|
Theory Of Automata
Automata theory is the study of abstract machines and automata, as well as the computational problems that can be solved using them. It is a theory in theoretical computer science. The word ''automata'' comes from the Greek word αὐτόματος, which means "self-acting, self-willed, self-moving". An automaton (automata in plural) is an abstract self-propelled computing device which follows a predetermined sequence of operations automatically. An automaton with a finite number of states is called a Finite Automaton (FA) or Finite-State Machine (FSM). The figure on the right illustrates a finite-state machine, which is a well-known type of automaton. This automaton consists of states (represented in the figure by circles) and transitions (represented by arrows). As the automaton sees a symbol of input, it makes a transition (or jump) to another state, according to its transition function, which takes the previous state and current input symbol as its arguments. Automata theo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abstract Algebra
In mathematics, more specifically algebra, abstract algebra or modern algebra is the study of algebraic structures. Algebraic structures include groups, rings, fields, modules, vector spaces, lattices, and algebras over a field. The term ''abstract algebra'' was coined in the early 20th century to distinguish this area of study from older parts of algebra, and more specifically from elementary algebra, the use of variables to represent numbers in computation and reasoning. Algebraic structures, with their associated homomorphisms, form mathematical categories. Category theory is a formalism that allows a unified way for expressing properties and constructions that are similar for various structures. Universal algebra is a related subject that studies types of algebraic structures as single objects. For example, the structure of groups is a single object in universal algebra, which is called the ''variety of groups''. History Before the nineteenth century, algebra meant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formal Grammars
In formal language theory, a grammar (when the context is not given, often called a formal grammar for clarity) describes how to form strings from a language's alphabet that are valid according to the language's syntax. A grammar does not describe the meaning of the strings or what can be done with them in whatever context—only their form. A formal grammar is defined as a set of production rules for such strings in a formal language. Formal language theory, the discipline that studies formal grammars and languages, is a branch of applied mathematics. Its applications are found in theoretical computer science, theoretical linguistics, formal semantics, mathematical logic, and other areas. A formal grammar is a set of rules for rewriting strings, along with a "start symbol" from which rewriting starts. Therefore, a grammar is usually thought of as a language generator. However, it can also sometimes be used as the basis for a "recognizer"—a function in computing that de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noam Chomsky
Avram Noam Chomsky (born December 7, 1928) is an American public intellectual: a linguist, philosopher, cognitive scientist, historian, social critic, and political activist. Sometimes called "the father of modern linguistics", Chomsky is also a major figure in analytic philosophy and one of the founders of the field of cognitive science. He is a Laureate Professor of Linguistics at the University of Arizona and an Institute Professor Emeritus at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), and is the author of more than 150 books on topics such as linguistics, war, politics, and mass media. Ideologically, he aligns with anarcho-syndicalism and libertarian socialism. Born to Ashkenazi Jewish immigrants in Philadelphia, Chomsky developed an early interest in anarchism from alternative bookstores in New York City. He studied at the University of Pennsylvania. During his postgraduate work in the Harvard Society of Fellows, Chomsky developed the theory of transformati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regular Languages
In theoretical computer science and formal language theory, a regular language (also called a rational language) is a formal language that can be defined by a regular expression, in the strict sense in theoretical computer science (as opposed to many modern regular expressions engines, which are augmented with features that allow recognition of non-regular languages). Alternatively, a regular language can be defined as a language recognized by a finite automaton. The equivalence of regular expressions and finite automata is known as Kleene's theorem (after American mathematician Stephen Cole Kleene). In the Chomsky hierarchy, regular languages are the languages generated by Type-3 grammars. Formal definition The collection of regular languages over an alphabet Σ is defined recursively as follows: * The empty language Ø is a regular language. * For each ''a'' ∈ Σ (''a'' belongs to Σ), the singleton language is a regular language. * If ''A'' is a regular language, ''A''* ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stephen Cole Kleene
Stephen Cole Kleene ( ; January 5, 1909 – January 25, 1994) was an American mathematician. One of the students of Alonzo Church, Kleene, along with Rózsa Péter, Alan Turing, Emil Post, and others, is best known as a founder of the branch of mathematical logic known as recursion theory, which subsequently helped to provide the foundations of theoretical computer science. Kleene's work grounds the study of computable functions. A number of mathematical concepts are named after him: Kleene hierarchy, Kleene algebra, the Kleene star (Kleene closure), Kleene's recursion theorem and the Kleene fixed-point theorem. He also invented regular expressions in 1951 to describe McCulloch-Pitts neural networks, and made significant contributions to the foundations of mathematical intuitionism. Biography Kleene was awarded a bachelor's degree from Amherst College in 1930. He was awarded a Ph.D. in mathematics from Princeton University in 1934, where his thesis, entitled ''A Theory of Positi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward F
Edward is an English given name. It is derived from the Anglo-Saxon name ''Ēadweard'', composed of the elements '' ēad'' "wealth, fortune; prosperous" and '' weard'' "guardian, protector”. History The name Edward was very popular in Anglo-Saxon England, but the rule of the Norman and Plantagenet dynasties had effectively ended its use amongst the upper classes. The popularity of the name was revived when Henry III named his firstborn son, the future Edward I, as part of his efforts to promote a cult around Edward the Confessor, for whom Henry had a deep admiration. Variant forms The name has been adopted in the Iberian peninsula since the 15th century, due to Edward, King of Portugal, whose mother was English. The Spanish/Portuguese forms of the name are Eduardo and Duarte. Other variant forms include French Édouard, Italian Edoardo and Odoardo, German, Dutch, Czech and Romanian Eduard and Scandinavian Edvard. Short forms include Ed, Eddy, Eddie, Ted, Teddy and Ned. Pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marvin Minsky
Marvin Lee Minsky (August 9, 1927 – January 24, 2016) was an American cognitive and computer scientist concerned largely with research of artificial intelligence (AI), co-founder of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology's AI laboratory, and author of several texts concerning AI and philosophy. Minsky received many accolades and honors, including the 1969 Turing Award. Biography Marvin Lee Minsky was born in New York City, to an eye surgeon father, Henry, and to a mother, Fannie (Reiser), who was a Zionist activist. His family was Jewish. He attended the Ethical Culture Fieldston School and the Bronx High School of Science. He later attended Phillips Academy in Andover, Massachusetts. He then served in the US Navy from 1944 to 1945. He received a B.A. in mathematics from Harvard University in 1950 and a Ph.D. in mathematics from Princeton University in 1954. His doctoral dissertation was titled "Theory of neural-analog reinforcement systems and its application to the brain- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Von Neumann
John von Neumann (; hu, Neumann János Lajos, ; December 28, 1903 – February 8, 1957) was a Hungarian-American mathematician, physicist, computer scientist, engineer and polymath. He was regarded as having perhaps the widest coverage of any mathematician of his time and was said to have been "the last representative of the great mathematicians who were equally at home in both pure and applied mathematics". He integrated pure and applied sciences. Von Neumann made major contributions to many fields, including mathematics (foundations of mathematics, measure theory, functional analysis, ergodic theory, group theory, lattice theory, representation theory, operator algebras, matrix theory, geometry, and numerical analysis), physics (quantum mechanics, hydrodynamics, ballistics, nuclear physics and quantum statistical mechanics), economics ( game theory and general equilibrium theory), computing ( Von Neumann architecture, linear programming, numerical meteo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Claude Shannon
Claude Elwood Shannon (April 30, 1916 – February 24, 2001) was an American people, American mathematician, electrical engineering, electrical engineer, and cryptography, cryptographer known as a "father of information theory". As a 21-year-old master's degree student at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), he wrote A Symbolic Analysis of Relay and Switching Circuits, his thesis demonstrating that electrical applications of Boolean algebra could construct any logical numerical relationship. Shannon contributed to the field of cryptanalysis for national defense of the United States during World War II, including his fundamental work on codebreaking and secure telecommunications. Biography Childhood The Shannon family lived in Gaylord, Michigan, and Claude was born in a hospital in nearby Petoskey, Michigan, Petoskey. His father, Claude Sr. (1862–1934), was a businessman and for a while, a judge of probate in Gaylord. His mother, Mabel Wolf Shannon (1890–1945), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pushdown Automata
In the theory of computation, a branch of theoretical computer science, a pushdown automaton (PDA) is a type of automaton that employs a stack. Pushdown automata are used in theories about what can be computed by machines. They are more capable than finite-state machines but less capable than Turing machines (see below). Deterministic pushdown automata can recognize all deterministic context-free languages while nondeterministic ones can recognize all context-free languages, with the former often used in parser design. The term "pushdown" refers to the fact that the stack can be regarded as being "pushed down" like a tray dispenser at a cafeteria, since the operations never work on elements other than the top element. A stack automaton, by contrast, does allow access to and operations on deeper elements. Stack automata can recognize a strictly larger set of languages than pushdown automata. A nested stack automaton allows full access, and also allows stacked values to be ent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
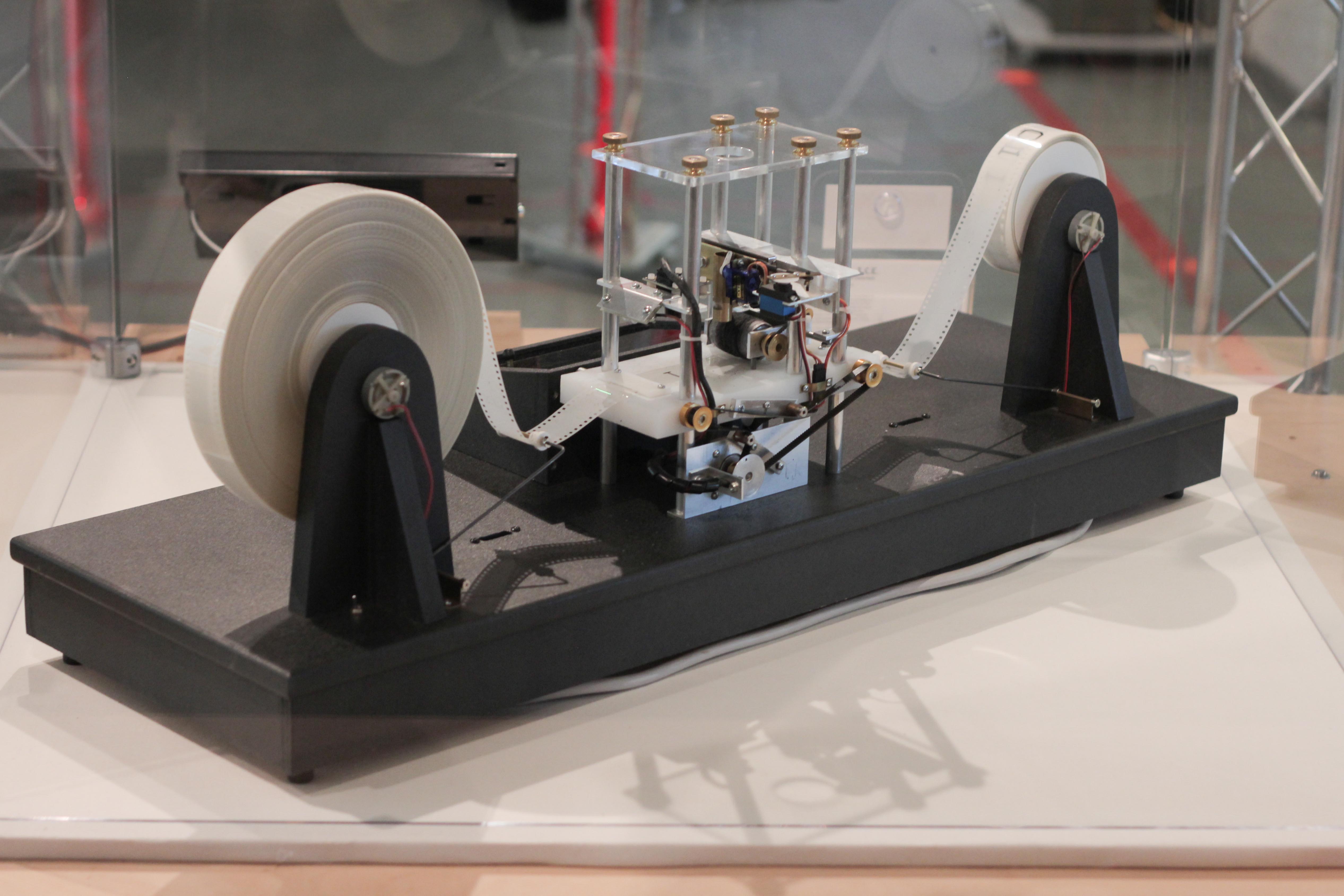
Turing Machine
A Turing machine is a mathematical model of computation describing an abstract machine that manipulates symbols on a strip of tape according to a table of rules. Despite the model's simplicity, it is capable of implementing any computer algorithm. The machine operates on an infinite memory tape divided into discrete cells, each of which can hold a single symbol drawn from a finite set of symbols called the alphabet of the machine. It has a "head" that, at any point in the machine's operation, is positioned over one of these cells, and a "state" selected from a finite set of states. At each step of its operation, the head reads the symbol in its cell. Then, based on the symbol and the machine's own present state, the machine writes a symbol into the same cell, and moves the head one step to the left or the right, or halts the computation. The choice of which replacement symbol to write and which direction to move is based on a finite table that specifies what to do for each comb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |