade computer networking routers and gateways powered by Broadcom chipsets. The firmware has been continually forked and modded by multiple individuals and organizations, with the most up-to-date fork provided by the FreshTomato project. History Tomato was originally released by Jonathan Zarate in 2006, using the Linux kernel and drawing extensively on the code of HyperWRT. It was targeted at many popular routers of the time, most notably the older Linksys WRT54G series, Buffalo AirStation, Asus routers and Netgear WNR3500L. His final release of the original Tomato firmware came in June 2010, by which point its popularity had grown large enough that development and support continued through the user community, resulting in a series of releases (dubbed " mods") by individual users or teams of them that continues to the present day. Fedor Kozhevnikov created a notable early mod he called ''TomatoUSB'', w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linux
Linux ( or ) is a family of open-source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically packaged as a Linux distribution, which includes the kernel and supporting system software and libraries, many of which are provided by the GNU Project. Many Linux distributions use the word "Linux" in their name, but the Free Software Foundation uses the name "GNU/Linux" to emphasize the importance of GNU software, causing some controversy. Popular Linux distributions include Debian, Fedora Linux, and Ubuntu, the latter of which itself consists of many different distributions and modifications, including Lubuntu and Xubuntu. Commercial distributions include Red Hat Enterprise Linux and SUSE Linux Enterprise. Desktop Linux distributions include a windowing system such as X11 or Wayland, and a desktop environment such as GNOME or KDE Plasma. Distributions intended for ser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quality Of Service
Quality of service (QoS) is the description or measurement of the overall performance of a service, such as a telephony or computer network, or a cloud computing service, particularly the performance seen by the users of the network. To quantitatively measure quality of service, several related aspects of the network service are often considered, such as packet loss, bit rate, throughput, transmission delay, availability, jitter, etc. In the field of computer networking and other packet-switched telecommunication networks, quality of service refers to traffic prioritization and resource reservation control mechanisms rather than the achieved service quality. Quality of service is the ability to provide different priorities to different applications, users, or data flows, or to guarantee a certain level of performance to a data flow. Quality of service is particularly important for the transport of traffic with special requirements. In particular, developers have introduced Voice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dropbear (software)
Dropbear is a software package written by Matt Johnston that provides a Secure Shell-compatible server and client. It is designed as a replacement for standard OpenSSH for environments with low memory and processor resources, such as embedded systems. It is a core component of OpenWrt and other router distributions. Dropbear was originally released in April 2003. Technology Dropbear implements version 2 of the Secure Shell (SSH) protocol. The cryptographic algorithms are implemented using third-party cryptographic libraries like LibTomCrypt included internally in the Dropbear distribution. It derives some parts from OpenSSH to handle BSD-style pseudo terminals. Features Dropbear implements the complete SSH version 2 protocol in both the client and the server. It does not support SSH version 1 backwards-compatibility in order to save space and resources, and to avoid the inherent security vulnerabilities in SSH version 1. SCP is also implemented. SFTP support relies on a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secure Shell
The Secure Shell Protocol (SSH) is a cryptographic network protocol for operating network services securely over an unsecured network. Its most notable applications are remote login and command-line execution. SSH applications are based on a client–server architecture, connecting an SSH client instance with an SSH server. SSH operates as a layered protocol suite comprising three principal hierarchical components: the ''transport layer'' provides server authentication, confidentiality, and integrity; the ''user authentication protocol'' validates the user to the server; and the ''connection protocol'' multiplexes the encrypted tunnel into multiple logical communication channels. SSH was designed on Unix-like operating systems, as a replacement for Telnet and for unsecured remote Unix shell protocols, such as the Berkeley Remote Shell (rsh) and the related rlogin and rexec protocols, which all use insecure, plaintext transmission of authentication tokens. SSH was first de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telnet
Telnet is an application protocol used on the Internet or local area network to provide a bidirectional interactive text-oriented communication facility using a virtual terminal connection. User data is interspersed in-band with Telnet control information in an 8-bit byte oriented data connection over the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP). Telnet was developed in 1969 beginning with , extended in , and standardized as Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) Internet Standard STD 8, one of the first Internet standards. The name stands for " teletype network". Historically, Telnet provided access to a command-line interface on a remote host. However, because of serious security concerns when using Telnet over an open network such as the Internet, its use for this purpose has waned significantly in favor of SSH. The term ''telnet'' is also used to refer to the software that implements the client part of the protocol. Telnet client applications are available for virtually all c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BusyBox
BusyBox is a software suite that provides several Unix utilities in a single executable file. It runs in a variety of POSIX environments such as Linux, Android, and FreeBSD, although many of the tools it provides are designed to work with interfaces provided by the Linux kernel. It was specifically created for embedded operating systems with very limited resources. The authors dubbed it "The Swiss Army knife of Embedded Linux", as the single executable replaces basic functions of more than 300 common commands. It is released as free software under the terms of the GNU General Public License v2, after controversially deciding not to move to version 3. History Origins Originally written by Bruce Perens in 1995 and declared complete for his intended usage in 1996, BusyBox initially aimed to put a complete bootable system on a single floppy disk that would serve both as a rescue disk and as an installer for the Debian distribution. Since that time, it has been extended ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Command-line Interface
A command-line interpreter or command-line processor uses a command-line interface (CLI) to receive commands from a user in the form of lines of text. This provides a means of setting parameters for the environment, invoking executables and providing information to them as to what actions they are to perform. In some cases the invocation is conditional based on conditions established by the user or previous executables. Such access was first provided by computer terminals starting in the mid-1960s. This provided an interactive environment not available with punched cards or other input methods. Today, many users rely upon graphical user interfaces and menu-driven interactions. However, some programming and maintenance tasks may not have a graphical user interface and use a command line. Alternatives to the command-line interface include text-based user interface menus (for example, IBM AIX SMIT), keyboard shortcuts, and various desktop metaphors centered on the pointer (usual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nginx
Nginx (pronounced "engine x" ) is a web server that can also be used as a reverse proxy, load balancer, mail proxy and HTTP cache. The software was created by Igor Sysoev and publicly released in 2004. Nginx is free and open-source software, released under the terms of the 2-clause BSD license. A large fraction of web servers use Nginx, often as a load balancer. A company of the same name was founded in 2011 to provide support and ''Nginx Plus'' paid software. In March 2019, the company was acquired by F5, Inc. for $670 million. Popularity W3Tech's web server count of all web sites ranked Nginx first with 33.6%. Apache was second at 31.4% and Cloudflare Server third at 21.6%. , Netcraft estimated that Nginx served 22.01% of the million busiest websites with Apache a little ahead at 23.04%. Cloudflare at 19.53% and Microsoft Internet Information Services at 5.78% rounded out the top four servers for the busiest websites. Some of Netcraft's other statistics show Ngi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
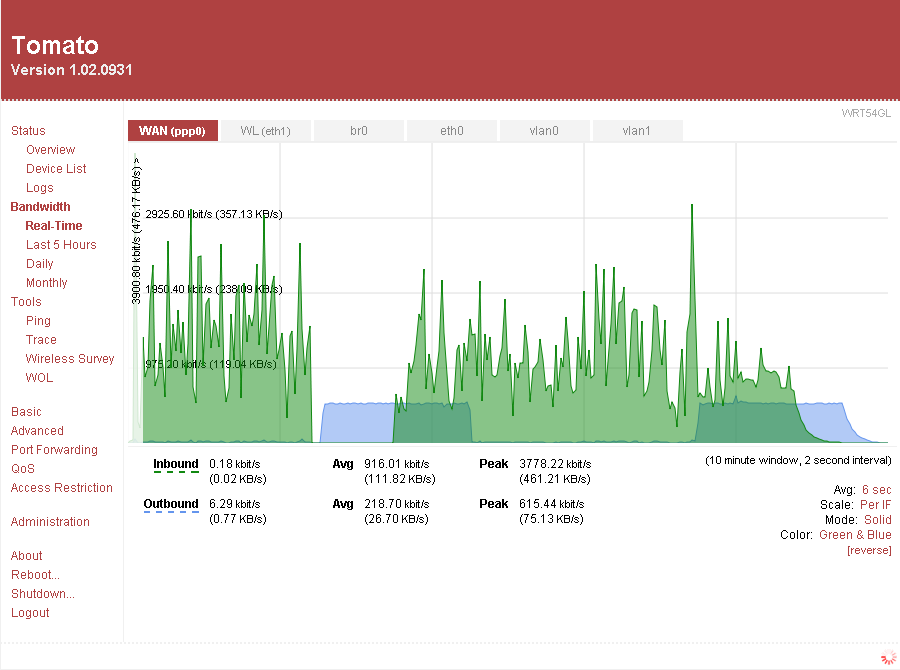
Tomato Bandbreite Real
The tomato is the edible berry of the plant ''Solanum lycopersicum'', commonly known as the tomato plant. The species originated in western South America, Mexico, and Central America. The Mexican Nahuatl word gave rise to the Spanish word , from which the English word ''tomato'' derived. Its domestication and use as a cultivated food may have originated with the indigenous peoples of Mexico. The Aztecs used tomatoes in their cooking at the time of the Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire, and after the Spanish encountered the tomato for the first time after their contact with the Aztecs, they brought the plant to Europe, in a widespread transfer of plants known as the Columbian exchange. From there, the tomato was introduced to other parts of the European-colonized world during the 16th century. Tomatoes are a significant source of umami flavor. They are consumed in diverse ways: raw or cooked, and in many dishes, sauces, salads, and drinks. While tomatoes are fruits—bota ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scalable Vector Graphics
Scalable Vector Graphics (SVG) is an XML-based vector image format for defining two-dimensional graphics, having support for interactivity and animation. The SVG specification is an open standard developed by the World Wide Web Consortium since 1999. SVG images are defined in a vector graphics format and stored in XML text files. SVG images can thus be scaled in size without loss of quality, and SVG files can be searched, indexed, scripted, and compressed. The XML text files can be created and edited with text editors or vector graphics editors, and are rendered by the most-used web browsers. Overview SVG has been in development within the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) since 1999 after six competing proposals for vector graphics languages had been submitted to the consortium during 1998 (see below). The early SVG Working Group decided not to develop any of the commercial submissions, but to create a new markup language that was informed by but not really based on any ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)