|
Terutroban
Terutroban is an antiplatelet agent developed by Servier Laboratories. It is a selective thromboxane prostanoid (TP) antagonist and is an orally active drug in clinical development for the secondary prevention of acute thrombotic complications. It has been tested in the Phase III clinical trial PERFORM (''Prevention of cerebrovascular and cardiovascular Events of ischemic origin with teRutroban in patients with a history oF ischemic strOke or tRansient ischeMic attack''). The study was prematurely stopped and it could not be determined whether terutroban has a better effect than aspirin. The 2011 clinical trial that studied the antiplatelet agent versus aspirin found that it was not superior in the prevention of cerebral and cardiovascular ischaemic events, although it was significantly better in patients who already suffered previous stroke to the qualifying event. Researchers from the University of Milan also found in a new research that terutroban can prevent the developme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium
Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na (from Latin ''natrium'') and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 of the periodic table. Its only stable isotope is 23Na. The free metal does not occur in nature, and must be prepared from compounds. Sodium is the sixth most abundant element in the Earth's crust and exists in numerous minerals such as feldspars, sodalite, and halite (NaCl). Many salts of sodium are highly water-soluble: sodium ions have been leached by the action of water from the Earth's minerals over eons, and thus sodium and chlorine are the most common dissolved elements by weight in the oceans. Sodium was first isolated by Humphry Davy in 1807 by the electrolysis of sodium hydroxide. Among many other useful sodium compounds, sodium hydroxide (lye) is used in soap manufacture, and sodium chloride (edible salt) is a de-icing agent and a nutrient for animals including h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiplatelet Agent
An antiplatelet drug (antiaggregant), also known as a platelet agglutination inhibitor or platelet aggregation inhibitor, is a member of a class of pharmaceuticals that decrease platelet aggregation and inhibit thrombus formation. They are effective in the arterial circulation where anticoagulants have little effect. They are widely used in primary and secondary prevention of thrombotic cerebrovascular or cardiovascular disease. Antiplatelet therapy with one or more of these drugs decreases the ability of blood clots to form by interfering with the platelet activation process in primary hemostasis. Antiplatelet drugs can reversibly or irreversibly inhibit the process involved in platelet activation resulting in decreased tendency of platelets to adhere to one another and to damaged blood vessels' endothelium. Choice A 2006 review states: "...low-dose aspirin increases the risk of major bleeding 2-fold compared with placebo. However, the annual incidence of major bleeding du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Servier Laboratories
Servier Laboratories (French: Laboratoires Servier, often abbreviated to Servier) is an international pharmaceutical company governed by a non-profit foundation, with its headquarters in France (Suresnes). The consolidated turnover for the 2018 financial year was €4.2 billion. Servier is the leading French independent pharmaceutical company, and the second largest French pharmaceutical company worldwide. It has branches in 149 countries, achieving 82% of its sales outside France. The company reportedly invests a little under 25% of its turnover in research and development, which occupies 3,000 of its 22,000 employees worldwide. The company's production sites produced 853 million drug boxes in 2013. The Servier Clinical Support Unit in Gidy (near Orléans), which produces drugs for clinical trials, is the largest unit of its kind in Europe. Servier Laboratories is a full member of the European Federation of Pharmaceutical Industries and Associations (EFPIA). In 2018, Servier f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phase III Clinical Trial
The phases of clinical research are the stages in which scientists conduct experiments with a health intervention to obtain sufficient evidence for a process considered effective as a medical treatment. For drug development, the clinical phases start with testing for safety in a few human subjects, then expand to many study participants (potentially tens of thousands) to determine if the treatment is effective. Clinical research is conducted on drug candidates, vaccine candidates, new medical devices, and new diagnostic assays. Summary Clinical trials testing potential medical products are commonly classified into four phases. The drug development process will normally proceed through all four phases over many years. If the drug successfully passes through Phases I, II, and III, it will usually be approved by the national regulatory authority for use in the general population. Phase IV trials are 'post-marketing' or 'surveillance' studies conducted to monitor safety over sever ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aspirin
Aspirin, also known as acetylsalicylic acid (ASA), is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to reduce pain, fever, and/or inflammation, and as an antithrombotic. Specific inflammatory conditions which aspirin is used to treat include Kawasaki disease, pericarditis, and rheumatic fever. Aspirin is also used long-term to help prevent further heart attacks, ischaemic strokes, and blood clots in people at high risk. For pain or fever, effects typically begin within 30 minutes. Aspirin works similarly to other NSAIDs but also suppresses the normal functioning of platelets. One common adverse effect is an upset stomach. More significant side effects include stomach ulcers, stomach bleeding, and worsening asthma. Bleeding risk is greater among those who are older, drink alcohol, take other NSAIDs, or are on other blood thinners. Aspirin is not recommended in the last part of pregnancy. It is not generally recommended in children with infections because of the risk of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thromboxane Receptor
The thromboxane receptor (TP) also known as the prostanoid TP receptor is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TBXA2R'' gene, The thromboxane receptor is one among the five classes of prostanoid receptors and was the first eicosanoid receptor cloned. The TP receptor derives its name from its preferred endogenous ligand thromboxane A2. Gene The gene responsible for directing the synthesis of the thromboxane receptor, ''TBXA2R'', is located on chromosome 19 at position p13.3, spans 15 kilobases, and contains 5 exons. ''TBXA2R'' codes for a member of the G protein-coupled super family of seven-transmembrane receptors. Heterogeneity Molecular biology findings have provided definitive evidence for two human TP receptor subtypes. The originally cloned TP from placenta (343 amino acids in length) is known as the α isoform and the splice variant cloned from endothelium (with 407 amino acids), termed the β isoform. The first 328 amino acids are the same for both isoforms, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Platelet Aggregation
Platelets, also called thrombocytes (from Greek θρόμβος, "clot" and κύτος, "cell"), are a component of blood whose function (along with the coagulation factors) is to react to bleeding from blood vessel injury by clumping, thereby initiating a blood clot. Platelets have no cell nucleus; they are fragments of cytoplasm that are derived from the megakaryocytes of the bone marrow or lung, which then enter the circulation. Platelets are found only in mammals, whereas in other vertebrates (e.g. birds, amphibians), thrombocytes circulate as intact mononuclear cells. One major function of platelets is to contribute to hemostasis: the process of stopping bleeding at the site of interrupted endothelium. They gather at the site and, unless the interruption is physically too large, they plug the hole. First, platelets attach to substances outside the interrupted endothelium: ''adhesion''. Second, they change shape, turn on receptors and secrete chemical messengers: ''activation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vasoconstriction
Vasoconstriction is the narrowing of the blood vessels resulting from contraction of the muscular wall of the vessels, in particular the large arteries and small arterioles. The process is the opposite of vasodilation, the widening of blood vessels. The process is particularly important in controlling hemorrhage and reducing acute blood loss. When blood vessels constrict, the flow of blood is restricted or decreased, thus retaining body heat or increasing vascular resistance. This makes the skin turn paler because less blood reaches the surface, reducing the radiation of heat. On a larger level, vasoconstriction is one mechanism by which the body regulates and maintains mean arterial pressure. Medications causing vasoconstriction, also known as vasoconstrictors, are one type of medicine used to raise blood pressure. Generalized vasoconstriction usually results in an increase in systemic blood pressure, but it may also occur in specific tissues, causing a localized reduction in bl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiplatelet Drugs
An antiplatelet drug (antiaggregant), also known as a platelet agglutination inhibitor or platelet aggregation inhibitor, is a member of a class of pharmaceuticals that decrease platelet aggregation and inhibit thrombus formation. They are effective in the arterial circulation where anticoagulants have little effect. They are widely used in primary and secondary prevention of thrombotic cerebrovascular or cardiovascular disease. Antiplatelet therapy with one or more of these drugs decreases the ability of blood clots to form by interfering with the platelet activation process in primary hemostasis. Antiplatelet drugs can reversibly or irreversibly inhibit the process involved in platelet activation resulting in decreased tendency of platelets to adhere to one another and to damaged blood vessels' endothelium. Choice A 2006 review states: "...low-dose aspirin increases the risk of major bleeding 2-fold compared with placebo. However, the annual incidence of major bleeding du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlorobenzenes
Chlorobenzene is an aromatic organic compound with the chemical formula C6H5Cl. This colorless, flammable liquid is a common solvent and a widely used intermediate in the manufacture of other chemicals. Uses Historical The major use of chlorobenzene is as an intermediate in the production of herbicides, dyestuffs, and rubber. Chlorobenzene is also used as a high-boiling solvent in industrial applications as well as in the laboratory. Chlorobenzene is nitrated on a large scale to give a mixture of 2-nitrochlorobenzene and 4-nitrochlorobenzene, which are separated. These mononitrochlorobenzenes are converted to related 2-nitrophenol, 2-nitroanisole, bis(2-nitrophenyl)disulfide, and 2-nitroaniline by nucleophilic displacement of the chloride, with respectively sodium hydroxide, sodium methoxide, sodium disulfide, and ammonia. The conversions of the 4-nitro derivative are similar. Chlorobenzene once was used in the manufacture of pesticides, most notably DDT, by reaction with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
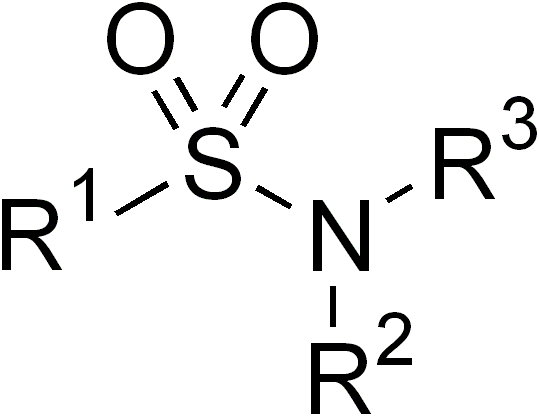
Sulfonamides
In organic chemistry, the sulfonamide functional group (also spelled sulphonamide) is an organosulfur group with the structure . It consists of a sulfonyl group () connected to an amine group (). Relatively speaking this group is unreactive. Because of the rigidity of the functional group, sulfonamides are typically crystalline; for this reason, the formation of a sulfonamide is a classic method to convert an amine into a crystalline derivative which can be identified by its melting point. Many important drugs contain the sulfonamide group. A sulfonamide (compound) is a chemical compound that contains this group. The general formula is or , where each R is some organic group; for example, "methanesulfonamide" (where R = methane, R' = R" = hydrogen) is . Any sulfonamide can be considered as derived from a sulfonic acid by replacing a hydroxyl group () with an amine group. In medicine, the term "sulfonamide" is sometimes used as a synonym for sulfa drug, a derivative or var ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |