|
Thoraco-abdominal Nerves
The anterior divisions of the seventh, eighth, ninth, tenth, and eleventh thoracic intercostal nerves are continued anteriorly from the intercostal spaces into the abdominal wall; hence they are named thoraco-abdominal nerves (or thoracicoabdominal intercostal nerves). They have the same arrangement as the upper ones as far as the anterior ends of the intercostal spaces, where they pass behind the costal cartilages, and between the Obliquus internus and Transversus abdominis, to the sheath of the Rectus abdominis, which they perforate. They supply the Rectus abdominis and end as the anterior cutaneous branches of the abdomen; they supply the skin of the front of the abdomen. The lower intercostal nerves supply the Intercostales and abdominal muscles; the last three send branches to the Serratus posterior inferior The serratus posterior inferior muscle, also known as the posterior serratus muscle, is a muscle of the human body. Structure The muscle is situated at the junc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rectus Abdominis Muscle
The rectus abdominis muscle, ( la, straight abdominal) also known as the "abdominal muscle" or simply the "abs", is a paired straight muscle. It is a paired muscle, separated by a midline band of connective tissue called the linea alba. It extends from the pubic symphysis, pubic crest and pubic tubercle inferiorly, to the xiphoid process and costal cartilages of ribs V to VII superiorly. The proximal attachments are the pubic crest and the pubic symphysis. It attaches distally at the costal cartilages of ribs 5-7 and the xiphoid process of the sternum. The rectus abdominis muscle is contained in the rectus sheath, which consists of the aponeuroses of the lateral abdominal muscles. The outer, most lateral line, defining the rectus is the linea semilunaris. Bands of connective tissue traverse the rectus abdominis, separating it into distinct muscle bellies. In the abdomens of people with low body fat, these muscle bellies can be viewed externally. They can appear in sets of as f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
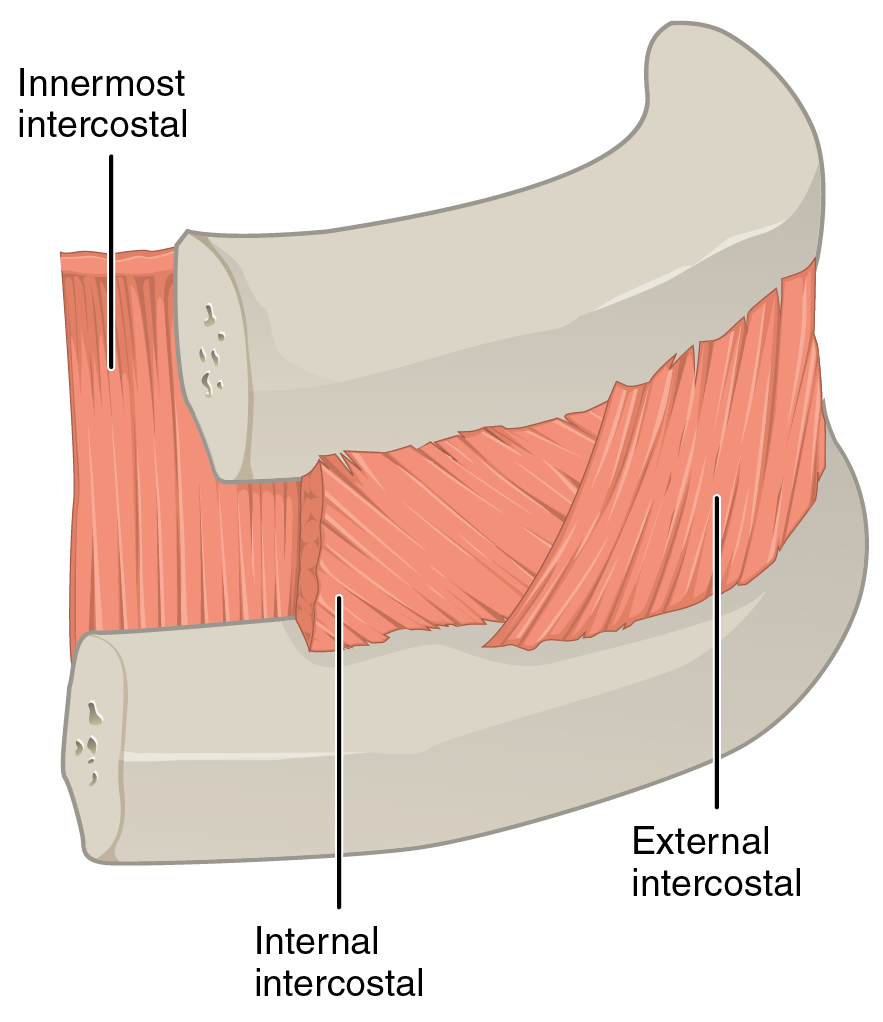
Intercostal Nerves
The intercostal nerves are part of the somatic nervous system, and arise from the anterior rami of the thoracic spinal nerves from T1 to T11. The intercostal nerves are distributed chiefly to the thoracic pleura and abdominal peritoneum, and differ from the anterior rami of the other spinal nerves in that each pursues an independent course without plexus formation. The first two nerves supply fibers to the upper limb and thorax; the next four distribute to the walls of the thorax; the lower five supply the walls of the thorax and abdomen. The 7th intercostal nerve end at the xyphoid process of the sternum. The 10th intercostal nerve terminates at the navel. The 12th ( subcostal) thoracic is distributed to the walls of the abdomen and groin. Each of these fibers contains around 1300 axons. Unlike the nerves from the autonomic nervous system that innervate the visceral pleura of the thoracic cavity, the intercostal nerves arise from the somatic nervous system. This enables them to c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obliquus Internus
The abdominal internal oblique muscle, also internal oblique muscle or interior oblique, is an abdominal muscle in the abdominal wall that lies below the external oblique muscle and just above the transverse abdominal muscle. Structure Its fibers run perpendicular to the external oblique muscle, beginning in the thoracolumbar fascia of the lower back, the anterior 2/3 of the iliac crest (upper part of hip bone) and the lateral half of the inguinal ligament. The muscle fibers run from these points superomedially (up and towards midline) to the muscle's insertions on the inferior borders of the 10th through 12th ribs and the linea alba. In males, the cremaster muscle is also attached to the internal oblique. Nerve supply The internal oblique is supplied by the lower intercostal nerves, as well as the iliohypogastric nerve and the ilioinguinal nerve. Function The internal oblique performs two major functions. Firstly as an accessory muscle of respiration, it acts as an anta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transversus Abdominis
The transverse abdominal muscle (TVA), also known as the transverse abdominis, transversalis muscle and transversus abdominis muscle, is a muscle layer of the anterior and lateral (front and side) abdominal wall which is deep to (layered below) the internal oblique muscle. It is thought by most fitness instructors to be a significant component of the core. Structure The transverse abdominal, so called for the direction of its fibers, is the innermost of the flat muscles of the abdomen. It is positioned immediately inside of the internal oblique muscle. The transverse abdominal arises as fleshy fibers, from the lateral third of the inguinal ligament, from the anterior three-fourths of the inner lip of the iliac crest, from the inner surfaces of the cartilages of the lower six ribs, interdigitating with the diaphragm, and from the thoracolumbar fascia. It ends anteriorly in a broad aponeurosis (the Spigelian fascia), the lower fibers of which curve inferomedially (medially and do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rectus Abdominis
The rectus abdominis muscle, ( la, straight abdominal) also known as the "abdominal muscle" or simply the "abs", is a paired straight muscle. It is a paired muscle, separated by a midline band of connective tissue called the linea alba. It extends from the pubic symphysis, pubic crest and pubic tubercle inferiorly, to the xiphoid process and costal cartilages of ribs V to VII superiorly. The proximal attachments are the pubic crest and the pubic symphysis. It attaches distally at the costal cartilages of ribs 5-7 and the xiphoid process of the sternum. The rectus abdominis muscle is contained in the rectus sheath, which consists of the aponeuroses of the lateral abdominal muscles. The outer, most lateral line, defining the rectus is the linea semilunaris. Bands of connective tissue traverse the rectus abdominis, separating it into distinct muscle bellies. In the abdomens of people with low body fat, these muscle bellies can be viewed externally. They can appear in sets of as f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abdomen
The abdomen (colloquially called the belly, tummy, midriff, tucky or stomach) is the part of the body between the thorax (chest) and pelvis, in humans and in other vertebrates. The abdomen is the front part of the abdominal segment of the torso. The area occupied by the abdomen is called the abdominal cavity. In arthropods it is the posterior (anatomy), posterior tagma (biology), tagma of the body; it follows the thorax or cephalothorax. In humans, the abdomen stretches from the thorax at the thoracic diaphragm to the pelvis at the pelvic brim. The pelvic brim stretches from the lumbosacral joint (the intervertebral disc between Lumbar vertebrae, L5 and Vertebra#Sacrum, S1) to the pubic symphysis and is the edge of the pelvic inlet. The space above this inlet and under the thoracic diaphragm is termed the abdominal cavity. The boundary of the abdominal cavity is the abdominal wall in the front and the peritoneal surface at the rear. In vertebrates, the abdomen is a large body c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intercostales
Intercostal muscles are many different groups of muscles that run between the ribs, and help form and move the chest wall. The intercostal muscles are mainly involved in the mechanical aspect of breathing by helping expand and shrink the size of the chest cavity. Structure There are three principal layers; # External intercostal muscles also known as intercostalis externus aid in quiet and forced inhalation. They originate on ribs 1–11 and have their insertion on ribs 2–12. The external intercostals are responsible for the elevation of the ribs and bending them more open, thus expanding the transverse dimensions of the thoracic cavity. The muscle fibers are directed downwards, forwards and medially in the anterior part. # Internal intercostal muscles also known as intercostalis internus aid in forced expiration (quiet expiration is a passive process). They originate on ribs 2–12 and have their insertions on ribs 1–11.Their fibers pass anterior and supe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serratus Posterior Inferior
The serratus posterior inferior muscle, also known as the posterior serratus muscle, is a muscle of the human body. Structure The muscle is situated at the junction of the thoracic and lumbar regions. It has an irregularly quadrilateral form, broader than the serratus posterior superior muscle, and separated from it by a wide interval. It arises by a thin aponeurosis from the spinous processes of the lower two thoracic and upper two or three lumbar vertebrae. Passing obliquely upward and lateralward, it becomes fleshy, and divides into four flat digitations. These are inserted into the inferior borders of the lower four ribs, a little beyond their angles. The thin aponeurosis of origin is intimately blended with the thoracolumbar fascia, and aponeurosis of the latissimus dorsi muscle. Function The serratus posterior inferior draws the lower ribs backward and downward to assist in rotation and extension of the trunk. This movement of the ribs may also contribute to inhalatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intercostales Externi
The external intercostal muscles, or external intercostals (Intercostales externi) are eleven in number on both sides. Structure The muscles extend from the tubercles of the ribs behind, to the cartilages of the ribs in front, where they end in thin membranes, the external intercostal membranes, which are continued forward to the sternum. These muscles work in unison when inhalation occurs. The internal intercostal muscles relax while the external muscles contract causing the expansion of the chest cavity and an influx of air into the lungs. Each arises from the lower border of a rib, and is inserted into the upper border of the rib below. In the two lower spaces they extend to the ends of the cartilages, and in the upper two or three spaces they do not quite reach the ends of the ribs. They are thicker than the internal intercostals, and their fibers are directed obliquely downward and laterally on the back of the thorax, and downward, forward, and medially on the front. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obliquus Externus Abdominis
The abdominal external oblique muscle (also external oblique muscle, or exterior oblique) is the largest and outermost of the three flat abdominal muscles of the lateral anterior abdomen. Structure The external oblique is situated on the lateral and anterior parts of the abdomen. It is broad, thin, and irregularly quadrilateral, its muscular portion occupying the side, its aponeurosis the anterior wall of the abdomen. In most humans (especially females), the oblique is not visible, due to subcutaneous fat deposits and the small size of the muscle. It arises from eight fleshy digitations, each from the external surfaces and inferior borders of the fifth to twelfth ribs (lower eight ribs). These digitations are arranged in an oblique line which runs inferiorly and anteriorly, with the upper digitations being attached close to the cartilages of the corresponding ribs, the lowest to the apex of the cartilage of the last rib, the intermediate ones to the ribs at some distance from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latissimus Dorsi
The latissimus dorsi () is a large, flat muscle on the back that stretches to the sides, behind the arm, and is partly covered by the trapezius on the back near the midline. The word latissimus dorsi (plural: ''latissimi dorsorum'') comes from Latin and means "broadest uscleof the back", from "latissimus" ( la, broadest)' and "dorsum" ( la, back). The pair of muscles are commonly known as "lats", especially among bodybuilders. The latissimus dorsi is the largest muscle in the upper body. The latissimus dorsi is responsible for extension, adduction, transverse extension also known as horizontal abduction (or horizontal extension), flexion from an extended position, and (medial) internal rotation of the shoulder joint. It also has a synergistic role in extension and lateral flexion of the lumbar spine. Due to bypassing the scapulothoracic joints and attaching directly to the spine, the actions the latissimi dorsi have on moving the arms can also influence the movement of the sca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |