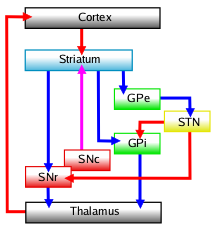
|
Thalamic Fasciculus
The thalamic fasciculus is a component of the subthalamus. It is synonymous with field H1 of Forel. Nerve fibres form a tract containing cerebellothalamic (crossed) and pallidothalamic (uncrossed) fibres, that is insinuated between the thalamus and the zona incerta. The thalamic fasciculus consists of fibers from the ansa lenticularis and from the lenticular fasciculus, coming from different portions of the medial globus pallidus, before they jointly enter the ventral anterior nucleus of the thalamus The thalamus (from Greek θάλαμος, "chamber") is a large mass of gray matter located in the dorsal part of the diencephalon (a division of the forebrain). Nerve fibers project out of the thalamus to the cerebral cortex in all directions, .... References External links * http://www.meddean.luc.edu/lumen/MedEd/Neuro/frames/nlDEs/nl06fr.htm * https://web.archive.org/web/20070419222336/http://www.endotext.org/neuroendo/neuroendo3b/neuroendo3b_2.htm (see figure #12) * https ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subthalamus
The subthalamus or prethalamus is a part of the diencephalon. Its most prominent structure is the subthalamic nucleus. The subthalamus connects to the globus pallidus, a basal nucleus of the telencephalon. Structure The subthalamus is located ventral to the thalamus, medial to the internal capsule and lateral to the hypothalamus. It is a region formed by several grey matter nuclei and their associated white matter structures, namely: *The subthalamic nucleus, whose neurons contain glutamate and have excitatory effects over neurons of globus pallidus and substantia nigra *Zona incerta, located between fields of Forel H1 and H2. It is continuous with the thalamic reticular nucleus and receives input from the precentral cortex. * Subthalamic fasciculus, formed by fibers that connect the globus pallidus with the subthalamic nucleus * Fields of Forel * Ansa lenticularis During development the subthalamus is continuous with the hypothalamus, but is separated by white matter fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fields Of Forel
The fields of Forel are areas in a deep part of the brain known as the diencephalon. They are below the thalamus and consist of three defined, white matter areas of the subthalamus. These three regions are also named "H fields": *Field H1, is the thalamic fasciculus, a horizontal white matter tract composed of the ansa lenticularis, lenticular fasciculus, and cerebellothalamic tracts between the subthalamus and the thalamus. These fibers are projections to the ventral anterior and ventral lateral thalamus from the basal ganglia ( globus pallidus) and the cerebellum. H1 is separated from H2 by the zona incerta. *Field H2 (synonymous with lenticular fasciculus) is also made up of projections from the pallidum to the thalamus, but these course the subthalamic nucleus (dorsal). *Field H (sometimes called field H3) is a large zone of mixed grey and white matter from the pallidothalamic tracts of the lenticular fasciculus and the ansa lenticularis which combine in an area just in fron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axon
An axon (from Greek ἄξων ''áxōn'', axis), or nerve fiber (or nerve fibre: see spelling differences), is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, in vertebrates, that typically conducts electrical impulses known as action potentials away from the nerve cell body. The function of the axon is to transmit information to different neurons, muscles, and glands. In certain sensory neurons (pseudounipolar neurons), such as those for touch and warmth, the axons are called afferent nerve fibers and the electrical impulse travels along these from the periphery to the cell body and from the cell body to the spinal cord along another branch of the same axon. Axon dysfunction can be the cause of many inherited and acquired neurological disorders that affect both the peripheral and central neurons. Nerve fibers are classed into three typesgroup A nerve fibers, group B nerve fibers, and group C nerve fibers. Groups A and B are myelinated, and group C are unmyelinated. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nerve Tract
A nerve tract is a bundle of nerve fibers (axons) connecting nuclei of the central nervous system. In the peripheral nervous system this is known as a nerve, and has associated connective tissue. The main nerve tracts in the central nervous system are of three types: association fibers, commissural fibers, and projection fibers. A tract may also be referred to as a commissure, decussation, pathway or fasciculus. A commissure connects the two cerebral hemispheres at the same levels, while a decussation connects at different levels (crosses obliquely). Types The nerve fibers in the central nervous system can be categorized into three groups on the basis of their course and connections. Different tracts may also be referred to as ''projections'' or ''radiations''. Association fibers The tracts that connect cortical areas within the same hemisphere are called association tracts. Long association fibers connect different lobes of a hemisphere to each other whereas short assoc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thalamus
The thalamus (from Greek θάλαμος, "chamber") is a large mass of gray matter located in the dorsal part of the diencephalon (a division of the forebrain). Nerve fibers project out of the thalamus to the cerebral cortex in all directions, allowing hub-like exchanges of information. It has several functions, such as the relaying of sensory signals, including motor signals to the cerebral cortex and the regulation of consciousness, sleep, and alertness. Anatomically, it is a paramedian symmetrical structure of two halves (left and right), within the vertebrate brain, situated between the cerebral cortex and the midbrain. It forms during embryonic development as the main product of the diencephalon, as first recognized by the Swiss embryologist and anatomist Wilhelm His Sr. in 1893. Anatomy The thalamus is a paired structure of gray matter located in the forebrain which is superior to the midbrain, near the center of the brain, with nerve fibers projecting out to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zona Incerta
The zona incerta (ZI) is a horizontally elongated region of gray matter in the subthalamus below the thalamus. Its connections project extensively over the brain from the cerebral cortex down into the spinal cord. Its function is unknown, though several potential functions related to "limbic–motor integration" have been proposed, such as controlling visceral activity and pain; gating sensory input and synchronizing cortical and subcortical brain rhythms. Its dysfunction may play a role in central pain syndrome. It has also been identified as a promising deep brain stimulation therapy target for treating Parkinson's disease. Its existence was first described by Auguste Forel in 1877 as a "region of which nothing certain can be said". A hundred and thirty years later in 2007, Nadia Urbain and Martin Deschênes of Université Laval noted that the "zona incerta is among the least studied regions of the brain; its name does not even appear in the index of many textbooks." Structure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ansa Lenticularis
The ansa lenticularis (''ansa lentiformis'' in older texts) is a part of the brain, making up the superior layer of the substantia innominata. Its fibers, derived from the medullary lamina of the lentiform nucleus, pass medially to end in the thalamus and subthalamic region, while others are said to end in the tegmentum and red nucleus. It is classified by NeuroNames as part of the subthalamus The subthalamus or prethalamus is a part of the diencephalon. Its most prominent structure is the subthalamic nucleus. The subthalamus connects to the globus pallidus, a basal nucleus of the telencephalon. Structure The subthalamus is locate .... References External links * {{Authority control Thalamic connections Basal ganglia connections ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lenticular Fasciculus
The lenticular fasciculus is a tract connecting the globus pallidus (internus) to the thalamus and is a part of the thalamic fasciculus. It is synonymous with field H2 of Forel. The thalamic fasciculus (composed of both the lenticular fasciculus and ansa lenticularis) runs to the thalamus The thalamus (from Greek θάλαμος, "chamber") is a large mass of gray matter located in the dorsal part of the diencephalon (a division of the forebrain). Nerve fibers project out of the thalamus to the cerebral cortex in all directions, .... Basically, it is part of a pathway that connects the globus pallidus and the thalamus. Lesions in this area can result in dyskinesias such as chorea-like movements. External links * https://web.archive.org/web/20070419222336/http://www.endotext.org/neuroendo/neuroendo3b/neuroendo3b_2.htm (see figure #12) * https://web.archive.org/web/20080504234454/http://isc.temple.edu/neuroanatomy/lab/atlas/mdbg/ {{Authority control Brainstem Thalamus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medial Globus Pallidus
The internal globus pallidus (GPi or medial globus pallidus; in rodents its homologue is known as the entopeduncular nucleus) and the external globus pallidus (GPe) make up the globus pallidus. The GPi is one of the output nuclei of the basal ganglia (the other being the substantia nigra pars reticulata). The GABAergic neurons of the GPi send their axons to the ventral anterior nucleus (VA) and the ventral lateral nucleus (VL) in the dorsal thalamus, to the centromedian complex, and to the pedunculopontine complex. The efferent bundle is constituted first of the ansa and lenticular fasciculus, then crosses the internal capsule within and in parallel to the Edinger's comb system then arrives at the laterosuperior corner of the subthalamic nucleus and constitutes the field H2 of Forel, then H, and suddenly changes its direction to form field H1 that goes to the inferior part of the thalamus. The distribution of axonal islands is widespread in the lateral region of the thalam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ventral Anterior Nucleus
The ventral anterior nucleus (VA) is a nucleus of the thalamus. It acts with the anterior part of the ventral lateral nucleus to modify signals from the basal ganglia. Inputs and outputs The ventral anterior nucleus receives neuronal inputs from the basal ganglia. Its main afferent fibres are from the globus pallidus. The efferent fibres from this nucleus pass into the premotor cortex The premotor cortex is an area of the motor cortex lying within the frontal lobe of the brain just anterior to the primary motor cortex. It occupies part of Brodmann's area 6. It has been studied mainly in primates, including monkeys and humans. ... for initiation and planning of movement. Functions It helps to function in movement by providing feedback for the outputs of the basal ganglia. Additional images File:Constudthal.gif, Thalamus File:Territoriostalamo.svg, Thalamus References {{DEFAULTSORT:Ventral Anterior Nucleus Thalamus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |