|
Two-part Tariff
A two-part tariff (TPT) is a form of price discrimination wherein the price of a product or service is composed of two parts – a lump-sum fee as well as a per-unit charge. In general, such a pricing technique only occurs in partially or fully monopolistic markets. It is designed to enable the firm to capture more consumer surplus than it otherwise would in a non-discriminating pricing environment. Two-part tariffs may also exist in competitive markets when consumers are uncertain about their ultimate demand. Health club consumers, for example, may be uncertain about their level of future commitment to an exercise regimen. Two-part tariffs are easy to implement when connection or entrance fees (first part) can be charged along with a price per unit consumed (second part). Depending on the homogeneity of demand, the lump-sum fee charged varies, but the rational firm will set the per unit charge above or equal to the marginal cost of production, and below or equal to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Price Discrimination
Price discrimination (differential pricing, equity pricing, preferential pricing, dual pricing, tiered pricing, and surveillance pricing) is a Microeconomics, microeconomic Pricing strategies, pricing strategy where identical or largely similar goods or services are sold at different Price, prices by the same provider to different buyers based on which Market segmentation, market segment they are perceived to be part of. Price discrimination is distinguished from product differentiation by the difference in production cost for the differently priced products involved in the latter strategy. Price discrimination essentially relies on the variation in customers' willingness to pay and in the Demand elasticity, elasticity of their demand. For price discrimination to succeed, a seller must have market power, such as a dominant market share, product uniqueness, sole pricing power, etc. Some prices under price discrimination may be lower than the price charged by a single-price monopoli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perfect Competition
In economics, specifically general equilibrium theory, a perfect market, also known as an atomistic market, is defined by several idealizing conditions, collectively called perfect competition, or atomistic competition. In Economic model, theoretical models where conditions of perfect competition hold, it has been demonstrated that a Market (economics), market will reach an Economic equilibrium, equilibrium in which the quantity supplied for every Goods and services, product or service, including Workforce, labor, equals the quantity demanded at the current price. This equilibrium would be a Pareto optimum. Perfect competition provides both allocative efficiency and productive efficiency: * Such markets are ''allocatively efficient'', as output will always occur where marginal cost is equal to average revenue i.e. price (MC = AR). In perfect competition, any Profit maximization, profit-maximizing producer faces a market price equal to its marginal cost (P = MC). This implies that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pricing
Pricing is the Business process, process whereby a business sets and displays the price at which it will sell its products and services and may be part of the business's marketing plan. In setting prices, the business will take into account the price at which it could acquire the goods, the manufacturing cost, the marketplace, competition, market condition, brand, and quality of the product. Pricing is a fundamental aspect of product management and is one of the four Ps of the marketing mix, the other three aspects being product, promotion, and Distribution (business), place. Price is the only revenue generating element among the four Ps, the rest being cost center (business), cost centers. However, the other Ps of marketing will contribute to decreasing price elasticity and so enable price increases to drive greater revenue and profits. Pricing can be a manual or automatic process of applying prices to purchase and sales orders, based on factors such as a fixed amount, quantit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microeconomics
Microeconomics is a branch of economics that studies the behavior of individuals and Theory of the firm, firms in making decisions regarding the allocation of scarcity, scarce resources and the interactions among these individuals and firms. Microeconomics focuses on the study of individual markets, sectors, or industries as opposed to the economy as a whole, which is studied in macroeconomics. One goal of microeconomics is to analyze the market mechanisms that establish relative prices among goods and services and allocate limited resources among alternative uses. Microeconomics shows conditions under which free markets lead to desirable allocations. It also analyzes market failure, where markets fail to produce Economic efficiency, efficient results. While microeconomics focuses on firms and individuals, macroeconomics focuses on the total of economic activity, dealing with the issues of Economic growth, growth, inflation, and unemployment—and with national policies relati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Personal Seat License
A personal seat license, or PSL, is a paid license that entitles the holder to the right to buy season tickets for a certain seat in a stadium. This holder can sell the seat license to someone else if they no longer wish to purchase season tickets. However, if the seat license holder chooses not to sell the seat licenses and does not renew the season tickets, the holder forfeits the license back to the team. Most seat licenses are valid for as long as the team plays in the current venue. As each PSL corresponds to a specific seat, the venue operator can charge different prices for each individual seat. From the fan's perspective, having a specific seat removed the necessity of searching for an open seat in a filled stadium. Newly built sporting venues often offer PSLs to help pay the debt incurred during the construction of the venue. Opponents of PSLs see this as another way to increase the price that fans must afford to attend the venue. Seat licenses have been given various ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indifference Curve
In economics, an indifference curve connects points on a graph representing different quantities of two goods, points between which a consumer is ''indifferent''. That is, any combinations of two products indicated by the curve will provide the consumer with equal levels of utility, and the consumer has no preference for one combination or bundle of goods over a different combination on the same curve. One can also refer to each point on the indifference curve as rendering the same level of utility (satisfaction) for the consumer. In other words, an indifference curve is the locus of various points showing different combinations of two goods providing equal utility to the consumer. Utility is then a device to represent preferences rather than something from which preferences come. The main use of indifference curves is in the representation of potentially observable demand patterns for individual consumers over commodity bundles. Indifference curve analysis is a purely technol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deadweight Loss
In economics, deadweight loss is the loss of societal economic welfare due to production/consumption of a good at a quantity where marginal benefit (to society) does not equal marginal cost (to society). In other words, there are either goods being produced despite the cost of doing so being larger than the benefit, or additional goods are not being produced despite the fact that the benefits of their production would be larger than the costs. The deadweight loss is the net benefit that is missed out on. While losses to one entity often lead to gains for another, deadweight loss represents the loss that is not regained by anyone else. This loss is therefore attributed to both producers and consumers. Deadweight loss can also be a measure of lost economic efficiency when the socially optimal quantity of a good or a service is not produced. Non-optimal production can be caused by monopoly pricing in the case of artificial scarcity, a positive or negative externality, a tax or s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
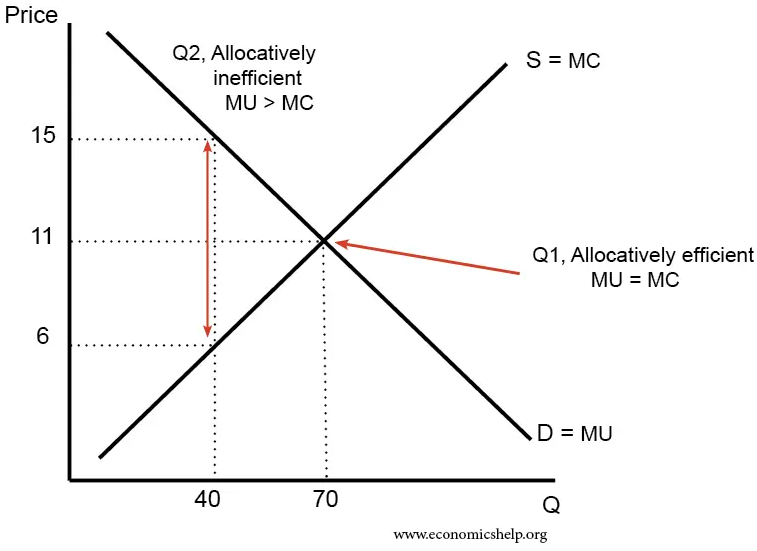
Allocative Efficiency
Allocative efficiency is a state of the economy in which production is aligned with the preferences of consumers and producers; in particular, the set of outputs is chosen so as to maximize the Economic surplus, social welfare of society. This is achieved if every produced good or service has a marginal benefit equal to or greater than the marginal cost of production. Description In economics, allocative efficiency entails production at the point on the production possibilities frontier that is optimal for society. In contract theory, allocative efficiency is achieved in a contract in which the skill demanded by the offering party and the skill of the agreeing party are the same. Resource allocation efficiency includes two aspects: # At the macro aspect, it is the allocation efficiency of social resources, which is achieved through the economic system arrangements of the entire society. # The micro aspect is the efficient use of resources, which can be understood as the produ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economic Profit
In economics, profit is the difference between revenue that an economic entity has received from its outputs and total costs of its inputs, also known as surplus value. It is equal to total revenue minus total cost, including both explicit and implicit costs. It is different from accounting profit, which only relates to the explicit costs that appear on a firm's financial statements. An accountant measures the firm's accounting profit as the firm's total revenue minus only the firm's explicit costs. An economist includes all costs, both explicit and implicit costs, when analyzing a firm. Therefore, economic profit is smaller than accounting profit. ''Normal profit'' is often viewed in conjunction with economic profit. Normal profits in business refer to a situation where a company generates revenue that is equal to the total costs incurred in its operation, thus allowing it to remain operational in a competitive industry. It is the minimum profit level that a company can ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Product (business)
In marketing, a product is an object, or system, or service made available for consumer use as of the consumer demand; it is anything that can be offered to a domestic or an international market to satisfy the desire or need of a customer. In retailing, products are often referred to as Merchandising, merchandise, and in manufacturing, products are bought as raw materials and then sold as finished goods. A Service (economics), service is also regarded as a type of product. In project management, products are the formal definition of the Product breakdown structure, project deliverables that make up or contribute to delivering the objectives of the project. A related concept is that of a sub-product, a secondary but useful result of a production (economics), production process. Dangerous products, particularly physical ones, that cause injuries to consumers or bystanders may be subject to product liability. Product classification A product can be classified as tangible asset, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |