|
Tolling (law)
Tolling is a legal doctrine that allows for the pausing or delaying of the running of the period of time set forth by a statute of limitations, such that a lawsuit may potentially be filed even after the statute of limitations has run. Although grounds for tolling the statute of limitations vary by jurisdiction, common grounds include: * The plaintiff was a minor at the time a cause of action accrued. * The plaintiff has been deemed mentally incompetent. * The plaintiff has been convicted of a felony and is imprisoned. * The defendant has filed a bankruptcy case triggering a stay of other lawsuits. * The defendant is not physically within a certain jurisdiction (state or country). * The parties were engaged in good-faith negotiations to resolve a dispute without litigation when the statute of limitations expired. Tolling may occur under a statute that specifically provides for the tolling of the statute of limitations during specified circumstances. It may also take the form of e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legal Doctrine
A legal doctrine is a framework, set of rules, procedural steps, or test, often established through precedent in the common law, through which judgments can be determined in a given legal case. A doctrine comes about when a judge makes a ruling where a process is outlined and applied, and allows for it to be equally applied to like cases. When enough judges make use of the process, it may become established as the ''de facto'' method of deciding like situations. Examples Examples of legal doctrines include: See also * Constitutionalism * Constitutional economics * Concept * Rule according to higher law * Legal fiction * Legal precedent * '' Ex aequo et bono'' References External links * *Pierre Schlag and Amy J. Griffin, "How to do Things with Legal Doctrine" (University of Chicago Press 2020) * Emerson H. Tiller and Frank B. Cross,What is Legal Doctrine?" ''Northwestern University Law Review The ''Northwestern University Law Review'' is a law review and student o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Due Diligence
Due diligence is the investigation or exercise of care that a reasonable business or person is normally expected to take before entering into an agreement or contract with another party or an act with a certain standard of care. It can be a legal obligation, but the term will more commonly apply to voluntary investigations. A common example of due diligence in various industries is the process through which a potential acquirer evaluates a target company or its assets for an acquisition. The theory behind due diligence holds that performing this type of investigation contributes significantly to informed decision making by enhancing the amount and quality of information available to decision makers and by ensuring that this information is systematically used to deliberate on the decision at hand and all its costs, benefits, and risks. Etymology The term “due diligence” means "required carefulness" or "reasonable care" in general usage, and has been used in the literal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
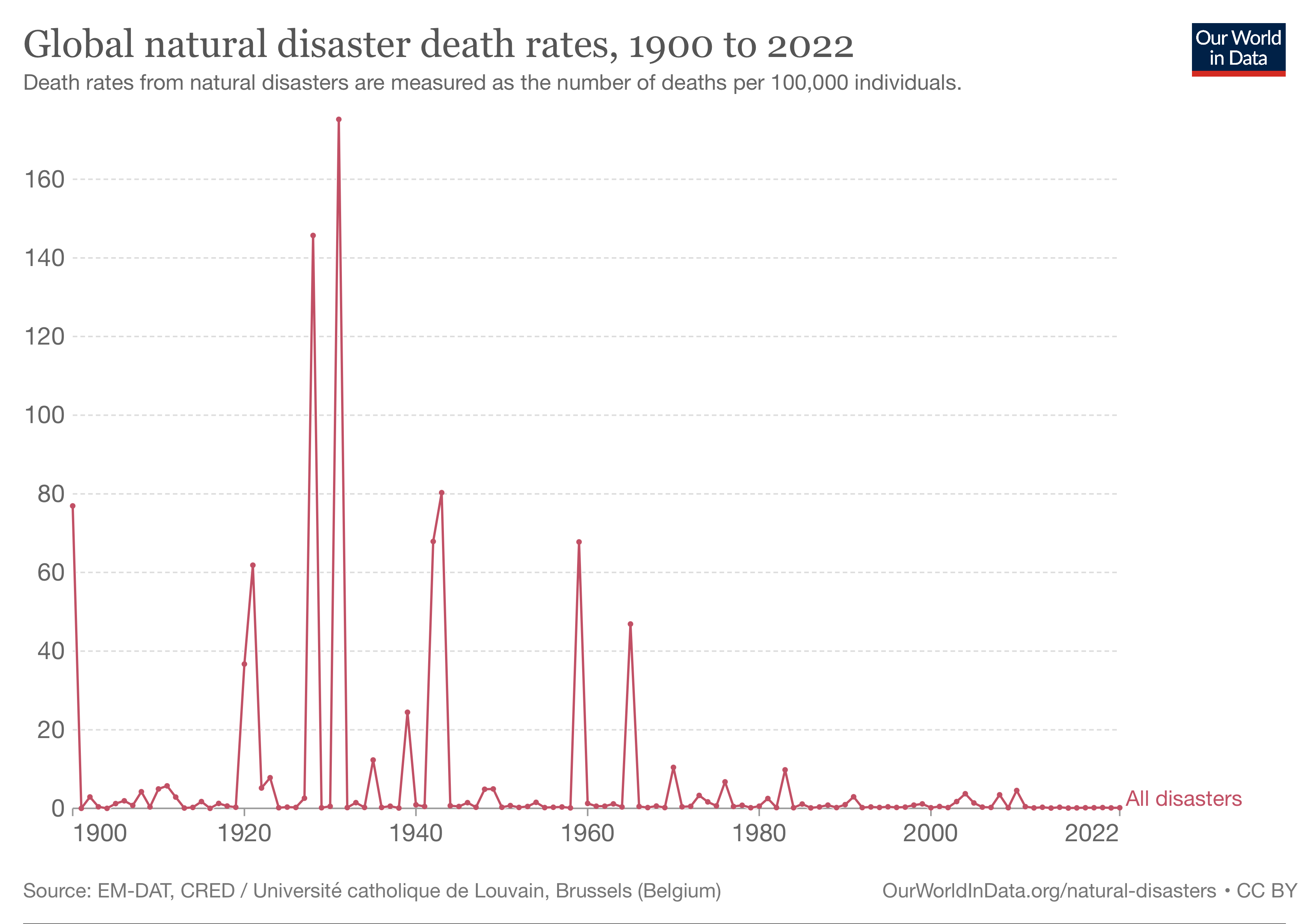
Natural Disasters
A natural disaster is "the negative impact following an actual occurrence of natural hazard in the event that it significantly harms a community". A natural disaster can cause loss of life or damage property, and typically leaves some economic damage in its wake. The severity of the damage depends on the affected population's resilience and on the infrastructure available. Examples of natural hazards include: avalanche, coastal flooding, cold wave, drought, earthquake, hail, heat wave, hurricane (tropical cyclone), ice storm, landslide, lightning, riverine flooding, strong wind, tornado, typhoon, tsunami, volcanic activity, wildfire, winter weather. In modern times, the divide between natural, man-made and man-accelerated disasters is quite difficult to draw. Human choices and activities like architecture, fire, resource management or even climate change potentially play a role in causing "natural disasters". In fact, the term "natural disaster" has been called a misnom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Construction Permit
Planning permission or developmental approval refers to the approval needed for construction or expansion (including significant renovation), and sometimes for demolition, in some jurisdictions. It is usually given in the form of a building permit (or construction permit). House building permits, for example, are subject to Building codes. There is also a "plan check" (PLCK) to check compliance with plans for the area, if any. For example, one cannot obtain permission to build a nightclub in an area where it is inappropriate such as a high-density suburb. The criteria for planning permission are a part of urban planning and construction law, and are usually managed by town planners employed by local governments. Failure to obtain a permit can result in fines, penalties, and demolition of unauthorized construction if it cannot be made to meet code. Generally, the new construction must be inspected during construction and after completion to ensure compliance with national ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federal Communications Commission
The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) is an independent agency of the United States federal government that regulates communications by radio, television, wire, satellite, and cable across the United States. The FCC maintains jurisdiction over the areas of broadband access, fair competition, radio frequency use, media responsibility, public safety, and homeland security. The FCC was formed by the Communications Act of 1934 to replace the radio regulation functions of the Federal Radio Commission. The FCC took over wire communication regulation from the Interstate Commerce Commission. The FCC's mandated jurisdiction covers the 50 states, the District of Columbia, and the territories of the United States. The FCC also provides varied degrees of cooperation, oversight, and leadership for similar communications bodies in other countries of North America. The FCC is funded entirely by regulatory fees. It has an estimated fiscal-2022 budget of US $388 million. It has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Hockey League
The National Hockey League (NHL; french: Ligue nationale de hockey—LNH, ) is a professional ice hockey sports league, league in North America comprising 32 teams—25 in the United States and 7 in Canada. It is considered to be the top ranked professional ice hockey league in the world, and is one of the four major professional sports leagues in the United States and Canada. The Stanley Cup, the oldest professional sports trophy in North America, is awarded annually to the league playoff champion at the end of each season. The NHL is the fifth-wealthiest professional sport league in the world by List of professional sports leagues by revenue, revenue, after the National Football League (NFL), Major League Baseball (MLB), the National Basketball Association (NBA), and the English Premier League (EPL). The National Hockey League was organized at the Windsor Hotel (Montreal), Windsor Hotel in Montreal on November 26, 1917, after the suspension of operations of its predecessor or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Service Of Process
Service of process is the procedure by which a party to a lawsuit gives an appropriate notice of initial legal action to another party (such as a defendant), court, or administrative body in an effort to exercise jurisdiction over that person so as to force that person to respond to the proceeding before the court, body, or other tribunal. Notice is furnished by delivering a set of court documents (called " process") to the person to be served. Service Each jurisdiction has rules regarding the appropriate service of process. Typically, a summons and other related documents must be served upon the defendant personally, or in some cases upon another person of suitable age and discretion at the person's residence or place of business or employment. In some cases, service of process may be effected through the mail as in some small claims court procedures. In exceptional cases, other forms of service may be authorized by procedural rules or court order, including service by publi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sovereign Immunity
Sovereign immunity, or crown immunity, is a legal doctrine whereby a sovereign or state cannot commit a legal wrong and is immune from civil suit or criminal prosecution, strictly speaking in modern texts in its own courts. A similar, stronger rule as regards foreign courts is named state immunity. History Sovereign immunity is the original forebear of state immunity based on the classical concept of sovereignty in the sense that a sovereign could not be subjected without his or her approval to the jurisdiction of another. In constitutional monarchies, the sovereign is the historical origin of the authority which creates the courts. Thus the courts had no power to compel the sovereign to be bound by them as they were created by the sovereign for the protection of his or her subjects. This rule was commonly expressed by the popular legal maxim ''rex non potest peccare'', meaning "the king can do no wrong". Forms There are two forms of sovereign immunity: * immunity from sui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spending Clause
The Taxing and Spending Clause (which contains provisions known as the General Welfare Clause and the Uniformity Clause), Article I, Section 8, Clause 1 of the United States Constitution, grants the federal government of the United States its power of taxation. While authorizing Congress to levy taxes, this clause permits the levying of taxes for two purposes only: to pay the debts of the United States, and to provide for the common defense and general welfare of the United States. Taken together, these purposes have traditionally been held to imply and to constitute the federal government's taxing and spending power. The text of the constitution reads thus: Background One of the most often claimed defects of the Articles of Confederation was its lack of a grant to the central government of the power to lay and collect taxes. Under the Articles, Congress was forced to rely on requisitions upon the governments of its member states. Without the power to independently raise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equitable Estoppel
Estoppel is a judicial device in common law legal systems whereby a court may prevent or "estop" a person from making assertions or from going back on his or her word; the person being sanctioned is "estopped". Estoppel may prevent someone from bringing a particular claim. Legal doctrines of estoppel are based in both common law and equity. It is also a concept in international law. Types of estoppel There are many different types of estoppel which can arise, but the common thread between them is that a person is restrained from asserting a particular position in law where it would be inequitable to do so. By way of illustration: * If a landlord promises the tenant that he will not exercise his right to terminate a lease, and relying upon that promise the tenant spends money improving the premises, the doctrine of ''promissory estoppel'' may prevent the landlord from exercising a right to terminate, even though his promise might not otherwise have been legally binding as a cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of United States Supreme Court Cases, Volume 498
This is a list of all the United States Supreme Court cases from volume 498 of the ''United States Reports The ''United States Reports'' () are the official record ( law reports) of the Supreme Court of the United States. They include rulings, orders, case tables (list of every case decided), in alphabetical order both by the name of the petitioner ...'': External links {{SCOTUSCases, 498 1990 in United States case law 1991 in United States case law ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federal Judiciary Of The United States
The federal judiciary of the United States is one of the three branches of the federal government of the United States organized under the United States Constitution and laws of the federal government. The U.S. federal judiciary consists primarily of the U.S. Supreme Court, the U.S. Courts of Appeals, and the U.S. District Courts. It also includes a variety of other lesser federal tribunals. Article III of the Constitution requires the establishment of a Supreme Court and permits the Congress to create other federal courts and place limitations on their jurisdiction. Article III states that federal judges are appointed by the president with the consent of the Senate to serve until they resign, are impeached and convicted, or die. Courts All federal courts can be readily identified by the words "United States" (abbreviated to "U.S.") in their official names; no state court may include this designation as part of its name. The federal courts are generally divided between tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |