|
Tax Efficiency
Economic theory evaluates how taxes are able to provide the government with required amount of the financial resources (fiscal efficiency) and what are the impacts of this tax system on overall economic efficiency. If tax efficiency needs to be assessed, tax cost must be taken into account, including administrative costs and excessive tax burden also known as the dead weight loss of taxation (DWL). Direct administrative costs include state administration costs for the organisation of the tax system, for the evidence of taxpayers, tax collection and control. Indirect administrative costs can include time spent filling out tax returns or money spent on paying tax advisors. Achieving an ideal tax system is not possible in practice. However, there is an effort to find the optimal form of taxation. For example personal income taxation should guarantee a high level of equity through progressiveness. A financial process is said to be tax efficient if it is taxed at a lower rate than an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heir
Inheritance is the practice of receiving private property, titles, debts, entitlements, privileges, rights, and obligations upon the death of an individual. The rules of inheritance differ among societies and have changed over time. Officially bequeathing private property and/or debts can be performed by a testator via will, as attested by a notary or by other lawful means. Terminology In law, an ''heir'' is a person who is entitled to receive a share of the deceased's (the person who died) property, subject to the rules of inheritance in the jurisdiction of which the deceased was a citizen or where the deceased (decedent) died or owned property at the time of death. The inheritance may be either under the terms of a will or by intestate laws if the deceased had no will. However, the will must comply with the laws of the jurisdiction at the time it was created or it will be declared invalid (for example, some states do not recognise handwritten wills as valid, or only in s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grantor Retained Annuity Trust
A grantor-retained annuity trust (commonly referred to by the acronym GRAT), is a financial instrument commonly used in the United States to make large financial gifts to family members without paying a U.S. gift tax. Basic mechanism A grantor transfers property into an irrevocable trust in exchange for the right to receive fixed payments at least annually, based on original fair market value of the property transferred. At the end of a specified time, any remaining value in the trust is passed on to a beneficiary of the trust as a gift. Beneficiaries are generally close family members of the grantor, such as children or grandchildren, who are prohibited from being named beneficiaries of another estate freeze technique, the grantor retained income trust. If a grantor dies before the trust period ends, the assets in the GRAT are included in the grantor's estate by operation of I.R.C. § 2036, eliminating any potential gift tax benefit; this is the GRAT's main weakness as a tax avo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inheritance
Inheritance is the practice of receiving private property, Title (property), titles, debts, entitlements, Privilege (law), privileges, rights, and Law of obligations, obligations upon the death of an individual. The rules of inheritance differ among societies and have changed over time. Officially bequest, bequeathing private property and/or debts can be performed by a testator via will (law), will, as attested by a notary or by other lawful means. Terminology In law, an ''heir'' is a person who is entitled to receive a share of the decedent, deceased's (the person who died) property, subject to the rules of inheritance in the jurisdiction of which the deceased was a citizen or where the deceased (decedent) died or owned property at the time of death. The inheritance may be either under the terms of a will or by intestate laws if the deceased had no will. However, the will must comply with the laws of the jurisdiction at the time it was created or it will be declared invalid ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
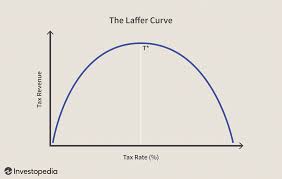
Laffer Curve Img
Laffer may refer to: * Laffer, South Australia, locality * Arthur Laffer (born 1940), American economist * George Laffer (1866–1933), South Australian politician * Jae Laffer, Australian rock singer-songwriter * Larry Laffer Lawrence Laffer is a player character and the protagonist in the ''Leisure Suit Larry'' series of adventure video games, created by Al Lowe and Mark Crowe for ''Leisure Suit Larry in the Land of the Lounge Lizards'' in 1987 and later voiced by ..., a fictional character from the ''Leisure Suit Larry'' game series See also * * Lafer, surname * Laugher (other) {{disambig, surname ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |