|
Theatre Ballistic Missile
A theatre ballistic missile (TBM) is any ballistic missile with a range less than , used against targets " in-theatre". Its range is thus between that of tactical and intermediate-range ballistic missiles. The term is a relatively new one, encompassing the former categories of short-range ballistic missile and medium-range ballistic missile. Examples of this type of in-theatre missile are the Soviet RT-15, TR-1 Temp and American PGM-19 Jupiter missile, both from the 1960s. Specific TBMs Specific types of TBMs (current, past and under development) include: * B-611 * BP-12/A * DF-11 * DF-12/M20 * DF-15 * Type 621 * Type 631 * DF-2 * DF-16 * DF-17 * DF-21 (China) , (Saudi Arabia) * Hadès * Pluton * SE.4200 * SSBS S1 * Agni I * K-15 * Prahaar * Pragati (planned) * Pralay * Pranash (planned) * Prithvi I * Prithvi II * Prithvi III * Shaurya * Agni II * Agni-P * Fateh-110 * Fateh-313 * Fateh Mobin * Naze'at * Qiam 1 * Ra'ad-5 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ballistic Missile
A ballistic missile is a type of missile that uses projectile motion to deliver warheads on a target. These weapons are guided only during relatively brief periods—most of the flight is unpowered. Short-range ballistic missiles stay within the Earth's atmosphere, while intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs) are launched on a sub-orbital flight. These weapons are in a distinct category from cruise missiles, which are aerodynamically guided in powered flight. Unlike cruise missiles, which are restricted to the atmosphere, it is advantageous for ballistic missiles to avoid the denser parts of the atmosphere and they may travel above the atmosphere into outer space. History The earliest form of ballistic missile dates from the 13th century with its use derived from the history of rockets. In the 14th century, the Ming Chinese navy used an early form of a ballistic missile weapon called the Huolongchushui in naval battles against enemy ships.Needham, Volume 5, Part 7, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
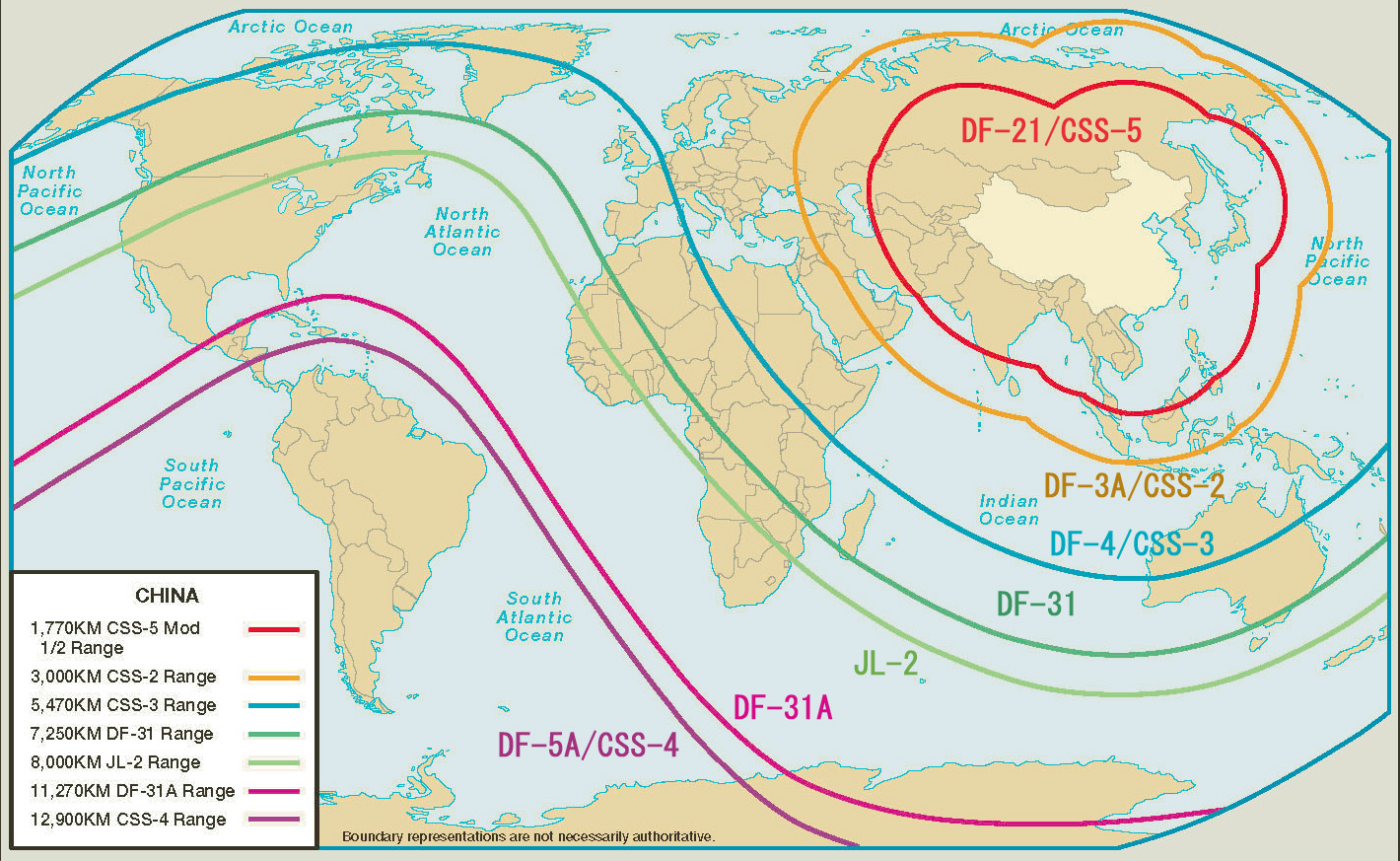
DF-16
The ''Dongfeng'' () series, typically abbreviated as "DF missiles", are a family of short, medium, intermediate-range and intercontinental ballistic missiles operated by the Chinese People's Liberation Army Rocket Force (formerly the Second Artillery Corps). History After the signing of the Sino-Soviet Treaty of Friendship, Alliance and Mutual Assistance in 1950, the Soviet Union assisted China's military R&D with training, technical documentation, manufacturing equipment and licensed production of Soviet weapons. In the area of ballistic missiles, the Soviets transferred R-1 (SS-1), R-2 (SS-2) and R-11F technology to China.13,000 km). Currently, an estimated 24-36 DF-5A's are in service as China's primary ICBM force. If the DF-5A is launched from the eastern part of the Qinghai province, it can reach cities like Los Angeles, Sacramento and San Francisco. If it is launched from the most eastern parts of northeastern provinces, it can cover all of the mainland of the Unit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prithvi Missile
Prithvi (Sanskrit: ''"Earth"'') is a tactical surface-to-surface short-range ballistic missile (SRBM) developed by Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) of India under the Integrated Guided Missile Development Program (IGMDP). It is deployed by India's Strategic Forces Command. Development and history The Government of India launched the Integrated Guided Missile Development Program in 1983 to achieve self-sufficiency in the development and production of wide range of ballistic missiles, surface-to-air missiles etc. Prithvi was the first missile to be developed under the program. DRDO attempted to build a surface-to-air missile under Project Devil. Variants make use of either liquid or both liquid and solid fuels. Developed as a battlefield missile, it could carry a nuclear warhead in its role as a tactical nuclear weapon. Variants The Prithvi missile project encompassed developing three variants for use by the Indian Army, Indian Air Force and the Indian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pralay (missile)
Pralay ("Pralaya : Apocalypse") is a canisterised tactical, surface-to-surface, and short-range ballistic missile (SRBM) for battlefield use developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) of India. The missile is an amalgamation of technologies developed for exoatmospheric interceptor missile Prithvi Defence Vehicle (PDV) from Indian Ballistic Missile Defence Programme and Prahaar tactical missile. The project to develop Pralay was sanctioned in March 2015 with a budget of . Development Research Centre Imarat (RCI) is the lead integrator in this project. Similar foreign missiles of the same class include Dongfeng 12 (CSS-X-15), Precision Strike Missile, 9K720 Iskander and Hyunmoo 2 missile. Powered by solid fuel rocket motor, the missile follows quasi-ballistic trajectory and able to perform mid-air maneuvers using maneuverable reentry vehicle (MaRV) to defeat anti-ballistic missile (ABM) interceptors. Pralay uses the same composite propellant develo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prahaar (missile)
Prahaar ("Strike") is an Indian solid-fuel rocket, solid-fuel road-mobile tactical ballistic missile developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO). Prahaar is expected to replace the Prithvi-I SRBM , short-range ballistic missile in Indian service. Development Prahaar is developed to provide a cost-effective, quick-reaction, all-weather, all-terrain, highly accurate battlefield support tactical weapon system. The development of the missile was carried out by the DRDO scientists in a span of less than two years. The maneuvering capability, greater acceleration, better accuracy and faster deployment fills the short-range tactical battlefield role as required by the Indian Army to take out strategic and tactical targets. The mobile launch platform will carry six missiles that can be deployed in stand-alone and canisterised mode, which can have different kind of warheads meant for different targets and can be fired in salvo mode in all directions covering t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prahaar Missile
Prahaar ("Strike") is an Indian solid-fuel road-mobile tactical ballistic missile developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO). Prahaar is expected to replace the Prithvi-I short-range ballistic missile in Indian service. Development Prahaar is developed to provide a cost-effective, quick-reaction, all-weather, all-terrain, highly accurate battlefield support tactical weapon system. The development of the missile was carried out by the DRDO scientists in a span of less than two years. The maneuvering capability, greater acceleration, better accuracy and faster deployment fills the short-range tactical battlefield role as required by the Indian Army to take out strategic and tactical targets. The mobile launch platform will carry six missiles that can be deployed in stand-alone and canisterised mode, which can have different kind of warheads meant for different targets and can be fired in salvo mode in all directions covering the entire azimuth plane. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sagarika (missile)
Sagarika (pronounced: sɑːgərikɑː), also known by the code names K-15 or B-05, is an Indian submarine-launched ballistic missile (SLBM) with a range of that was designed for retaliatory nuclear strikes. It belongs to the K Missile family and forms a part of India's nuclear triad. Description The K-15 is a two-stage submarine-launched ballistic missile which uses a gas booster to eject out of its launch platform and rise up to the surface of water. A solid rocket motor is fired after the missile reaches a fixed altitude. The missile has a range of around . Development Development of the K-15 missile started in the late 1990s with the goal of building a submarine-launched ballistic missile for use with the Indian Navy nuclear-powered s. It was developed at the Defence Research and Development Organisation’s (DRDO) missile complex in Hyderabad. The development of the underwater missile launcher, known as Project 420, was completed in 2001 and handed over to the Indian N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agni-I
Agni-I (Agni ''"Fire"'') is a medium-range ballistic missile that was developed by DRDO of India in the Integrated Guided Missile Development Program. It is a single-stage missile that was developed after the Kargil War to fill the gap between the range of the Prithvi (missile)#Prithvi II, Prithvi-II missile and the range of the Agni-II. It was first launched from a road mobile launcher at Integrated Test Range (ITR), Wheeler Island, India, Wheeler Island, on 25 January 2002. Less than 75 launchers are deployed. History and development Agni-I was first tested at the Interim Test Range in Chandipur, Orissa, Chandipur at 7:17AM on 22 May 1989, and is capable of carrying a conventional payload of 1,000 kg (2,200 lb) or a nuclear weapon, nuclear warhead. Agni missiles consist of one (short range) or two multistage rocket, stages (intermediate range). These are rail and road mobile and powered by solid rocket fuel, propellants. The Agni I has a range of 700–1,200 km ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SSBS S1
The SSBS was a series of French military medium-range ballistic missile A medium-range ballistic missile (MRBM) is a type of ballistic missile with medium range, this last classification depending on the standards of certain organizations. Within the U.S. Department of Defense, a medium-range missile is defined by ...s. Overview The first series, SSBS S1, was launched between 1965 and 1968. It had a maximum altitude of , a lift off thrust of 440 kN, total mass of , a diameter of and a total length of . References Ballistic missiles of France Experimental rockets Cancelled spacecraft Cancelled space launch vehicles Projects established in 1965 1960s in France {{Rocket-stub Medium-range ballistic missiles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pluton (missile)
The Pluton missile was a French nuclear-armed tactical ballistic missile (short-range ballistic missile, SRBM) system launched from a transporter erector launcher (TEL) platform mounted on an AMX-30 tank chassis. It was designed to provide the tactical part of French nuclear deterrence during the Cold War. Development The Pluton came in replacement of the U.S.-built '' Honest John'' missile. It had an operating range between , with a CEP of 150 m. This short range only allowed strikes on targets in West Germany or within France itself, which led to the development of the longer ranged ''Hadès'' missile. The system was relatively light-weight, which allowed its deployment in difficult conditions. A CT-20 drone was available to provide last-minute information about the target before launch, making the ''Pluton'' system battle-capable. A project for an updated version, called ''Super-Pluton'', was dropped in favour of the ''Hadès'' project, and the aging ''Pluton'' was grad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hadès
The Hadès system was a short-range ballistic pre-strategic nuclear weapon system designed by France, as a last warning before use of strategic nuclear weapons, in the perspective of a Soviet invasion of Western Europe. It was designed from July 1984 as a replacement for the tactical road-mobile Pluton missile. Initially 120 missiles were planned to be deployed. A wheeled trailer and launcher, each carrying two missiles in containers, was planned for deploying the Hadès. The original design had a range of 250 km, which was later increased to 480 km. The guidance system was an inertial platform which could be programmed to execute evasive maneuvers before hitting the target. A version designed to hit hardened underground targets also had a final guidance system which used a GPS-based digital system, resulting in a Circular Error Probable of only 5 m, compared to a CEP of 100 m for the standard version. Development Hadès began with project definition in 1975 as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in Western Asia. It covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula, and has a land area of about , making it the fifth-largest country in Asia, the second-largest in the Arab world, and the largest in Western Asia and the Middle East. It is bordered by the Red Sea to the west; Jordan, Iraq, and Kuwait to the north; the Persian Gulf, Qatar and the United Arab Emirates to the east; Oman to the southeast; and Yemen to the south. Bahrain is an island country off the east coast. The Gulf of Aqaba in the northwest separates Saudi Arabia from Egypt. Saudi Arabia is the only country with a coastline along both the Red Sea and the Persian Gulf, and most of its terrain consists of arid desert, lowland, steppe, and mountains. Its capital and largest city is Riyadh. The country is home to Mecca and Medina, the two holiest cities in Islam. Pre-Islamic Arabia, the territory that constitutes modern-day Saudi Ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |