|
Time Consistent
Time consistency in the context of finance is the property of not having mutually contradictory evaluations of risk at different points in time. This property implies that if investment A is considered riskier than B at some future time, then A will also be considered riskier than B at every prior time. Time consistency and financial risk Time consistency is a property in financial risk related to dynamic risk measures. The purpose of the time the consistent property is to categorize the risk measures which satisfy the condition that if portfolio (A) is riskier than portfolio (B) at some time in the future, then it is guaranteed to be riskier at any time prior to that point. This is an important property since if it were not to hold then there is an event (with probability of occurring greater than 0) such that B is riskier than A at time t although it is certain that A is riskier than B at time t+1. As the name suggests a time inconsistent risk measure can lead to inconsistent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finance
Finance is the study and discipline of money, currency and capital assets. It is related to, but not synonymous with economics, the study of production, distribution, and consumption of money, assets, goods and services (the discipline of financial economics bridges the two). Finance activities take place in financial systems at various scopes, thus the field can be roughly divided into personal, corporate, and public finance. In a financial system, assets are bought, sold, or traded as financial instruments, such as currencies, loans, bonds, shares, stocks, options, futures, etc. Assets can also be banked, invested, and insured to maximize value and minimize loss. In practice, risks are always present in any financial action and entities. A broad range of subfields within finance exist due to its wide scope. Asset, money, risk and investment management aim to maximize value and minimize volatility. Financial analysis is viability, stability, and profitability asse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Average Value At Risk
Expected shortfall (ES) is a risk measure—a concept used in the field of financial risk measurement to evaluate the market risk or credit risk A credit risk is risk of default on a debt that may arise from a borrower failing to make required payments. In the first resort, the risk is that of the lender and includes lost principal and interest, disruption to cash flows, and increased ... of a portfolio. The "expected shortfall at q% level" is the expected return on the portfolio in the worst q\% of cases. ES is an alternative to value at risk that is more sensitive to the shape of the tail of the loss distribution. Expected shortfall is also called conditional value at risk (CVaR), average value at risk (AVaR), expected tail loss (ETL), and superquantile. ES estimates the risk of an investment in a conservative way, focusing on the less profitable outcomes. For high values of q it ignores the most profitable but unlikely possibilities, while for small values of q it focuses ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Financial Risk Modeling
Financial risk modeling is the use of formal mathematical and econometric techniques to measure, monitor and control the market risk, credit risk, and operational risk on a firm's balance sheet, on a bank's trading book, or re a fund manager's portfolio value; see Financial risk management. Risk modeling is one of many subtasks within the broader area of financial modeling. Application Risk modeling uses a variety of techniques including market risk, value at risk (VaR), historical simulation (HS), or extreme value theory (EVT) in order to analyze a portfolio and make forecasts of the likely losses that would be incurred for a variety of risks. As above, such risks are typically grouped into credit risk, market risk, model risk, liquidity risk, and operational risk categories. Many large financial intermediary firms use risk modeling to help portfolio managers assess the amount of capital reserves to maintain, and to help guide their purchases and sales of various classes of f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
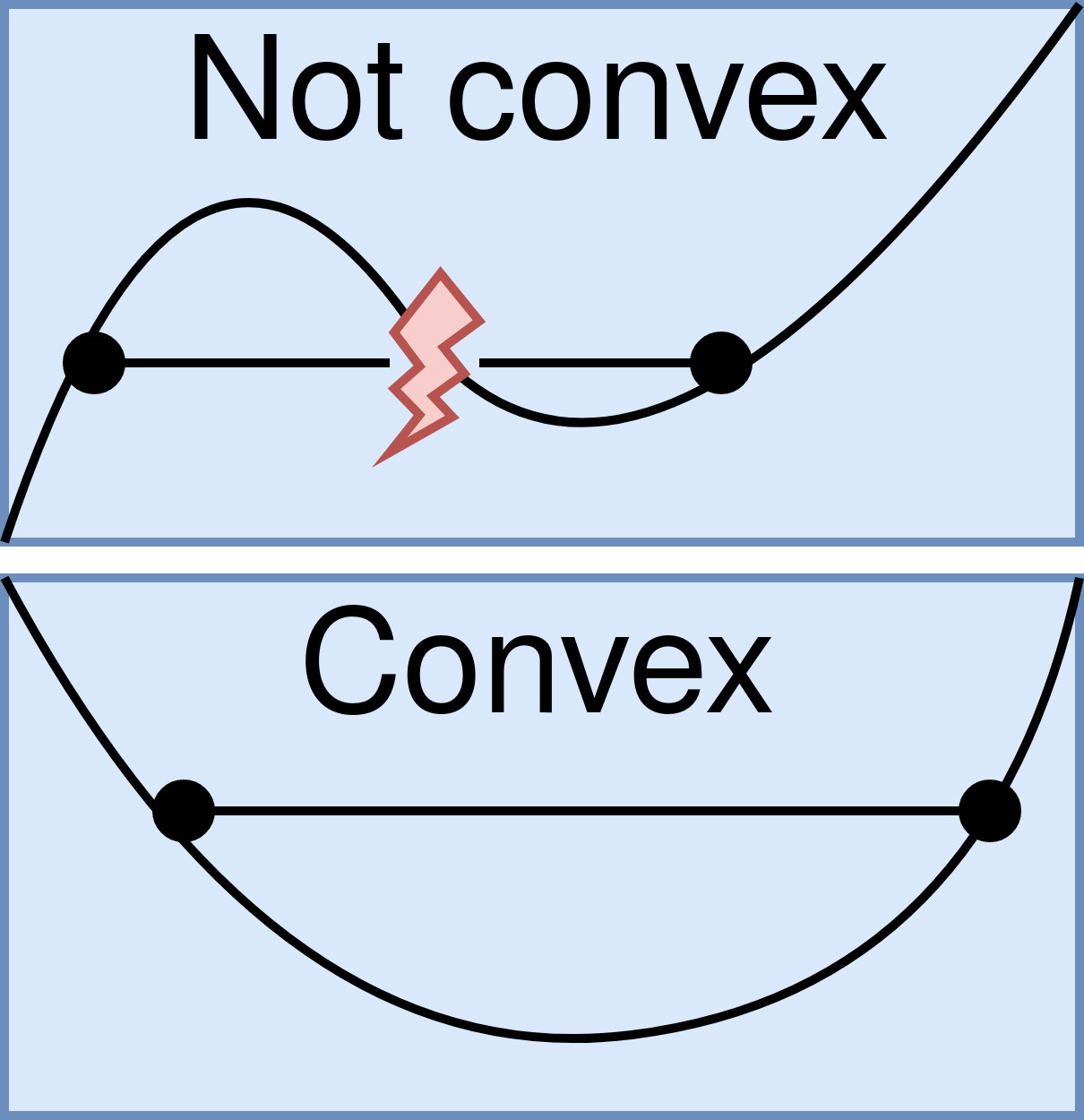
Convex Function
In mathematics, a real-valued function is called convex if the line segment between any two points on the graph of a function, graph of the function lies above the graph between the two points. Equivalently, a function is convex if its epigraph (mathematics), epigraph (the set of points on or above the graph of the function) is a convex set. A twice-differentiable function of a single variable is convex if and only if its second derivative is nonnegative on its entire domain. Well-known examples of convex functions of a single variable include the quadratic function x^2 and the exponential function e^x. In simple terms, a convex function refers to a function whose graph is shaped like a cup \cup, while a concave function's graph is shaped like a cap \cap. Convex functions play an important role in many areas of mathematics. They are especially important in the study of optimization problems where they are distinguished by a number of convenient properties. For instance, a st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
G-expectation
In probability theory, the g-expectation is a nonlinear expectation based on a backwards stochastic differential equation (BSDE) originally developed by Shige Peng. Definition Given a probability space (\Omega,\mathcal,\mathbb) with (W_t)_ is a (''d''-dimensional) Wiener process (on that space). Given the filtration generated by (W_t), i.e. \mathcal_t = \sigma(W_s: s \in ,t, let X be \mathcal_T measurable. Consider the BSDE given by: : \begindY_t &= g(t,Y_t,Z_t) \, dt - Z_t \, dW_t\\ Y_T &= X\end Then the g-expectation for X is given by \mathbb^g := Y_0. Note that if X is an ''m''-dimensional vector, then Y_t (for each time t) is an ''m''-dimensional vector and Z_t is an m \times d matrix. In fact the conditional expectation is given by \mathbb^g \mid \mathcal_t:= Y_t and much like the formal definition for conditional expectation it follows that \mathbb^g _A \mathbb^g[X \mid \mathcal_t = \mathbb^g[1_A X">_\mid_\mathcal_t.html" ;"title="_A \mathbb^g[X \mid \mathcal_t">_A \mat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sublinear
In linear algebra, a sublinear function (or functional as is more often used in functional analysis), also called a quasi-seminorm or a Banach functional, on a vector space X is a real-valued function with only some of the properties of a seminorm. Unlike seminorms, a sublinear function does not have to be nonnegative-valued and also does not have to be absolutely homogeneous. Seminorms are themselves abstractions of the more well known notion of norms, where a seminorm has all the defining properties of a norm that it is not required to map non-zero vectors to non-zero values. In functional analysis the name Banach functional is sometimes used, reflecting that they are most commonly used when applying a general formulation of the Hahn–Banach theorem. The notion of a sublinear function was introduced by Stefan Banach when he proved his version of the Hahn-Banach theorem. There is also a different notion in computer science, described below, that also goes by the name "subline ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Risk Aversion
In economics and finance, risk aversion is the tendency of people to prefer outcomes with low uncertainty to those outcomes with high uncertainty, even if the average outcome of the latter is equal to or higher in monetary value than the more certain outcome. Risk aversion explains the inclination to agree to a situation with a more predictable, but possibly lower payoff, rather than another situation with a highly unpredictable, but possibly higher payoff. For example, a risk-averse investor might choose to put their money into a bank account with a low but guaranteed interest rate, rather than into a stock that may have high expected returns, but also involves a chance of losing value. Example A person is given the choice between two scenarios: one with a guaranteed payoff, and one with a risky payoff with same average value. In the former scenario, the person receives $50. In the uncertain scenario, a coin is flipped to decide whether the person receives $100 or nothing. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entropic Risk Measure
In financial mathematics (concerned with mathematical modeling of financial markets), the entropic risk measure is a risk measure which depends on the risk aversion of the user through the exponential utility function. It is a possible alternative to other risk measures as value-at-risk or expected shortfall. It is a theoretically interesting measure because it provides different risk values for different individuals whose attitudes toward risk may differ. However, in practice it would be difficult to use since quantifying the risk aversion for an individual is difficult to do. The entropic risk measure is the prime example of a convex risk measure which is not coherent. Given the connection to utility functions, it can be used in utility maximization problems. Mathematical definition The entropic risk measure with the risk aversion parameter \theta > 0 is defined as : \rho^(X) = \frac\log\left(\mathbb ^right) = \sup_ \left\ \, where H(Q, P) = E\left frac\log\frac\right/math> ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superhedging Price
The superhedging price is a coherent risk measure. The superhedging price of a portfolio (A) is equivalent to the smallest amount necessary to be paid for an admissible portfolio (B) at the current time so that at some specified future time the value of B is at least as great as A. In a complete market the superhedging price is equivalent to the price for hedging the initial portfolio. Mathematical definition If the set of equivalent martingale measures is denoted by EMM then the superhedging price of a portfolio ''X'' is \rho(-X) where \rho is defined by : \rho(X) = \sup_ \mathbb^Q X/math>. \rho defined as above is a coherent risk measure. Acceptance set The acceptance set for the superhedging price is the negative of the set of values of a self-financing portfolio at the terminal time. That is : A = \. Subhedging price The subhedging price is the greatest value that can be paid so that in any possible situation at the specified future time you have a second portfolio worth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Value At Risk
Value at risk (VaR) is a measure of the risk of loss for investments. It estimates how much a set of investments might lose (with a given probability), given normal market conditions, in a set time period such as a day. VaR is typically used by firms and regulators in the financial industry to gauge the amount of assets needed to cover possible losses. For a given portfolio, time horizon, and probability ''p'', the ''p'' VaR can be defined informally as the maximum possible loss during that time after excluding all worse outcomes whose combined probability is at most ''p''. This assumes mark-to-market pricing, and no trading in the portfolio. For example, if a portfolio of stocks has a one-day 95% VaR of $1 million, that means that there is a 0.05 probability that the portfolio will fall in value by more than $1 million over a one-day period if there is no trading. Informally, a loss of $1 million or more on this portfolio is expected on 1 day out of 20 days (because of 5% proba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Risk
In simple terms, risk is the possibility of something bad happening. Risk involves uncertainty about the effects/implications of an activity with respect to something that humans value (such as health, well-being, wealth, property or the environment), often focusing on negative, undesirable consequences. Many different definitions have been proposed. The international standard definition of risk for common understanding in different applications is “effect of uncertainty on objectives”. The understanding of risk, the methods of assessment and management, the descriptions of risk and even the definitions of risk differ in different practice areas (business, economics, environment, finance, information technology, health, insurance, safety, security etc). This article provides links to more detailed articles on these areas. The international standard for risk management, ISO 31000, provides principles and generic guidelines on managing risks faced by organizations. Definitions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Essential Supremum
In mathematics, the concepts of essential infimum and essential supremum are related to the notions of infimum and supremum, but adapted to measure theory and functional analysis, where one often deals with statements that are not valid for ''all'' elements in a set, but rather ''almost everywhere'', i.e., except on a set of measure zero. While the exact definition is not immediately straightforward, intuitively the essential supremum of a function is the smallest value that is greater than or equal to the function values everywhere while ignoring what the function does at a set of points of measure zero. For example, if one takes the function f(x) that is equal to zero everywhere except at x=0 where f(0)=1, then the supremum of the function equals one. However, its essential supremum is zero because we are allowed to ignore what the function does at the single point where f is peculiar. The essential infimum is defined in a similar way. Definition As is often the case in meas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |