|
Thyrohyoid
The thyrohyoid muscle is a small skeletal muscle of the neck. Above, it attaches onto the greater cornu of the hyoid bone; below, it attaches onto the oblique line of the thyroid cartilage. It is innervated by fibres derived from the cervical spinal nerve 1 that run with the hypoglossal nerve (CN XII) to reach this muscle. The thyrohyoid muscle depresses the hyoid bone and elevates the larynx during swallowing. By controlling the position and shape of the larynx, it aids in making sound. Structure The thyrohyoid muscle is a small, broad and short muscle. It is quadrilateral in shape. It may be considered a superior-ward continuation of sternothyroid muscle. It belongs to the infrahyoid muscles group and the outer laryngeal muscle group. Attachments Its superior attachment is the inferior border of the greater cornu of the hyoid bone and adjacent portions of the body of hyoid bone. Its inferior attachment is the oblique line of the thyroid cartilage (alongside the ster ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Thyrohyoid Branch Of Ansa Cervicalis
The thyrohyoid branch (also: thyrohyoid branch of ansa cervicalis, or nerve to thyrohyoid (muscle)) is a motor branch derived from the cervical plexus formed by fibres of (the anterior ramus of) the cervical spinal nerve 1 (C1) (and - according to some sources - cervical spinal nerve 2 (C2) as well) that join and travel with the hypoglossal nerve (cranial nerve XII) to reach the suprahyoid region, branching away from CN XII distal to the superior root of ansa cervicalis (which is a branching other fibres of C1-C2 that had traveled with the CN XII), near the posterior border of the hyoglossus muscle. The thyrohyoid branch of ansa cervicalis innervates the thyrohyoid muscle The thyrohyoid muscle is a small skeletal muscle of the neck. Above, it attaches onto the greater cornu of the hyoid bone; below, it attaches onto the oblique line of the thyroid cartilage. It is innervated by fibres derived from the cervical spin .... References {{Reflist Nerves of the head and neck [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hyoid Bone
The hyoid-bone (lingual-bone or tongue-bone) () is a horseshoe-shaped bone situated in the anterior midline of the neck between the chin and the thyroid-cartilage. At rest, it lies between the base of the mandible and the third cervical vertebra. Unlike other bones, the hyoid is only distantly articulated to other bones by muscles or ligaments. It is the only bone in the human body that is not connected to any other bones. The hyoid is anchored by muscles from the anterior, posterior and inferior directions, and aids in tongue movement and swallowing. The hyoid bone provides attachment to the muscles of the floor of the mouth and the tongue above, the larynx below, and the epiglottis and pharynx behind. Its name is derived . Structure The hyoid bone is classed as an irregular bone and consists of a central part called the body, and two pairs of horns, the greater and lesser horns. Body The body of the hyoid bone is the central part of the hyoid bone. *At the fron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Infrahyoid Muscles
The infrahyoid muscles, or strap muscles, are a group of four pairs of muscles in the anterior (frontal) part of the neck. The four infrahyoid muscles are the sternohyoid, sternothyroid, thyrohyoid and omohyoid muscles. Excluding the sternothyroid, the infrahyoid muscles either originate from or insert on to the hyoid bone. The term ''infrahyoid'' refers to the region below the hyoid bone, while the term strap muscles refers to the long and flat muscle shapes which resembles a strap. The stylopharyngeus muscle is considered by many to be one of the strap muscles, but is not an infrahyoid muscle. Individual muscles The origin, insertion and innervation of the individual muscles: Nerve supply All of the infrahyoid muscles are innervated by the ansa cervicalis from the cervical plexus ( C1- C3) except the thyrohyoid muscle, which is innervated by fibers only from the first cervical spinal nerve travelling with the hypoglossal nerve. Function The infrahyoid muscles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Superior Thyroid Artery
The superior thyroid artery arises from the external carotid artery just below the level of the greater cornu of the hyoid bone and ends in the thyroid gland. Structure From its origin under the anterior border of the sternocleidomastoid the superior thyroid artery runs upward and forward for a short distance in the carotid triangle, where it is covered by the skin, platysma, and fascia; it then arches downward beneath the omohyoid, sternohyoid, and sternothyroid muscles. To its medial side are the inferior pharyngeal constrictor muscle and the external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve. Branches It distributes twigs to the adjacent muscles, and numerous branches to the thyroid gland, connecting with its fellow of the opposite side, and with the inferior thyroid arteries. The branches to the gland are generally two in number. One, the larger, supplies principally the anterior surface; on the isthmus of the gland it connects with the corresponding artery of the opposite s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
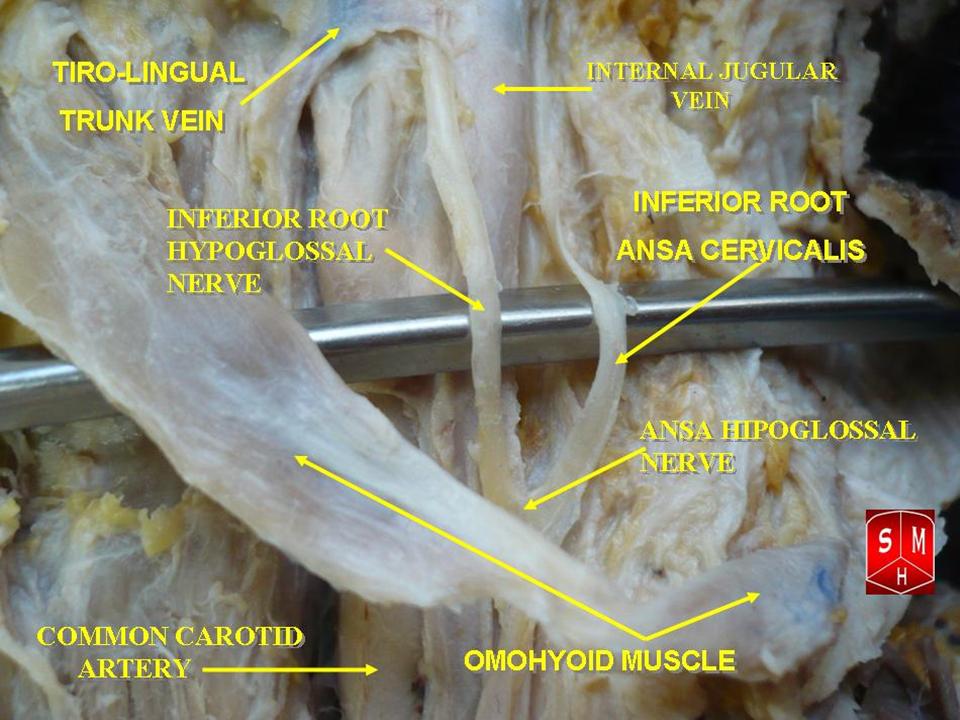
Ansa Cervicalis
The ansa cervicalis (or ansa hypoglossi in older literature) is a loop formed by muscular branches of the cervical plexus formed by branches of cervical spinal nerves C1-C3. The ansa cervicalis has two roots - a superior root (formed by branch of C1) and an inferior root (formed by union of branches of C2 and C3) - that unite distally, forming a loop. It is situated anterior to the carotid sheath. Branches of the ansa cervicalis innervate three of the four infrahyoid muscles: the sternothyroid, sternohyoid, and omohyoid muscles (note that the thyrohyoid muscle is the one infrahyoid muscle not innervated by the ansa cervicalis - it is instead innervated by cervical spinal nerve 1 via a separate thyrohyoid branch). Its name means "handle of the neck" in Latin. Anatomy The ansa cervicalis is typically embedded within the anterior wall of the carotid sheath anterior to the internal jugular vein. Superior root The superior root of the ansa cervicalis (formerly known as d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Superior Root Of Ansa Cervicalis
The ansa cervicalis (or ansa hypoglossi in older literature) is a loop formed by muscular branches of the cervical plexus formed by branches of cervical spinal nerves C1-C3. The ansa cervicalis has two roots - a superior root (formed by branch of C1) and an inferior root (formed by union of branches of C2 and C3) - that unite distally, forming a loop. It is situated anterior to the carotid sheath. Branches of the ansa cervicalis innervate three of the four infrahyoid muscles: the sternothyroid, sternohyoid, and omohyoid muscles (note that the thyrohyoid muscle is the one infrahyoid muscle not innervated by the ansa cervicalis - it is instead innervated by cervical spinal nerve 1 via a separate thyrohyoid branch). Its name means "handle of the neck" in Latin. Anatomy The ansa cervicalis is typically embedded within the anterior wall of the carotid sheath anterior to the internal jugular vein. Superior root The superior root of the ansa cervicalis (formerly known as desc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Sternothyroid Muscle
The sternothyroid muscle (or sternothyroideus) is an infrahyoid muscle of the neck. It acts to depress the hyoid bone. Structure The two muscles are in contact with each other proximally (close to their origin), but diverge distally (towards their insertions). Origin The sternothyroid arises from the posterior surface of the manubrium of the sternum from the midline to the notch for the first rib (inferior to the origin of the sternohyoid muscle), and the posterior margin of the first costal cartilage. Insertion It inserts onto the oblique line of the lamina of thyroid cartilage. Innervation The sternothyroid muscle receives motor innervation from branches of the ansa cervicalis (ultimately derived from cervical spinal nerves C1-C3). Relations The sternothyroid muscle is shorter and wider than the sternohyoid muscle and is situated deep to and partially medial to it. Variations The muscle may be absent or doubled. It may issue accessory slips to the thyrohyoid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Neck
The neck is the part of the body in many vertebrates that connects the head to the torso. It supports the weight of the head and protects the nerves that transmit sensory and motor information between the brain and the rest of the body. Additionally, the neck is highly flexible, allowing the head to turn and move in all directions. Anatomically, the human neck is divided into four compartments: vertebral, visceral, and two vascular compartments. Within these compartments, the neck houses the cervical vertebrae, the cervical portion of the spinal cord, upper parts of the respiratory and digestive tracts, endocrine glands, nerves, arteries and veins. The muscles of the neck, which are separate from the compartments, form the boundaries of the neck triangles. In anatomy, the neck is also referred to as the or . However, when the term ''cervix'' is used alone, it often refers to the uterine cervix, the neck of the uterus. Therefore, the adjective ''cervical'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |