|
Thalamic
The thalamus (from Greek θάλαμος, "chamber") is a large mass of gray matter located in the dorsal part of the diencephalon (a division of the forebrain). Nerve fibers project out of the thalamus to the cerebral cortex in all directions, allowing hub-like exchanges of information. It has several functions, such as the relaying of sensory signals, including motor signals to the cerebral cortex and the regulation of consciousness, sleep, and alertness. Anatomically, it is a paramedian symmetrical structure of two halves (left and right), within the vertebrate brain, situated between the cerebral cortex and the midbrain. It forms during embryonic development as the main product of the diencephalon, as first recognized by the Swiss embryologist and anatomist Wilhelm His Sr. in 1893. Anatomy The thalamus is a paired structure of gray matter located in the forebrain which is superior to the midbrain, near the center of the brain, with nerve fibers projecting out to the cere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
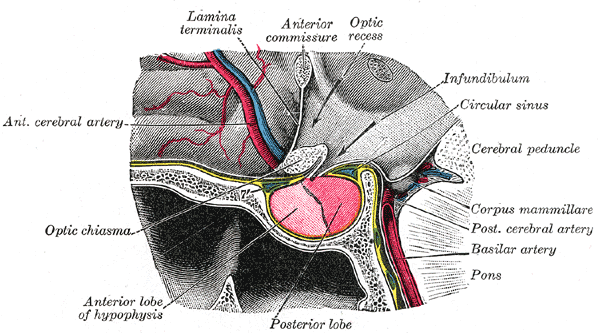
Third Ventricle
The third ventricle is one of the four connected ventricles of the ventricular system within the mammalian brain. It is a slit-like cavity formed in the diencephalon between the two thalami, in the midline between the right and left lateral ventricles, and is filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Running through the third ventricle is the interthalamic adhesion, which contains thalamic neurons and fibers that may connect the two thalami. Structure The third ventricle is a narrow, laterally flattened, vaguely rectangular region, filled with cerebrospinal fluid, and lined by ependyma. It is connected at the superior anterior corner to the lateral ventricles, by the interventricular foramina, and becomes the cerebral aqueduct (''aqueduct of Sylvius'') at the posterior caudal corner. Since the interventricular foramina are on the lateral edge, the corner of the third ventricle itself forms a bulb, known as the ''anterior recess'' (it is also known as the ''bulb of the ventricl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interthalamic Adhesion
The interthalamic adhesion (also known as the intermediate mass or middle commissure) is a flattened band of tissue that connects both parts of the thalamus at their medial surfaces. The medial surfaces form the upper part of the lateral wall to the third ventricle. In humans, it is only about one centimeter long – though in females, it is about 50% larger on average. Sometimes, it is in two parts – and 20% of the time, it is absent. In other mammals, it is larger. In 1889, a Portuguese anatomist by the name of Macedo examined 215 brains, showing that male humans are approximately twice as likely to lack an interthalamic adhesion as are female humans. He also reported its absence, still reported today in about 20% of humans. Its absence is seen to be of no consequence. The interthalamic adhesion contains nerve cells and nerve fibers; a few of the latter may cross the middle line, but most of them pass toward the middle line and then curve laterally on the same side. It is sti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lateral Geniculate Nucleus
In neuroanatomy, the lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN; also called the lateral geniculate body or lateral geniculate complex) is a structure in the thalamus and a key component of the mammalian visual pathway. It is a small, ovoid, ventral projection of the thalamus where the thalamus connects with the optic nerve. There are two LGNs, one on the left and another on the right side of the thalamus. In humans, both LGNs have six layers of neurons (grey matter) alternating with optic fibers (white matter). The LGN receives information directly from the ascending retinal ganglion cells via the optic tract and from the reticular activating system. Neurons of the LGN send their axons through the optic radiation, a direct pathway to the primary visual cortex. In addition, the LGN receives many strong feedback connections from the primary visual cortex. In humans as well as other mammals, the two strongest pathways linking the eye to the brain are those projecting to the dorsal part of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medial Geniculate Nucleus
The medial geniculate nucleus (MGN) or medial geniculate body (MGB) is part of the auditory thalamus and represents the thalamic relay between the inferior colliculus (IC) and the auditory cortex (AC). It is made up of a number of sub-nuclei that are distinguished by their neuronal morphology and density, by their afferent and efferent connections, and by the coding properties of their neurons. It is thought that the MGN influences the direction and maintenance of attention. Divisions The MGN has three major divisions; ventral (VMGN), dorsal (DMGN) and medial (MMGN). Whilst the VMGN is specific to auditory information processing, the DMGN and MMGN also receive information from non-auditory pathways. Ventral subnucleus Cell types There are two main cell types in the ventral subnucleus of the medial geniculate body (VMGN): * Thalamocortical relay cells (or principal neurons): The dendritic input to these cells comes from two sets of dendritic trees oriented on opposite poles of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Thalamic Nuclei
This traditional list does not accord strictly with human thalamic anatomy. Nuclear groups of the thalamus include: *anterior nuclear group ** anteroventral nucleus ** anterodorsal nucleus ** anteromedial nucleus **superficial ("lateral dorsal") *medial nuclear group (or dorsomedial nucleus) ** parvocellular part **magnocellular part *midline nuclear group or paramedian **paratenial nucleus ** paraventricular nucleus of thalamus **reuniens nucleus **rhomboidal nucleus *Intralaminar nuclear group ( Intralaminar nuclei) **anterior (rostral) group *** paracentral nucleus ***central lateral nucleus ***central medial nucleus **posterior (caudal) intralaminar group ***centromedian nucleus ***parafascicular nucleus *lateral nuclear group in fact a false entity replaced by **posterior region *** pulvinar ****anterior pulvinar nucleus **** lateral pulvinar nucleus **** medial pulvinar nucleus **** inferior pulvinar nucleus *** lateral posterior nucleus belongs to pulvinar ***( lateral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebral Cortex
The cerebral cortex, also known as the cerebral mantle, is the outer layer of neural tissue of the cerebrum of the brain in humans and other mammals. The cerebral cortex mostly consists of the six-layered neocortex, with just 10% consisting of allocortex. It is separated into two cortices, by the longitudinal fissure that divides the cerebrum into the left and right cerebral hemispheres. The two hemispheres are joined beneath the cortex by the corpus callosum. The cerebral cortex is the largest site of neural integration in the central nervous system. It plays a key role in attention, perception, awareness, thought, memory, language, and consciousness. The cerebral cortex is part of the brain responsible for cognition. In most mammals, apart from small mammals that have small brains, the cerebral cortex is folded, providing a greater surface area in the confined volume of the cranium. Apart from minimising brain and cranial volume, cortical folding is crucial for the brain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posterior Cerebral Artery
The posterior cerebral artery (PCA) is one of a pair of cerebral arteries that supply oxygenated blood to the occipital lobe, part of the back of the human brain. The two arteries originate from the distal end of the basilar artery, where it bifurcates into the left and right posterior cerebral arteries. These anastomose with the middle cerebral arteries and internal carotid arteries via the posterior communicating arteries. Structure The posterior cerebral artery is subdivided into 4 sections P1: pre-communicating segment * Originated at the termination of the basilar artery * May give rise to the artery of Percheron if present P2: post-communicating segment * From the PCOM around the midbrain * Terminates as it enters the quadrigeminal ganglion * Gives rise to the choroidal branches (medial and lateral posterior choroidal arteries) P3: quadrigeminal segment * Courses posteromedially through the quadrigeminal cistern * Terminates as it enters the sulk of the occipital ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulvinar Nuclei
The pulvinar nuclei or nuclei of the pulvinar (nuclei pulvinares) are the nuclei (cell bodies of neurons) located in the thalamus (a part of the vertebrate brain). As a group they make up the collection called the pulvinar of the thalamus (pulvinar thalami), usually just called the pulvinar. The pulvinar is usually grouped as one of the ''lateral thalamic nuclei'' in rodents and carnivores, and stands as an independent complex in primates. Structure By convention, the pulvinar is divided into four nuclei: Their connectomic details are as follows: * The ''lateral'' and ''inferior'' pulvinar nuclei have widespread connections with early visual cortical areas. * The dorsal part of the ''lateral'' pulvinar nucleus predominantly has connections with posterior parietal cortex and the dorsal stream cortical areas. * The ''medial'' pulvinar nucleus has widespread connections with cingulate, posterior parietal, premotor and prefrontal cortical areas. * The pulvinar also has input fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Midbrain
The midbrain or mesencephalon is the forward-most portion of the brainstem and is associated with vision, hearing, motor control, sleep and wakefulness, arousal (alertness), and temperature regulation. The name comes from the Greek ''mesos'', "middle", and ''enkephalos'', "brain". Structure The principal regions of the midbrain are the tectum, the cerebral aqueduct, tegmentum, and the cerebral peduncles. Rostrally the midbrain adjoins the diencephalon (thalamus, hypothalamus, etc.), while caudally it adjoins the hindbrain (pons, medulla and cerebellum). In the rostral direction, the midbrain noticeably splays laterally. Sectioning of the midbrain is usually performed axially, at one of two levels – that of the superior colliculi, or that of the inferior colliculi. One common technique for remembering the structures of the midbrain involves visualizing these cross-sections (especially at the level of the superior colliculi) as the upside-down face of a be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Matter
White matter refers to areas of the central nervous system (CNS) that are mainly made up of myelinated axons, also called tracts. Long thought to be passive tissue, white matter affects learning and brain functions, modulating the distribution of action potentials, acting as a relay and coordinating communication between different brain regions. White matter is named for its relatively light appearance resulting from the lipid content of myelin. However, the tissue of the freshly cut brain appears pinkish-white to the naked eye because myelin is composed largely of lipid tissue veined with capillaries. Its white color in prepared specimens is due to its usual preservation in formaldehyde. Structure White matter White matter is composed of bundles, which connect various grey matter areas (the locations of nerve cell bodies) of the brain to each other, and carry nerve impulses between neurons. Myelin acts as an insulator, which allows electrical signals to jump, rather than c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gray Matter
Grey matter is a major component of the central nervous system, consisting of neuronal cell bodies, neuropil (dendrites and unmyelinated axons), glial cells (astrocytes and oligodendrocytes), synapses, and capillaries. Grey matter is distinguished from white matter in that it contains numerous cell bodies and relatively few myelinated axons, while white matter contains relatively few cell bodies and is composed chiefly of long-range myelinated axons. The colour difference arises mainly from the whiteness of myelin. In living tissue, grey matter actually has a very light grey colour with yellowish or pinkish hues, which come from capillary blood vessels and neuronal cell bodies. Structure Grey matter refers to unmyelinated neurons and other cells of the central nervous system. It is present in the brain, brainstem and cerebellum, and present throughout the spinal cord. Grey matter is distributed at the surface of the cerebral hemispheres (cerebral cortex) and of the cerebellum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilhelm His Sr , the Dutch national anthem
{{Disambiguation ...
Wilhelm may refer to: People and fictional characters * William Charles John Pitcher, costume designer known professionally as "Wilhelm" * Wilhelm (name), a list of people and fictional characters with the given name or surname Other uses * Mount Wilhelm, the highest mountain in Papua New Guinea * Wilhelm Archipelago, Antarctica * Wilhelm (crater), a lunar crater See also * Wilhelm scream, a stock sound effect * SS ''Kaiser Wilhelm II'', or USS ''Agamemnon'', a German steam ship * Wilhelmus "Wilhelmus van Nassouwe", usually known just as "Wilhelmus" ( nl, Het Wilhelmus, italic=no; ; English translation: "The William"), is the national anthem of both the Netherlands and the Kingdom of the Netherlands. It dates back to at least 1572 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |