|
Tendinous Arch Of Pelvic Fascia
At the level of a line extending from the lower part of the pubic symphysis to the spine of the ischium is a thickened whitish band in this upper layer of the diaphragmatic part of the pelvic fascia. It is termed the tendinous arch or white line of the pelvic fascia, and marks the line of attachment of the special fascia (pars endopelvina fasciae pelvis) which is associated with the pelvic viscera In biology, an organ is a collection of tissues joined in a structural unit to serve a common function. In the hierarchy of life, an organ lies between tissue and an organ system. Tissues are formed from same type cells to act together in a f .... It joins the fascia of the pubocervical fascia that covers the anterior wall of the vagina. If this fascia falls, the ipsilateral side of the vagina falls, carrying with it the bladder and the urethra, and thus contributing to urinary incontinence. References External links * - "The Female Pelvis: Muscles of the Pelvic Diaphragm" * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
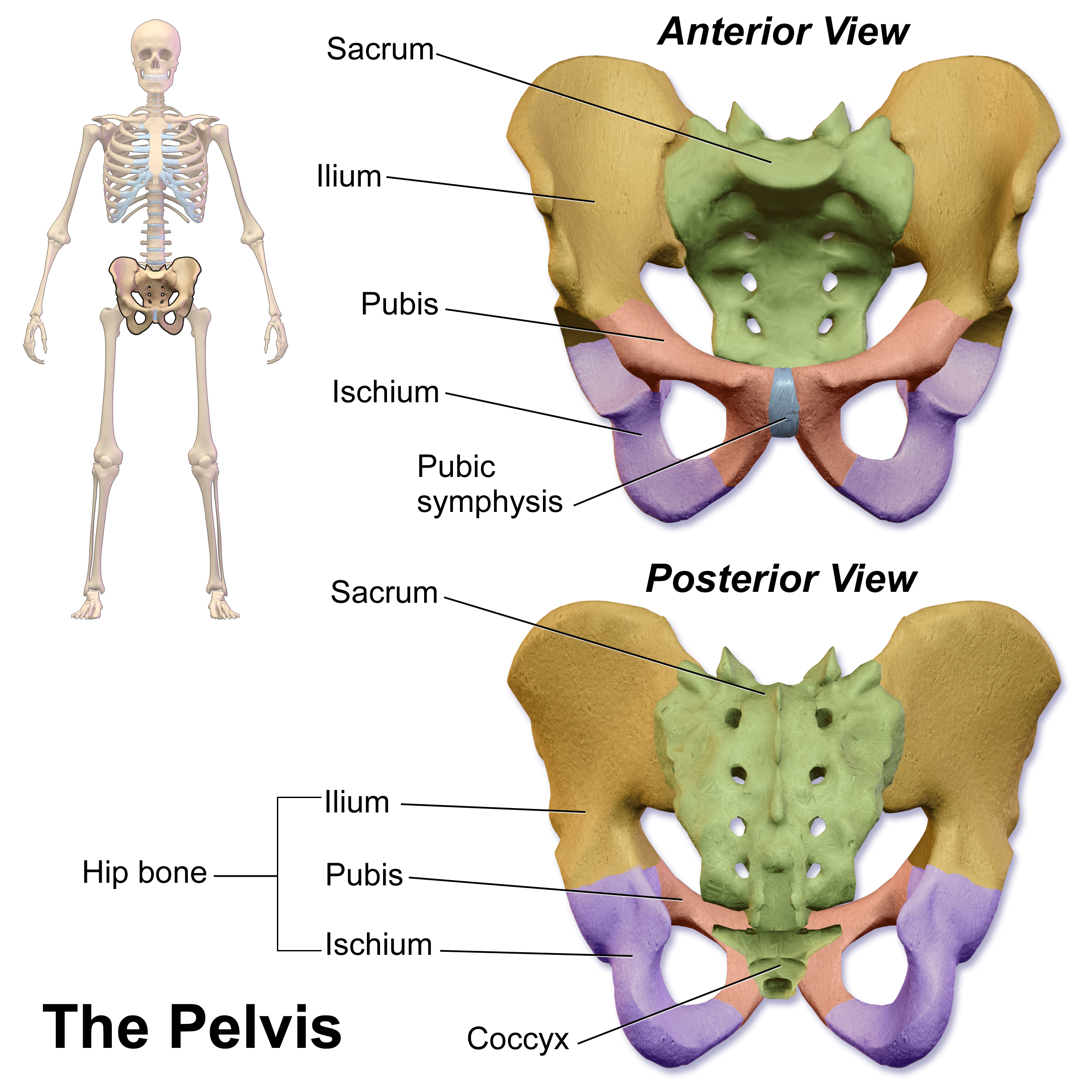
Pelvis
The pelvis (plural pelves or pelvises) is the lower part of the trunk, between the abdomen and the thighs (sometimes also called pelvic region), together with its embedded skeleton (sometimes also called bony pelvis, or pelvic skeleton). The pelvic region of the trunk includes the bony pelvis, the pelvic cavity (the space enclosed by the bony pelvis), the pelvic floor, below the pelvic cavity, and the perineum, below the pelvic floor. The pelvic skeleton is formed in the area of the back, by the sacrum and the coccyx and anteriorly and to the left and right sides, by a pair of hip bones. The two hip bones connect the spine with the lower limbs. They are attached to the sacrum posteriorly, connected to each other anteriorly, and joined with the two femurs at the hip joints. The gap enclosed by the bony pelvis, called the pelvic cavity, is the section of the body underneath the abdomen and mainly consists of the reproductive organs (sex organs) and the rectum, while the pelvic f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pubic Symphysis
The pubic symphysis is a secondary cartilaginous joint between the left and right superior rami of the pubis of the hip bones. It is in front of and below the urinary bladder. In males, the suspensory ligament of the penis attaches to the pubic symphysis. In females, the pubic symphysis is close to the clitoris. In most adults it can be moved roughly 2 mm and with 1 degree rotation. This increases for women at the time of childbirth. The name comes from the Greek word ''symphysis'', meaning 'growing together'. Structure The pubic symphysis is a nonsynovial amphiarthrodial joint. The width of the pubic symphysis at the front is 3–5 mm greater than its width at the back. This joint is connected by fibrocartilage and may contain a fluid-filled cavity; the center is avascular, possibly due to the nature of the compressive forces passing through this joint, which may lead to harmful vascular disease. The ends of both pubic bones are covered by a thin layer of hyaline ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spine Of The Ischium
The ischial spine is part of the posterior border of the body of the ischium bone of the pelvis. It is a thin and pointed triangular eminence, more or less elongated in different subjects. Structure The pudendal nerve travels close to the ischial spine. Clinical significance The ischial spine can serve as a landmark in pudendal anesthesia, as the pudendal nerve The pudendal nerve is the main nerve of the perineum. It carries sensation from the external genitalia of both sexes and the skin around the anus and perineum, as well as the motor supply to various pelvic muscles, including the male or fem ... lies close to the ischial spine. Additional images File:Sciatic notches.png, Right hip bone, external surface, showing the greater and lesser sciatic notches, separated by the ischial spine. File:Gray319.png, Articulations of pelvis. Anterior view. File:Slide3ADA.JPG, PELVIS. ANTERIOR VIEW. References External links * - "The Female Perineum: Osteology" * - "Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pelvic Fascia
The pelvic fasciae are the fascia of the pelvis and can be divided into: * (a) the fascial sheaths of ** the Obturator internus muscle ( Fascia of the Obturator internus) ** the Piriformis muscle ( Fascia of the Piriformis) ** the pelvic floor * (b) fascia associated with the organs of the pelvis. Structure Fascia of pelvic organs Pelvic fascia extends to cover the organs within the pelvis. It is attached to the fascia that runs along the pelvic floor along the tendinous arch. The fascia which covers pelvic organs can be divided according to the organs that are covered: * The front is known as the "vesical layer". It forms the anterior and lateral ligaments of the bladder. * In males, its middle lamina crosses the floor of the pelvis between the rectum and vesiculæ seminales as the ''rectovesical septum''; in the female this is perforated by the cervix and is named the transverse cervical ligament. * At the back, the fascia passes to the side of the rectum; it forms a loose s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viscera
In biology, an organ is a collection of tissues joined in a structural unit to serve a common function. In the hierarchy of life, an organ lies between tissue and an organ system. Tissues are formed from same type cells to act together in a function. Tissues of different types combine to form an organ which has a specific function. The intestinal wall for example is formed by epithelial tissue and smooth muscle tissue. Two or more organs working together in the execution of a specific body function form an organ system, also called a biological system or body system. An organ's tissues can be broadly categorized as parenchyma, the functional tissue, and stroma, the structural tissue with supportive, connective, or ancillary functions. For example, the gland's tissue that makes the hormones is the parenchyma, whereas the stroma includes the nerves that innervate the parenchyma, the blood vessels that oxygenate and nourish it and carry away its metabolic wastes, and the co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pelvis
The pelvis (plural pelves or pelvises) is the lower part of the trunk, between the abdomen and the thighs (sometimes also called pelvic region), together with its embedded skeleton (sometimes also called bony pelvis, or pelvic skeleton). The pelvic region of the trunk includes the bony pelvis, the pelvic cavity (the space enclosed by the bony pelvis), the pelvic floor, below the pelvic cavity, and the perineum, below the pelvic floor. The pelvic skeleton is formed in the area of the back, by the sacrum and the coccyx and anteriorly and to the left and right sides, by a pair of hip bones. The two hip bones connect the spine with the lower limbs. They are attached to the sacrum posteriorly, connected to each other anteriorly, and joined with the two femurs at the hip joints. The gap enclosed by the bony pelvis, called the pelvic cavity, is the section of the body underneath the abdomen and mainly consists of the reproductive organs (sex organs) and the rectum, while the pelvic f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |