|
Tissue Microarray
Tissue microarrays (also TMAs) consist of paraffin blocks in which up to 1000 separate tissue cores are assembled in array fashion to allow multiplex histological analysis. History The major limitations in molecular clinical analysis of tissues include the cumbersome nature of procedures, limited availability of diagnostic reagents and limited patient sample size. The technique of tissue microarray was developed to address these issues. Multi-tissue blocks were first introduced by H. Battifora in 1986 with his so-called “multitumor (sausage) tissue block" and modified in 1990 with its improvement, "the checkerboard tissue block" . In 1998, J. Kononen and collaborators developed the current technique, which uses a novel sampling approach to produce tissues of regular size and shape that can be more densely and precisely arrayed. Procedure In the tissue microarray technique, a hollow needle is used to remove tissue cores as small as 0.6 mm in diameter from regions of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tissue MicroArray Block
Tissue may refer to: Biology * Tissue (biology), an ensemble of similar (or dissimilar in structure but same in origin) cells that together carry out a specific function * ''Triphosa haesitata'', a species of geometer moth ("tissue moth") found in North America * ''Triphosa dubitata'', a species of geometer moth ("tissue") found in Afro-Eurasia Paper products * Tissue paper, a type of thin, gauzy translucent paper used for wrapping and cushioning items ** Facial tissue, tissue paper used for cleaning the face ** Japanese tissue, tissue paper from Japan made of vegetable fibers ** Toilet paper, tissue paper used for cleaning the anus ** Wrapping tissue, tissue paper used for wrapping and cushioning items Other * Aerial tissue Aerial silks (also known as aerial contortion, aerial ribbons, aerial tissues, fabric, ribbon, or ''tissu'') is a type of performance in which one or more artists perform aerial acrobatics while hanging from a specialist fabric. The fabric may b ..., an ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histological Section
Histology, also known as microscopic anatomy or microanatomy, is the branch of biology which studies the microscopic anatomy of biological tissues. Histology is the microscopic counterpart to gross anatomy, which looks at larger structures visible without a microscope. Although one may divide microscopic anatomy into ''organology'', the study of organs, ''histology'', the study of tissues, and ''cytology'', the study of cells, modern usage places all of these topics under the field of histology. In medicine, histopathology is the branch of histology that includes the microscopic identification and study of diseased tissue. In the field of paleontology, the term paleohistology refers to the histology of fossil organisms. Biological tissues Animal tissue classification There are four basic types of animal tissues: muscle tissue, nervous tissue, connective tissue, and epithelial tissue. All animal tissues are considered to be subtypes of these four principal tissue types (fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytomics
Cytomics is the study of cell biology (cytology) and biochemistry in cellular systems at the single cell level. It combines all the bioinformatic knowledge to attempt to understand the molecular architecture and functionality of the cell system (Cytome). Much of this is achieved by using molecular and microscopic techniques that allow the various components of a cell to be visualised as they interact ''in vivo''. Cytome Cytomes are the cellular systems, subsystems, and functional components of the body. The cytome is the collection of the complex and dynamic cellular processes (structure and function) underlying physiological processes. It describes the structural and functional heterogeneity of the cellular diversity of an organism. Human Cytome Project The Human Cytome Project is aimed at the study of the biological system structure and function of an organism at the cytome level.Valet G., Predictive medicine by cytomics and the challenges of a human cytome project, Business ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cancer Biomarkers
A cancer biomarker refers to a substance or process that is indicative of the presence of cancer in the body. A biomarker may be a molecule secreted by a tumor or a specific response of the body to the presence of cancer. Genetic, epigenetic, proteomic, glycomic, and imaging biomarkers can be used for cancer diagnosis, prognosis, and epidemiology. Ideally, such biomarkers can be assayed in non-invasively collected biofluids like blood or serum. While numerous challenges exist in translating biomarker research into the clinical space; a number of gene and protein based biomarkers have already been used at some point in patient care; including, AFP (liver cancer), BCR-ABL (chronic myeloid leukemia), BRCA1 / BRCA2 (breast/ovarian cancer), BRAF V600E (melanoma/colorectal cancer), CA-125 (ovarian cancer), CA19.9 (pancreatic cancer), CEA (colorectal cancer), EGFR (Non-small-cell lung carcinoma), HER-2 (Breast Cancer), KIT (gastrointestinal stromal tumor), PSA (prostate specific a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cohort Study
A cohort study is a particular form of longitudinal study that samples a cohort (a group of people who share a defining characteristic, typically those who experienced a common event in a selected period, such as birth or graduation), performing a cross-section at intervals through time. It is a type of panel study where the individuals in the panel share a common characteristic. Cohort studies represent one of the fundamental designs of epidemiology which are used in research in the fields of medicine, pharmacy, nursing, psychology, social science, and in any field reliant on 'difficult to reach' answers that are based on evidence (statistics). In medicine for instance, while clinical trials are used primarily for assessing the safety of newly developed pharmaceuticals before they are approved for sale, epidemiological analysis on how risk factors affect the incidence of diseases is often used to identify the causes of diseases in the first place, and to help provide pre-clinica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frozen Tissue Array
Frozen tissue array consists of fresh frozen tissues in which up to 50 separate tissue cores are assembled in array fashion to allow simultaneous histological analysis. History Paraffin tissue array was developed during late years in the 1980s; this array can help scientists high throughput analyze gene and protein expressions in multiple tissue samples, especially analyze different protein levels with antibodies by immunohistochemistry. Various paraffin tissue arrays are now commercially available from many biotech companies. Most of the arrays can be easily made by microarraying instrument (Beecher Instruments Inc.). However, paraffin embedded tissues have limitations. Buffered formalin solutions cross link proteins and nucleic acids when they are used for fix tissues. The DNA, RNA, and protein within the tissues are damaged in various levels during the fixation. Therefore, many scientific experimental results from formalin fixed tissues are not reliable. Since frozen tissue s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal bleeding, prolonged cough, unexplained weight loss, and a change in bowel movements. While these symptoms may indicate cancer, they can also have other causes. Over 100 types of cancers affect humans. Tobacco use is the cause of about 22% of cancer deaths. Another 10% are due to obesity, poor diet, lack of physical activity or excessive drinking of alcohol. Other factors include certain infections, exposure to ionizing radiation, and environmental pollutants. In the developing world, 15% of cancers are due to infections such as ''Helicobacter pylori'', hepatitis B, hepatitis C, human papillomavirus infection, Epstein–Barr virus and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). These factors act, at least partly, by changing the genes of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization
Fluorescence ''in situ'' hybridization (FISH) is a molecular cytogenetic technique that uses fluorescent probes that bind to only particular parts of a nucleic acid sequence with a high degree of sequence complementarity. It was developed by biomedical researchers in the early 1980s to detect and localize the presence or absence of specific DNA sequences on chromosomes. Fluorescence microscopy can be used to find out where the fluorescent probe is bound to the chromosomes. FISH is often used for finding specific features in DNA for use in genetic counseling, medicine, and species identification. FISH can also be used to detect and localize specific RNA targets (mRNA, lncRNA and miRNA) in cells, circulating tumor cells, and tissue samples. In this context, it can help define the spatial-temporal patterns of gene expression within cells and tissues. Probes – RNA and DNA In biology, a probe is a single strand of DNA or RNA that is complementary to a nucleotide sequence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
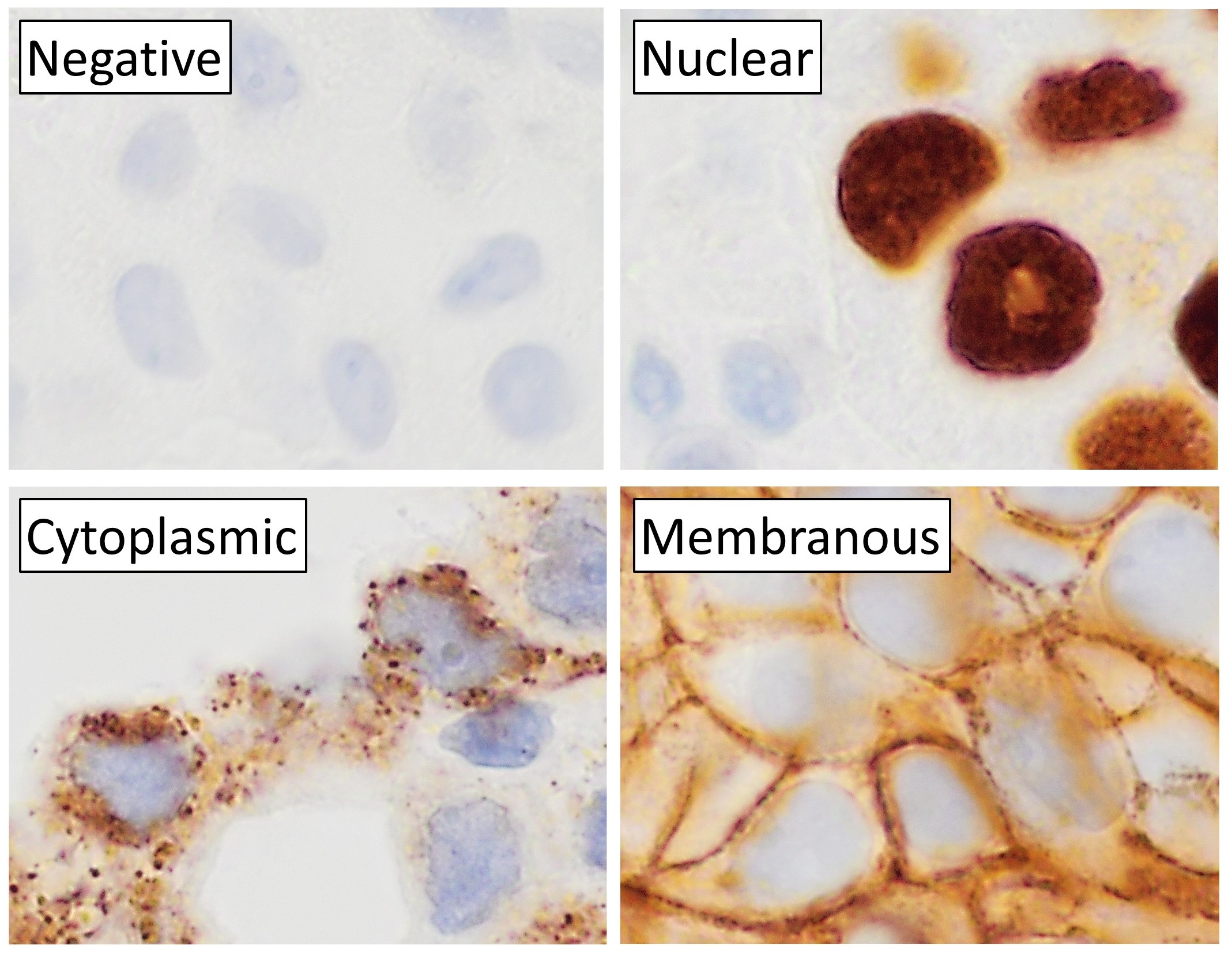
Immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) is the most common application of immunostaining. It involves the process of selectively identifying antigens (proteins) in cells of a tissue section by exploiting the principle of antibodies binding specifically to antigens in biological tissues. IHC takes its name from the roots "immuno", in reference to antibodies used in the procedure, and "histo", meaning tissue (compare to immunocytochemistry). Albert Coons conceptualized and first implemented the procedure in 1941. Visualising an antibody-antigen interaction can be accomplished in a number of ways, mainly either of the following: * ''Chromogenic immunohistochemistry'' (CIH), wherein an antibody is conjugated to an enzyme, such as peroxidase (the combination being termed immunoperoxidase), that can catalyse a colour-producing reaction. * '' Immunofluorescence'', where the antibody is tagged to a fluorophore, such as fluorescein or rhodamine. Immunohistochemical staining is widely used in the dia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microtome
A microtome (from the Greek ''mikros'', meaning "small", and ''temnein'', meaning "to cut") is a cutting tool used to produce extremely thin slices of material known as ''sections''. Important in science, microtomes are used in microscopy, allowing for the preparation of samples for observation under transmitted light or electron radiation. Microtomes use steel, glass or diamond blades depending upon the specimen being sliced and the desired thickness of the sections being cut. Steel blades are used to prepare histological sections of animal or plant tissues for light microscopy. Glass knives are used to slice sections for light microscopy and to slice very thin sections for electron microscopy. Industrial grade diamond knives are used to slice hard materials such as bone, teeth and tough plant matter for both light microscopy and for electron microscopy. Gem-quality diamond knives are also used for slicing thin sections for electron microscopy. Microtomy is a method for the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tumor
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists in growing abnormally, even if the original trigger is removed. This abnormal growth usually forms a mass, when it may be called a tumor. ICD-10 classifies neoplasms into four main groups: benign neoplasms, in situ neoplasms, malignant neoplasms, and neoplasms of uncertain or unknown behavior. Malignant neoplasms are also simply known as cancers and are the focus of oncology. Prior to the abnormal growth of tissue, as neoplasia, cells often undergo an abnormal pattern of growth, such as metaplasia or dysplasia. However, metaplasia or dysplasia does not always progress to neoplasia and can occur in other conditions as well. The word is from Ancient Greek 'new' and 'formation, creation'. Types A neoplasm can be benign, potentially m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tissue MicroArray Slide
Tissue may refer to: Biology * Tissue (biology), an ensemble of similar (or dissimilar in structure but same in origin) cells that together carry out a specific function * ''Triphosa haesitata'', a species of geometer moth ("tissue moth") found in North America * ''Triphosa dubitata'', a species of geometer moth ("tissue") found in Afro-Eurasia Paper products * Tissue paper, a type of thin, gauzy translucent paper used for wrapping and cushioning items ** Facial tissue, tissue paper used for cleaning the face ** Japanese tissue, tissue paper from Japan made of vegetable fibers ** Toilet paper, tissue paper used for cleaning the anus ** Wrapping tissue, tissue paper used for wrapping and cushioning items Other * Aerial tissue Aerial silks (also known as aerial contortion, aerial ribbons, aerial tissues, fabric, ribbon, or ''tissu'') is a type of performance in which one or more artists perform aerial acrobatics while hanging from a specialist fabric. The fabric may b ..., an ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |