|
Tangent Half-angle Substitution
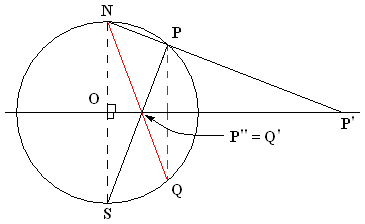
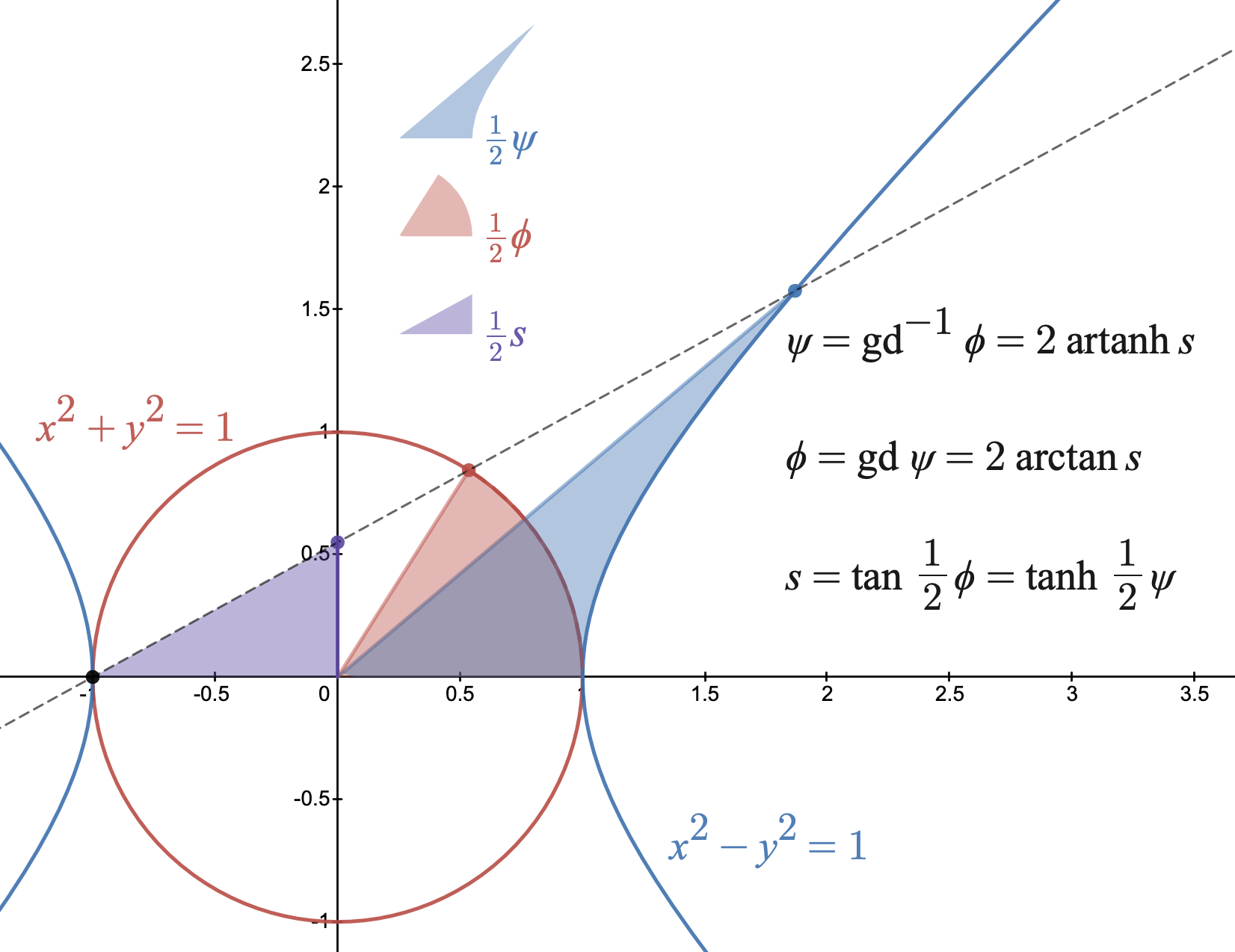
In integral calculus, the tangent half-angle substitution is a change of variables used for evaluating integrals, which converts a rational function of trigonometric functions of x into an ordinary rational function of t by setting t = \tan \tfrac x2. This is the one-dimensional stereographic projection of the unit circle parametrized by angle measure onto the real line. The general transformation formula is: \int f(\sin x, \cos x)\, dx =\int f \frac. The tangent of half an angle is important in spherical trigonometry and was sometimes known in the 17th century as the half tangent or semi-tangent. Leonhard Euler used it to evaluate the integral \int dx / (a + b\cos x) in his 1768 integral calculus textbook, and Adrien-Marie Legendre described the general method in 1817. The substitution is described in most integral calculus textbooks since the late 19th century, usually without any special name. It is known in Russia as the universal trigonometric substitution, and also known ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integral Calculus
In mathematics, an integral assigns numbers to Function (mathematics), functions in a way that describes Displacement (geometry), displacement, area, volume, and other concepts that arise by combining infinitesimal data. The process of finding integrals is called integration. Along with Derivative, differentiation, integration is a fundamental, essential operation of calculus,Integral calculus is a very well established mathematical discipline for which there are many sources. See and , for example. and serves as a tool to solve problems in mathematics and physics involving the area of an arbitrary shape, the length of a curve, and the volume of a solid, among others. The integrals enumerated here are those termed definite integrals, which can be interpreted as the signed area of the region in the plane that is bounded by the Graph of a function, graph of a given function between two points in the real line. Conventionally, areas above the horizontal axis of the plane are posi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael Spivak
Michael David Spivak (25 May 19401 October 2020)Biographical sketch in Notices of the AMS', Vol. 32, 1985, p. 576. was an American mathematician specializing in differential geometry, an expositor of mathematics, and the founder of Publish-or-Perish Press. Spivak was the author of the five-volume ''A Comprehensive Introduction to Differential Geometry''. Biography Spivak was born in Queens, New York (state), New York. He received an Bachelor of Arts, A.B. from Harvard University in 1960, while in 1964 he received a Doctor of Philosophy, Ph.D. from Princeton University under the supervision of John Milnor, with thesis ''On Spaces Satisfying Poincaré Duality''. In 1985 Spivak received the Leroy P. Steele Prize. Spivak lectured on elementary physics. Spivak's book, ''Physics for Mathematicians: Mechanics I'' (published December 6, 2010), contains the material that these lectures stemmed from and more. Spivak was also the designer of the MathTime Professional 2 fonts (which are wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trigonometric Substitution
In mathematics, trigonometric substitution is the replacement of trigonometric functions for other expressions. In calculus, trigonometric substitution is a technique for evaluating integrals. Moreover, one may use the trigonometric identities to simplify certain integrals containing radical expressions. Like other methods of integration by substitution, when evaluating a definite integral, it may be simpler to completely deduce the antiderivative before applying the boundaries of integration. Case I: Integrands containing ''a''2 − ''x''2 Let x = a \sin \theta, and use the identity 1-\sin^2 \theta = \cos^2 \theta. Examples of Case I Example 1 In the integral :\int\frac, we may use :x=a\sin \theta,\quad dx=a\cos\theta\, d\theta, \quad \theta=\arcsin\frac. Then, :\begin \int\frac &= \int\frac \\ pt &= \int\frac \\ pt &= \int\frac \\ pt &= \int d\theta \\ pt &= \theta + C \\ pt &= \arcsin\frac+C. \end The above step requires that a > 0 and \cos \theta > 0. We c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stereographic Projection
In mathematics, a stereographic projection is a perspective projection of the sphere, through a specific point on the sphere (the ''pole'' or ''center of projection''), onto a plane (geometry), plane (the ''projection plane'') perpendicular to the diameter through the point. It is a smooth function, smooth, bijection, bijective function (mathematics), function from the entire sphere except the center of projection to the entire plane. It maps circle of a sphere, circles on the sphere to generalised circle, circles or lines on the plane, and is conformal map, conformal, meaning that it preserves angles at which curves meet and thus Local property, locally approximately preserves similarity (geometry), shapes. It is neither isometry, isometric (distance preserving) nor Equiareal map, equiareal (area preserving). The stereographic projection gives a way to representation (mathematics), represent a sphere by a plane. The metric tensor, metric induced metric, induced by the inverse s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rational Curve
In mathematics, an affine algebraic plane curve is the zero set of a polynomial in two variables. A projective algebraic plane curve is the zero set in a projective plane of a homogeneous polynomial in three variables. An affine algebraic plane curve can be completed in a projective algebraic plane curve by homogenizing its defining polynomial. Conversely, a projective algebraic plane curve of homogeneous equation can be restricted to the affine algebraic plane curve of equation . These two operations are each inverse to the other; therefore, the phrase algebraic plane curve is often used without specifying explicitly whether it is the affine or the projective case that is considered. More generally, an algebraic curve is an algebraic variety of dimension one. Equivalently, an algebraic curve is an algebraic variety that is birationally equivalent to an algebraic plane curve. If the curve is contained in an affine space or a projective space, one can take a projection for such a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poincaré Disk Model
In geometry, the Poincaré disk model, also called the conformal disk model, is a model of 2-dimensional hyperbolic geometry in which all points are inside the unit disk, and straight lines are either circular arcs contained within the disk that are orthogonal to the unit circle or diameters of the unit circle. The group of orientation preserving isometries of the disk model is given by the projective special unitary group , the quotient of the special unitary group SU(1,1) by its center . Along with the Klein model and the Poincaré half-space model, it was proposed by Eugenio Beltrami who used these models to show that hyperbolic geometry was equiconsistent with Euclidean geometry. It is named after Henri Poincaré, because his rediscovery of this representation fourteen years later became better known than the original work of Beltrami. The Poincaré ball model is the similar model for ''3'' or ''n''-dimensional hyperbolic geometry in which the points of the geometry are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tangent Half-angle Formula
In trigonometry, tangent half-angle formulas relate the tangent of half of an angle to trigonometric functions of the entire angle. The tangent of half an angle is the stereographic projection of the circle onto a line. Among these formulas are the following: : \begin \tan \tfrac12( \eta \pm \theta) &= \frac = \frac = -\frac, \\ 0pt \tan \tfrac12 \theta &= \frac = \frac = \frac, & & (\eta = 0) \\ 0pt \tan \tfrac12 \theta &= \frac = \frac = \csc\theta-\cot\theta, & & (\eta = 0) \\ 0pt \tan \tfrac12 \big(\theta \pm \tfrac12\pi \big) &= \frac = \sec\theta \pm \tan\theta = \frac, & & \big(\eta = \tfrac12\pi \big) \\ 0pt \tan \tfrac12 \big(\theta \pm \tfrac12\pi \big) &= \frac = \frac = \frac, & & \big(\eta = \tfrac12\pi \big) \\ 0pt \frac &= \pm\sqrt \\ 0pt \tan \tfrac12 \theta &= \pm \sqrt \\ 0pt \end From these one can derive identities expressing the sine, cosine, and tangent as functions of tangents of half-angles: : \begin \sin \alpha & = \frac \\ pt\cos \alpha & = \frac \\ pt\ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weierstrass
Karl Theodor Wilhelm Weierstrass (german: link=no, Weierstraß ; 31 October 1815 – 19 February 1897) was a German mathematician often cited as the "father of modern mathematical analysis, analysis". Despite leaving university without a degree, he studied mathematics and trained as a school teacher, eventually teaching mathematics, physics, botany and gymnastics. He later received an honorary doctorate and became professor of mathematics in Berlin. Among many other contributions, Weierstrass formalized the definition of the Continuous function, continuity of a function, proved the intermediate value theorem and the Bolzano–Weierstrass theorem, and used the latter to study the properties of continuous functions on closed bounded intervals. Biography Weierstrass was born into a Roman Catholic family in Ostenfelde, a village near Ennigerloh, in the Province of Westphalia. Weierstrass was the son of Wilhelm Weierstrass, a government official, and Theodora Vonderforst both of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asymptote
In analytic geometry, an asymptote () of a curve is a line such that the distance between the curve and the line approaches zero as one or both of the ''x'' or ''y'' coordinates tends to infinity. In projective geometry and related contexts, an asymptote of a curve is a line which is tangent to the curve at a point at infinity. The word asymptote is derived from the Greek ἀσύμπτωτος (''asumptōtos'') which means "not falling together", from ἀ priv. + σύν "together" + πτωτ-ός "fallen". The term was introduced by Apollonius of Perga in his work on conic sections, but in contrast to its modern meaning, he used it to mean any line that does not intersect the given curve. There are three kinds of asymptotes: ''horizontal'', ''vertical'' and ''oblique''. For curves given by the graph of a function , horizontal asymptotes are horizontal lines that the graph of the function approaches as ''x'' tends to Vertical asymptotes are vertical lines near which the fun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematical Singularity
In mathematics, a singularity is a point at which a given mathematical object is not defined, or a point where the mathematical object ceases to be well-behaved in some particular way, such as by lacking differentiability or analyticity. For example, the real function : f(x) = \frac has a singularity at x = 0, where the numerical value of the function approaches \pm\infty so the function is not defined. The absolute value function g(x) = , x, also has a singularity at x = 0, since it is not differentiable there. The algebraic curve defined by \left\ in the (x, y) coordinate system has a singularity (called a cusp) at (0, 0). For singularities in algebraic geometry, see singular point of an algebraic variety. For singularities in differential geometry, see singularity theory. Real analysis In real analysis, singularities are either discontinuities, or discontinuities of the derivative (sometimes also discontinuities of higher order derivatives). There are four kinds of discon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limits Of Integration
In calculus and mathematical analysis the limits of integration (or bounds of integration) of the integral : \int_a^b f(x) \, dx of a Riemann integrable function f defined on a closed and bounded interval are the real numbers a and b , in which a is called the lower limit and b the upper limit. The region that is bounded can be seen as the area inside a and b . For example, the function f(x)=x^3 is defined on the interval , 4 \int_2^4 x^3 \, dx with the limits of integration being 2 and 4. Integration by Substitution (U-Substitution) In Integration by substitution, the limits of integration will change due to the new function being integrated. With the function that is being derived, a and b are solved for f(u). In general, \int_a^b f(g(x))g'(x) \ dx where u=g(x) and du=g'(x)\ dx . Thus, a and b will be solved in terms of u ; the lower bound is g(a) and the upper bound is g(b). For example, \int_0^2 2x\cos(x^2)dx = \int_0^4\cos(u)du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integral Of The Secant Function
In calculus, the integral of the secant function can be evaluated using a variety of methods and there are multiple ways of expressing the antiderivative, all of which can be shown to be equivalent via trigonometric identities, : \int \sec \theta \, d\theta = \begin \dfrac12 \ln \left, \dfrac\ + C \\ 5pt\ln\left, \sec\theta + \tan\theta\ + C \\ 5pt\ln\left, \tan\left(\dfrac + \dfrac\right) \ + C\\ 5pt\end This formula is useful for evaluating various trigonometric integrals. In particular, it can be used to evaluate the integral of the secant cubed, which, though seemingly special, comes up rather frequently in applications. Proof that the different antiderivatives are equivalent Trigonometric forms : \int \sec \theta \, d\theta = \left\\text The second of these follows by first multiplying top and bottom of the interior fraction by . This gives in the denominator, and the result follows by moving the factor of into the logarithm as a square root. Leaving out the const ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |