|
Taijin Kyofusho
''Taijin kyofusho'' ( ja, 対人恐怖症, TKS, for ''taijin kyofusho symptoms'') is a Japanese culture-specific syndrome. The term taijin kyofusho translates into the disorder (sho) of fear (kyofu) of interpersonal relations (taijin). Those who have taijin kyofusho are likely to be extremely embarrassed about themselves or fearful of displeasing others when it comes to the functions of their bodies or their appearances. These bodily functions and appearances include their faces, odor, actions, or even looks. They do not want to embarrass other people with their presence. This culture-bound syndrome is a social phobia based on fear and anxiety. The symptoms of this disorder include avoiding social outings and activities, rapid heartbeat, shortness of breath, panic attacks, trembling, and feelings of dread and panic when around people. The causes of this disorder are mainly from emotional trauma or psychological defense mechanism. It is more common in men than women.] Lifetime preva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Culture-specific Syndrome
In medicine and medical anthropology, a culture-bound syndrome, culture-specific syndrome, or folk illness is a combination of psychiatric and somatic symptoms that are considered to be a recognizable disease only within a specific society or culture. There are no objective biochemical or structural alterations of body organs or functions, and the disease is not recognized in other cultures. The term ''culture-bound syndrome'' was included in the fourth version of the '' Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders'' (American Psychiatric Association, 1994) which also includes a list of the most common culture-bound conditions (DSM-IV: Appendix I). Counterpart within the framework of ICD-10 (Chapter V) are the ''culture-specific disorders'' defined in Annex 2 of the ''Diagnostic criteria for research''. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bed Rest
Bed rest, also referred to as the rest-cure, is a medical treatment in which a person lies in bed for most of the time to try to cure an illness. Bed rest refers to voluntarily lying in bed as a treatment and not being confined to bed because of a health impairment which physically prevents leaving bed. The practice is still used although a 1999 systematic review found no benefits for any of the 17 conditions studied and no proven benefit for any conditions at all, beyond that imposed by symptoms. In the United States, nearly 20% of pregnant women have some degree of restricted activity prescribed despite the growing data showing it to be dangerous, causing some experts to call its use "unethical". Medical uses Extended bed rest has been proven to be a potentially harmful treatment needing more careful evaluation. Pregnancy Women who are pregnant and are experiencing early labor, vaginal bleeding, and cervix complications have been prescribed bed rest. This practice in 2013 wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Culture-bound Syndromes
In medicine and medical anthropology, a culture-bound syndrome, culture-specific syndrome, or folk illness is a combination of psychiatric and somatic symptoms that are considered to be a recognizable disease only within a specific society or culture. There are no objective biochemical or structural alterations of body organs or functions, and the disease is not recognized in other cultures. The term ''culture-bound syndrome'' was included in the fourth version of the ''Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders'' (American Psychiatric Association, 1994) which also includes a list of the most common culture-bound conditions (DSM-IV: Appendix I). Counterpart within the framework of ICD-10 (Chapter V) are the ''culture-specific disorders'' defined in Annex 2 of the ''Diagnostic criteria for research''. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anxiety Disorders
Anxiety disorders are a cluster of mental disorders characterized by significant and uncontrollable feelings of anxiety and fear such that a person's social, occupational, and personal function are significantly impaired. Anxiety may cause physical and cognitive symptoms, such as restlessness, irritability, easy fatiguability, difficulty concentrating, increased heart rate, chest pain, abdominal pain, and a variety of other symptoms that may vary based on the individual. In casual discourse, the words ''anxiety'' and ''fear'' are often used interchangeably. In clinical usage, they have distinct meanings: anxiety is defined as an unpleasant emotional state for which the cause is either not readily identified or perceived to be uncontrollable or unavoidable, whereas fear is an emotional and physiological response to a recognized external threat. The umbrella term ''anxiety disorder'' refers to a number of specific disorders that include fears (phobias) or anxiety symptoms. There a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obsessive–compulsive Disorder
Obsessive–compulsive disorder (OCD) is a mental and behavioral disorder in which an individual has intrusive thoughts and/or feels the need to perform certain routines repeatedly to the extent where it induces distress or impairs general function. As indicated by the disorder's name, the primary symptoms of OCD are obsessions and compulsions. Obsessions are persistent unwanted thoughts, mental images, or urges that generate feelings of anxiety, disgust, or discomfort. Common obsessions include fear of contamination, obsession with symmetry, and intrusive thoughts about religion, sex, and harm. Compulsions are repeated actions or routines that occur in response to obsessions. Common compulsions include excessive hand washing, cleaning, counting, ordering, hoarding, neutralizing, seeking assurance, and checking things. Washing is in response to the fear of contamination. Ordering is the preference for tasks to be completed a specific way (e.g., organizing clothes a specific w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NEET
NEET, an acronym for "Not in Education, Employment, or Training", refers to a person who is unemployed and not receiving an education or vocational training. The classification originated in the United Kingdom in the late 1990s, and its use has spread, in varying degrees, to other countries, including Japan, South Korea, China, Taiwan, Canada, and the United States. The NEET category includes the unemployed (individuals without a job and seeking one), as well as individuals outside the labour force (without a job and not seeking one). It is usually age-bounded to exclude people in old-age retirement. In the United Kingdom, the classification comprises people aged between 16 and 24 (some 16 and 17 year-olds are still of compulsory school age); the subgroup of NEETs aged 16–18 is frequently of particular focus. In Japan, the classification comprises people aged between 15 and 34 who are not employed, not engaged in housework, not enrolled in school or work-related training, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hikikomori
, also known as acute social withdrawal, is total withdrawal from society and seeking extreme degrees of social isolation and confinement. ''Hikikomori'' refers to both the phenomenon in general and the recluses themselves. ''Hikikomori'' have been described as loners or "modern-day hermits". Estimates suggest that half a million Japanese youths have become social recluses, as well as more than half a million middle-aged individuals. Definition The Japanese Ministry of Health, Labour, and Welfare defines ''hikikomori'' as a condition in which the affected individuals refuse to leave their parents' house, do not work or go to school and isolate themselves away from society and family in a single room for a period exceeding six months. The psychiatrist Tamaki Saitō defines ''hikikomori'' as "a state that has become a problem by the late twenties, that involves cooping oneself up in one's own home and not participating in society for six months or longer, but that does not see ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avoidant Personality Disorder
Avoidant personality disorder (AvPD) is a Cluster C personality disorder characterized by excessive social anxiety and inhibition, fear of intimacy (despite an intense desire for it), severe feelings of inadequacy and inferiority, and an overreliance on avoidance of feared stimuli (e.g. self-imposed social isolation) as a maladaptive coping method.''Anxious voidant personality disorder' in ICD-10Diagnostic Criteria anClinical descriptions and guidelines. Those affected typically display a pattern of extreme sensitivity to negative evaluation and rejection, a belief that one is socially inept or personally unappealing to others, and avoidance of social interaction despite a strong desire for it. It appears to affect an approximately equal number of men and women. People with AvPD often avoid social interaction for fear of being ridiculed, humiliated, rejected, or disliked. They typically avoid becoming involved with others unless they are certain they will not be rejected, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthropophobia
Social anxiety disorder (SAD), also known as social phobia, is an anxiety disorder characterized by sentiments of fear and anxiety in social situations, causing considerable distress and impaired ability to function in at least some aspects of daily life.National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence: GuidanceSocial Anxiety Disorder: Recognition, Assessment, and Treatment Leicester (UK): British Psychological Society; 2013. These fears can be triggered by perceived or actual scrutiny from others. Individuals with social anxiety disorder fear negative evaluations from other people. Physical symptoms often include excessive blushing, excess sweating, trembling, palpitations, and nausea. Stammering may be present, along with rapid speech. Panic attacks can also occur under intense fear and discomfort. Some affected individuals may use alcohol or other drugs to reduce fears and inhibitions at social events. It is common for those with social phobia to self-medicate in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shyness
Shyness (also called diffidence) is the feeling of apprehension, lack of comfort, or awkwardness especially when a person is around other people. This commonly occurs in new situations or with unfamiliar people; a shy person may simply opt to avoid these situations. Although shyness can be a characteristic of people who have low self-esteem, the primary defining characteristic of shyness is a fear of what other people will think of a person's behavior. This fear of negative reactions such as being laughed at, humiliated or patronized, criticized or rejected can cause a shy person to retreat. Stronger forms of shyness can be referred to as social anxiety or social phobia. Origins The initial cause of shyness varies. Scientists believe that they have located genetic data supporting the hypothesis that shyness is, at least, partially genetic. However, there is also evidence that suggests the environment in which a person is raised can also be responsible for their shyness. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Anxiety Disorder
Social anxiety disorder (SAD), also known as social phobia, is an anxiety disorder characterized by sentiments of fear and anxiety in social situations, causing considerable distress and impaired ability to function in at least some aspects of daily life.National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence: GuidanceSocial Anxiety Disorder: Recognition, Assessment, and Treatment Leicester (UK): British Psychological Society; 2013. These fears can be triggered by perceived or actual scrutiny from others. Individuals with social anxiety disorder fear negative evaluations from other people. Physical symptoms often include excessive blushing, excess sweating, trembling, palpitations, and nausea. Stammering may be present, along with rapid speech. Panic attacks can also occur under intense fear and discomfort. Some affected individuals may use alcohol or other drugs to reduce fears and inhibitions at social events. It is common for those with social phobia to self-medicate in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
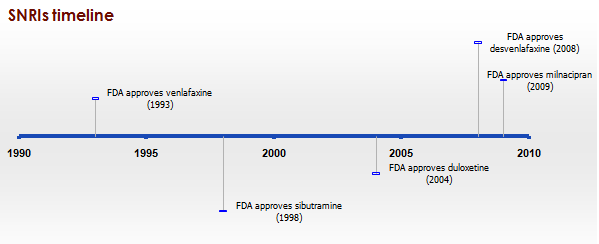
Serotonin–norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitor
Serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) are a class of antidepressant drugs used to treat major depressive disorder (MDD), anxiety disorders, obsessive–compulsive disorder (OCD), social phobia, attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), chronic neuropathic pain, fibromyalgia syndrome (FMS), and menopausal symptoms. SNRIs are monoamine reuptake inhibitors; specifically, they inhibit the reuptake of serotonin and norepinephrine. These neurotransmitters are thought to play an important role in mood regulation. SNRIs can be contrasted with the more widely used selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), which act upon serotonin only. The human serotonin transporter (SERT) and noradrenaline transporter (NAT) are membrane transport proteins that are responsible for the reuptake of serotonin and noradrenaline from the synaptic cleft back into the presynaptic nerve terminal. Dual inhibition of serotonin and noradrenaline reuptake can offer advantages over othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)