|
Tasmanite
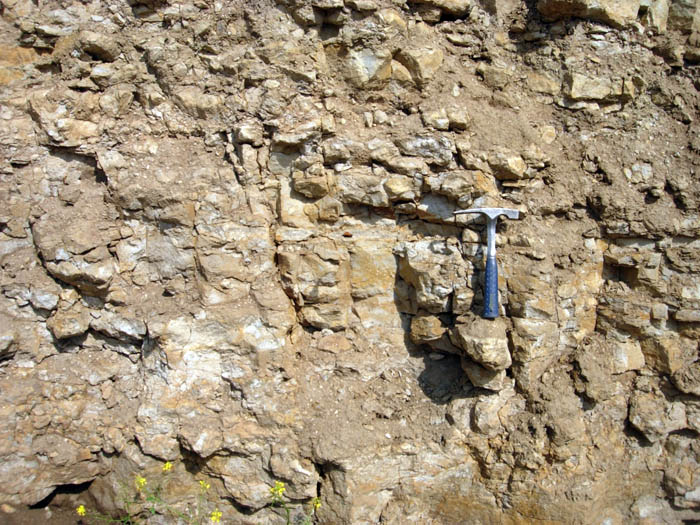
Tasmanite is a sedimentary rock type almost entirely consisting of the prasinophyte alga ''Tasmanites''. It is commonly associated with high-latitude, nutrient-rich, marginal marine settings find in Tasmania. It is classified as marine type oil shale.Hutton, A.C. 1987. Petrographic classification of oil shales // Intern. J. Coal Geol. 1987. Vol. 8. P. 203–231. It is found in many oil-prone source rocks and, when present, contributes to the oil generation potential of the rock. Some sources also produce a red-brown translucent material similar to amber which has also been called tasmanite. See also *Cannel coal * Kukersite * Lamosite * Marinite *Torbanite *Oil shale geology Oil shale geology is a branch of geologic sciences which studies the formation and composition of oil shales–fine-grained sedimentary rocks containing significant amounts of kerogen, and belonging to the group of sapropel fuels. Oil shale f ... References Oil shale geology Oil shale in Australia< ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oil Shale Geology
Oil shale geology is a branch of geologic sciences which studies the formation and composition of oil shales–fine-grained sedimentary rocks containing significant amounts of kerogen, and belonging to the group of sapropel fuels. Oil shale formation takes place in a number of depositional settings and has considerable compositional variation. Oil shales can be classified by their composition (carbonate minerals such as calcite or detrital minerals such as quartz and clays) or by their depositional environment (large lakes, shallow marine, and lagoon/small lake settings). Much of the organic matter in oil shales is of algal origin, but may also include remains of vascular land plants. Three major type of organic matter ( macerals) in oil shale are telalginite, lamalginite, and bituminite. Some oil shale deposits also contain metals which include vanadium, zinc, copper, and uranium. Most oil shale deposits were formed during Middle Cambrian, Early and Middle Ordovician, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cannel Coal
Cannel coal or candle coal is a type of bituminous coal, also classified as terrestrial type oil shale. Hutton(1987) Dyni (2006), pp. 3–4 Speight (2012), pp. 6–7 Due to its physical morphology and low mineral content cannel coal is considered to be coal but by its texture and composition of the organic matter it is considered to be oil shale. Han et al. (1999) Although historically the term cannel coal has been used interchangeably with boghead coal, a more recent classification system restricts cannel coal to terrestrial origin, and boghead coal to lacustrine environments. Composition Cannel coal is brown to black oil shale. It comes from resins, spores, waxes, and cutinaceous and corky materials of terrestrial vascular plants, in part from Lycopsid (scale tree). Cannel coal was accumulated in ponds and shallow lakes in peat-forming swamps and bogs of the Carboniferous age under oxygen-deficient conditions. Stach (1975), p. 428 Thus cannel coal seams are shallow and often fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oil Shale
Oil shale is an organic-rich fine-grained sedimentary rock containing kerogen (a solid mixture of organic chemical compounds) from which liquid hydrocarbons can be produced. In addition to kerogen, general composition of oil shales constitutes inorganic substance and bitumens. Based on their deposition environment, oil shales are classified as marine, lacustrine and terrestrial oil shales. Oil shales differ from oil-''bearing'' shales, shale deposits that contain petroleum (tight oil) that is sometimes produced from drilled wells. Examples of oil-''bearing'' shales are the Bakken Formation, Pierre Shale, Niobrara Formation, and Eagle Ford Formation. Accordingly, shale oil produced from oil shale should not be confused with tight oil, which is also frequently called shale oil. Deposits of oil shale occur around the world, including major deposits in the United States. A 2016 estimate of global deposits set the total world resources of oil shale equivalent of of oil in place. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kukersite
Kukersite is a light-brown marine type oil shale of Ordovician age. It is found in the Baltic Oil Shale Basin in Estonia and North-West Russia. It is of the lowest Upper Ordovician formation, formed some 460 million years ago. It was named after the German name of the Kukruse Manor in the north-east of Estonia by the Russian paleobotanist Mikhail Zalessky in 1917. Some minor kukersite resources occur in sedimentary basins of Michigan, Illinois, Wisconsin, North Dakota, and Oklahoma in North America and in the Amadeus and Canning basins of Australia. Baltic Oil Shale Basin The Baltic Oil Shale Basin covers about . Main kukersite deposits are Estonian and Tapa deposits in Estonia, and Leningrad deposit in Russia (also known as Gdov or Oudova deposit). Other occurrences in Russia are Veimarn and Chudovo–Babinskoe deposits. The Estonian deposit, which covers about , is exploited industrially; the Tapa deposit is not accounted as reserves due its lower valu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lamosite
Lamosite is an olive-gray brown or dark gray to brownish black lacustrine-type oil shale, in which the chief organic constituent is lamalginite derived from lacustrine planktonic algae. In minor scale it also consists of vitrinite, inertinite, telalginite, and bitumen. Lamosite deposits are the most abundant and largest oil shale deposits beside of marinite deposits. The largest lacustrine-type oil shale deposits are the Green River Formation in western United States, a number deposits in eastern Queensland, Australia, and the New Brunswick Albert Formation and several other deposits in Canada. See also * Cannel coal * Kukersite * Marinite *Tasmanite *Torbanite *Oil shale geology Oil shale geology is a branch of geologic sciences which studies the formation and composition of oil shales–fine-grained sedimentary rocks containing significant amounts of kerogen, and belonging to the group of sapropel fuels. Oil shale f ... References Oil shale geology {{petrology- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marinite
Marinite is a gray to dark-gray or black oil shale of marine origin in which the chief organic components are lamalginite and bituminite derived from marine phytoplankton, with varied admixtures of bitumen, telalginite and vitrinite. Marinite deposits are the most abundant oil-shale deposits. They are generally widespread but at the same time they are relatively thin and often of restricted economic importance. Typical environments for marinite deposits are found in epeiric seas (e.g. on broad shallow marine shelves or below inland seas where wave action is restricted and currents are minimal). The largest marinite-type oil-shale deposits are the Devonian– Mississippian oil-shales deposits in eastern United States. In Canada, the marinite-type of oil-shale deposits include the Devonian Kettle Point Formation and the Ordovician Collingwood Shale of southern Ontario, the Cretaceous Boyne and Favel deposits in the Prairie Provinces of Manitoba, Saskatchewan, and Alberta, and the A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torbanite
Torbanite, also known as boghead coal or channel coal, is a variety of fine-grained black oil shale. It usually occurs as lenticular masses, often associated with deposits of Permian coals. Torbanite is classified as lacustrine type oil shale. Torbanite is named after Torbane Hill near Bathgate in Scotland, its main location of occurrence. Torbanite found in Bathgate may have formations of bathvillite found within it. Other major deposits of torbanite are found in Pennsylvania and Illinois, USA, in Mpumalanga Province in South Africa, in the Sydney Basin of New South Wales, Australia, the largest deposit of which is located at Glen Davis, and in Nova Scotia, Canada. Organic matter ( telalginite) in torbanite is derived from lipid-rich microscopic plant remains similar in appearance to the fresh-water colonial green alga '' Botryococcus braunii''. This evidence and extracellular hydrocarbons produced by the alga have led scientists to examine the alga as a source o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
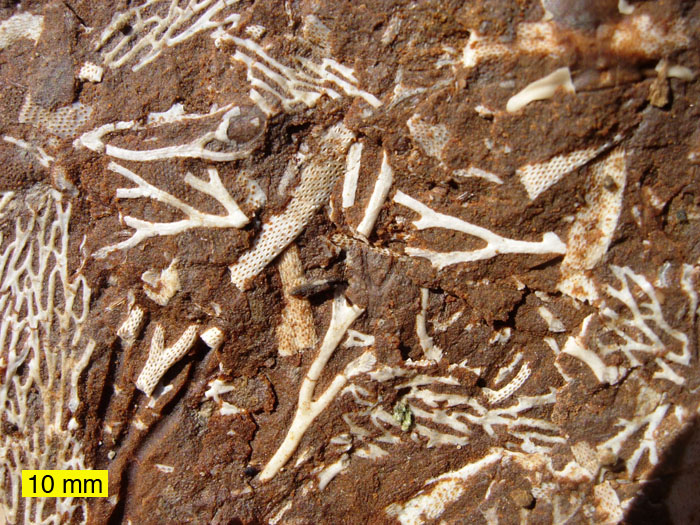
Sedimentary Rock
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock that are formed by the accumulation or deposition of mineral or organic particles at Earth's surface, followed by cementation. Sedimentation is the collective name for processes that cause these particles to settle in place. The particles that form a sedimentary rock are called sediment, and may be composed of geological detritus (minerals) or biological detritus (organic matter). The geological detritus originated from weathering and erosion of existing rocks, or from the solidification of molten lava blobs erupted by volcanoes. The geological detritus is transported to the place of deposition by water, wind, ice or mass movement, which are called agents of denudation. Biological detritus was formed by bodies and parts (mainly shells) of dead aquatic organisms, as well as their fecal mass, suspended in water and slowly piling up on the floor of water bodies (marine snow). Sedimentation may also occur as dissolved minerals precipitate from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prasinophyte
The prasinophytes are a group of unicellular green algae. Prasinophytes mainly include marine planktonic species, as well as some freshwater representatives.Sym, S. D. and Pienaar, R. N. 1993. The class Prasinophyceae. In Round, F. E. and Chapman, D. J. (eds) ''Progress in Phycological Research'', Vol. 9. Biopress Ltd., Bristol, pp. 281-376. The prasinophytes are morphologically diverse, including flagellates with one to eight flagella and non-motile (coccoid) unicells. The cells of many species are covered with organic body scales; others are naked. Well studied genera include ''Ostreococcus'', considered to be the smallest (ca. 0.95 μm) free-living eukaryote, and ''Micromonas'', both of which are found in marine waters worldwide. Prasinophytes have simple cellular structures, containing a single chloroplast and a single mitochondrion. The genomes are relatively small compared to other eukaryotes (about 12 Mbp for ''Ostreococcus'' and 21 Mbp for ''Micromonas''). At least one spe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
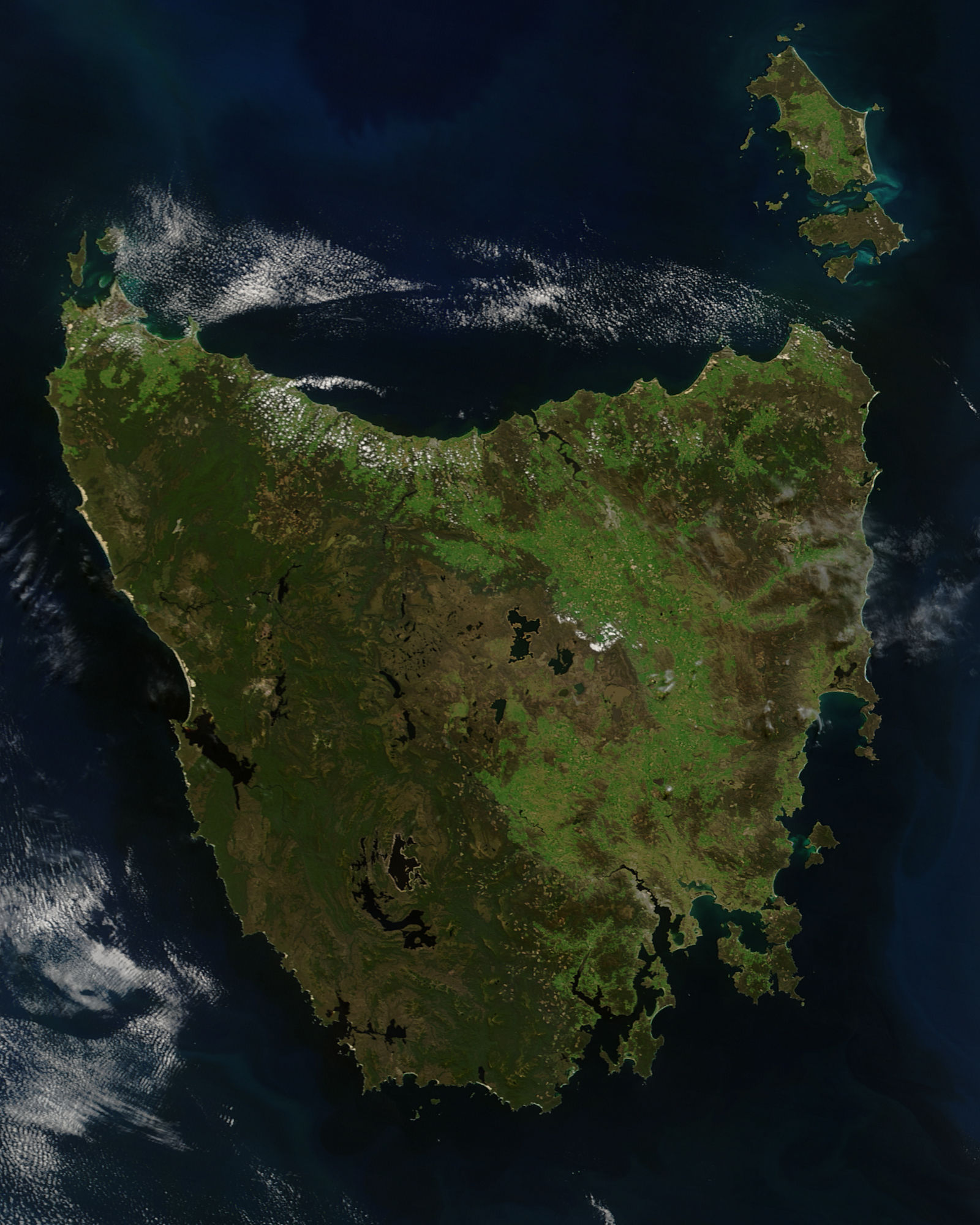
Tasmania
) , nickname = , image_map = Tasmania in Australia.svg , map_caption = Location of Tasmania in AustraliaCoordinates: , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = Australia , established_title = Before federation , established_date = Colony of Tasmania , established_title2 = Federation , established_date2 = 1 January 1901 , named_for = Abel Tasman , demonym = , capital = Hobart , largest_city = capital , coordinates = , admin_center = 29 local government areas , admin_center_type = Administration , leader_title1 = Monarch , leader_name1 = Charles III , leader_title2 = Governor , leader_name2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Source Rock
In petroleum geology, source rock is rock which has generated hydrocarbons or which could generate hydrocarbons. Source rocks are one of the necessary elements of a working petroleum system. They are organic-rich sediments that may have been deposited in a variety of environments including deep water marine, lacustrine and deltaic. Oil shale can be regarded as an organic-rich but immature source rock from which little or no oil has been generated and expelled. Subsurface source rock mapping methodologies make it possible to identify likely zones of petroleum occurrence in sedimentary basins as well as shale gas plays. Types of source rocks Source rocks are classified from the types of kerogen that they contain, which in turn governs the type of hydrocarbons that will be generated: * Type I source rocks are formed from algal remains deposited under anoxic conditions in deep lakes: they tend to generate waxy crude oils when submitted to thermal stress during deep burial. * Type ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amber
Amber is fossilized tree resin that has been appreciated for its color and natural beauty since Neolithic times. Much valued from antiquity to the present as a gemstone, amber is made into a variety of decorative objects."Amber" (2004). In Maxine N. Lurie and Marc Mappen (eds.) ''Encyclopedia of New Jersey'', Rutgers University Press, . Amber is used in jewelry and has been used as a healing agent in folk medicine. There are five classes of amber, defined on the basis of their chemical constituents. Because it originates as a soft, sticky tree resin, amber sometimes contains animal and plant material as inclusions. Amber occurring in coal seams is also called resinite, and the term ''ambrite'' is applied to that found specifically within New Zealand coal seams. Etymology The English word ''amber'' derives from Arabic (ultimately from Middle Persian ''ambar'') via Middle Latin ''ambar'' and Middle French ''ambre''. The word was adopted in Middle English in the 14th century ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |