|
Turbo-compound
A turbo-compound engine is a reciprocating engine that employs a turbine to recover energy from the exhaust gases. Instead of using that energy to drive a turbocharger as found in many high-power aircraft engines, the energy is instead sent to the output shaft to increase the total power delivered by the engine. The turbine is usually mechanically connected to the crankshaft, as on the Wright R-3350 Duplex-Cyclone, but electric and hydraulic power recovery systems have been investigated as well. As this recovery process does not increase fuel consumption, it has the effect of reducing the specific fuel consumption, the ratio of fuel use to power. Turbo-compounding was used for commercial airliners and similar long-range, long-endurance roles before the introduction of turbojet engines. Examples using the Duplex-Cyclone include the Douglas DC-7B and Lockheed L-1049 Super Constellation, while other designs did not see production use. Concept Most piston engines have a hot exhau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Napier Nomad
The Napier Nomad is a British diesel aircraft engine designed and built by Napier & Son in 1949. They combined a piston engine with a turbine to recover energy from the exhaust and thereby improve fuel economy. Two versions were tested, the complex Nomad I which used two propellers, each driven by the mechanically independent stages, and the Nomad II, using the turbo-compound principle, coupled the two parts to drive a single propeller. The Nomad II had the lowest specific fuel consumption figures seen up to that time. Despite this the Nomad project was cancelled in 1955 having spent £5.1 million on development, as most interest had passed to turboprop designs. Design and development In 1945 the Air Ministry asked for proposals for a new class engine with good fuel economy. Curtiss-Wright was designing an engine of this sort of power known as the turbo-compound engine, but Sir Harry Ricardo, one of Britain's great engine designers, suggested that the most economical comb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
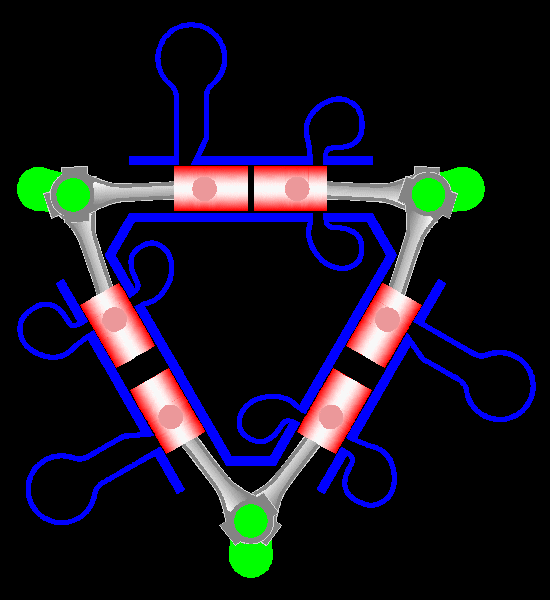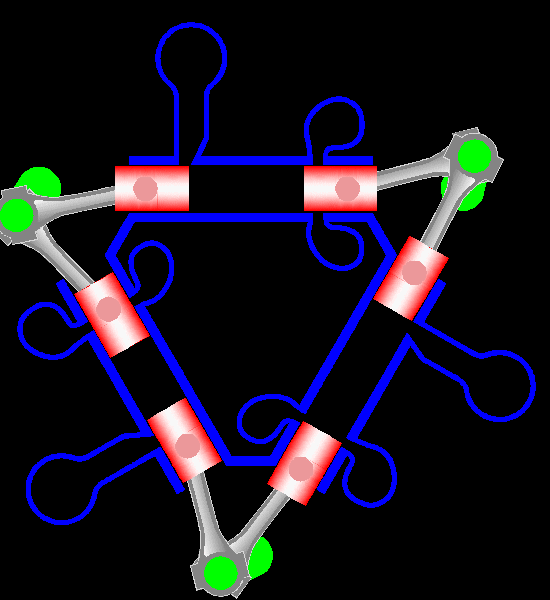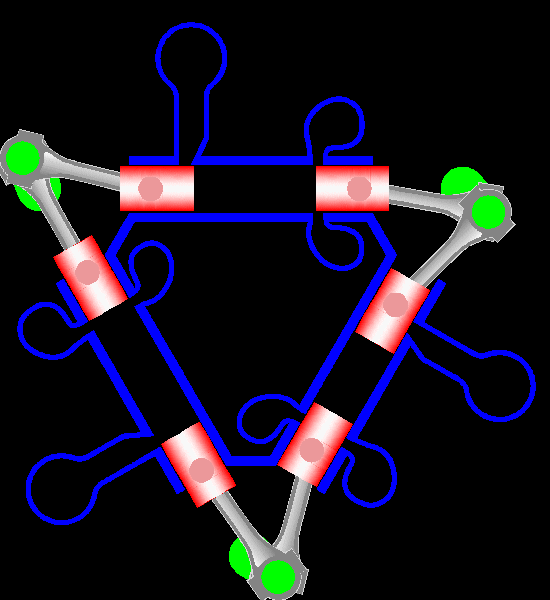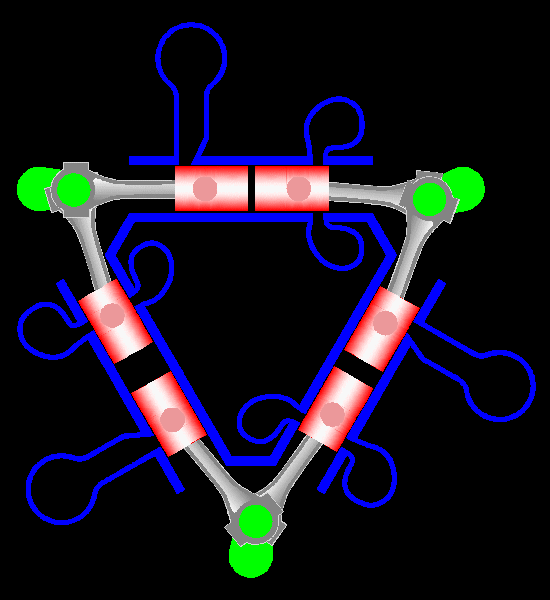
Napier Deltic
The Napier Deltic engine is a British opposed-piston valveless, supercharged uniflow scavenged, two-stroke diesel engine used in marine and locomotive applications, designed and produced by D. Napier & Son. Unusually, the cylinders were disposed in a three-bank triangle, with a crankshaft at each corner of the triangle. The term Deltic (meaning "in the form of the Greek letter (capital) delta") is used to refer to both the Deltic E.130 opposed-piston, high-speed diesel engine and the locomotives produced by English Electric using these engines, including its demonstrator locomotive named ''DELTIC'' and the production version for British Railways, which designated these as (TOPS) Class 55. A single, half-sized, turbocharged Deltic power unit also featured in the English Electric-built Type 2 locomotive, designated as the Class 23. Both locomotive and engine became better known as the "Baby Deltic". History and design The Deltic story began in 1943 when the British Admiral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
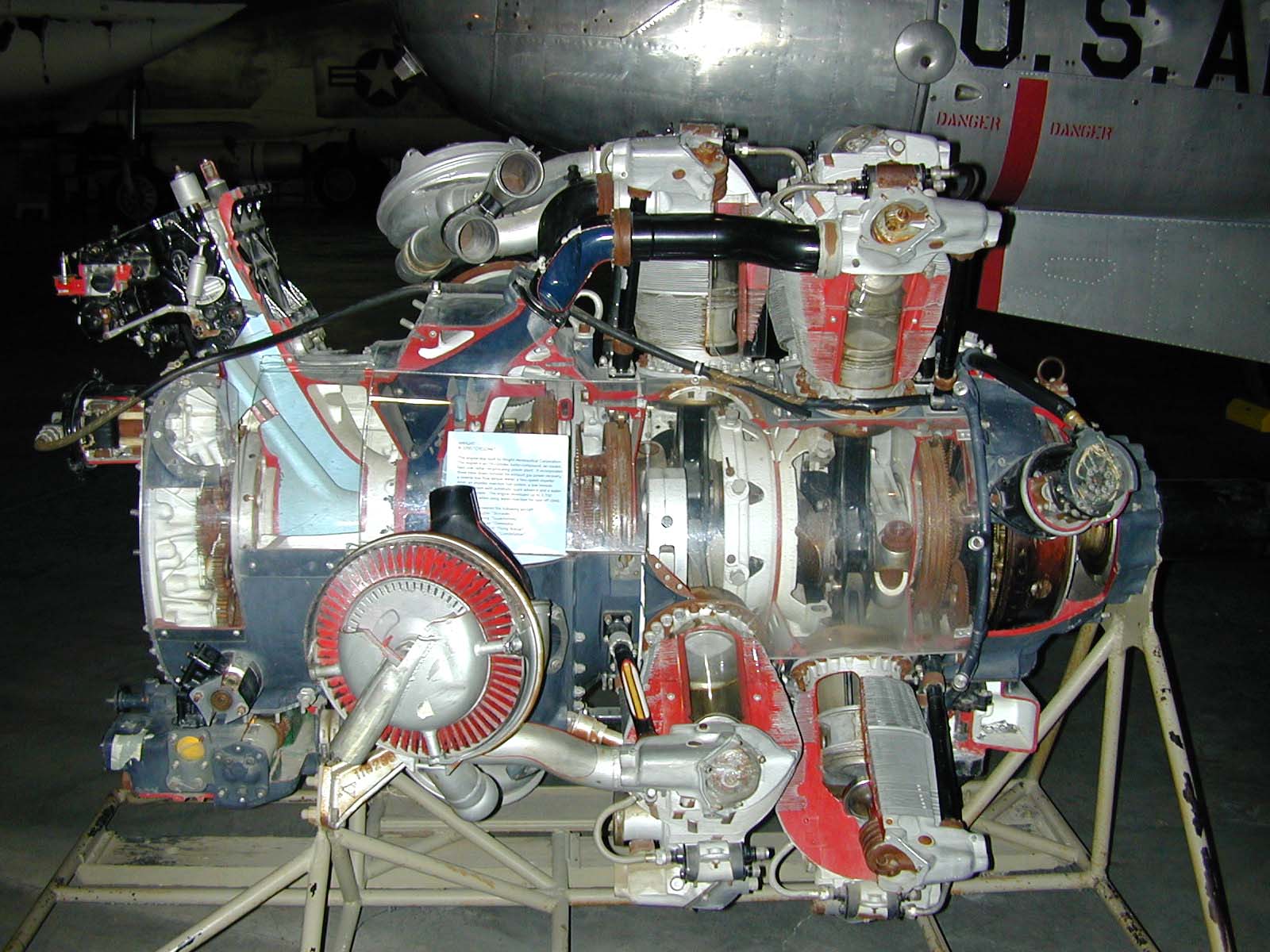
Wright R-3350 Duplex-Cyclone
The Wright R-3350 Duplex-Cyclone is an American twin-row, supercharged, air-cooled, radial aircraft engine with 18 cylinders displacing nearly . Power ranged from 2,200 to over 3,700 hp (1,640 to 2,760 kW), depending on the model. Developed before World War II, the R-3350's design required a long time to mature before finally being used to power the Boeing B-29 Superfortress. After the war, the engine had matured sufficiently to become a major civilian airliner design, notably in its turbo-compound forms, and was used in the Lockheed L-1049 Super Constellation airliners into the 1990s. The engine is commonly used on Hawker Sea Fury and Grumman F8F Bearcat Unlimited Class Racers at the Reno Air Races. Its main rival was the , Pratt & Whitney R-4360 Wasp Major, first run some seven years after the Duplex-Cyclone's beginnings. Design and development In 1927, Wright Aeronautical introduced its famous "Cyclone" engine, which powered a number of designs in the 1930s. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lockheed L-1049 Super Constellation
The Lockheed L-1049 Super Constellation is an American aircraft, a member of the Lockheed Constellation aircraft line. The L-1049 was Lockheed's response to the successful Douglas DC-6 airliner, first flying in 1950. The aircraft was also produced for both the United States Navy as the WV / R7V and U.S. Air Force as the C-121 for transport, electronics, and airborne early warning and control aircraft. Development Beginning in 1943, Lockheed planned stretched variants of the Constellation family. The first was the L-049 with a fuselage lengthened by 13 feet (4 meters) and the second the L-749 stretched 18 feet (5.5 meters). Douglas launched a stretched version of its DC-6 airliner as a cargo transport, designated DC-6A, for both military and civilian operators. Douglas was soon to launch a passenger version (the DC-6B) of this new aircraft. The DC-6B could carry 23 more passengers than Lockheed's current production L-749 Constellation. In 1950, Lockheed had repurchased the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Douglas DC-7B
The Douglas DC-7 is an American transport aircraft built by the Douglas Aircraft Company from 1953 to 1958. A derivative of the DC-6, it was the last major piston engine-powered transport made by Douglas, being developed shortly after the earliest jet airliner—the de Havilland Comet—entered service and only a few years before the jet-powered Douglas DC-8 first flew in 1958. Unlike other aircraft in Douglas's line of propeller-driven aircraft, no examples remain in service in the present day, as compared to the far more successful DC-3 and DC-6. Design and development In 1945 Pan American World Airways requested a DC-7, a civil version of the Douglas C-74 Globemaster military transport. Pan Am soon canceled their order. That proposed DC-7 was unrelated to the later DC-6-derived airliner. American Airlines revived the designation when they requested an aircraft that could fly the USA coast-to-coast non-stop in about eight hours. (Civil Air Regulations then limited domesti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formula One Engines
Since its inception in 1947, Formula One has used a variety of engine regulations. "Formulae" limiting engine capacity had been used in Grand Prix racing on a regular basis since after World War I. The engine formulae are divided according to era. Operation Formula One currently uses 1.6 litre four-stroke turbocharged 90 degree V6 double-overhead camshaft (DOHC) reciprocating engines. They were introduced in 2014 and have been developed over the subsequent seasons. The power a Formula One engine produces is generated by operating at a very high rotational speed, up to 20,000 revolutions per minute (rpm). However, they are electronically limited to 15,000 as of 2021 season. This contrasts with road car engines of a similar size, which typically operate at less than 6,000 rpm. The basic configuration of a naturally aspirated Formula One engine had not been greatly modified since the 1967 Ford Cosworth DFV and the mean effective pressure had stayed at around 14 b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allison V-1710
The Allison V-1710 aircraft engine designed and produced by the Allison Engine Company was the only US-developed V-12 liquid-cooled engine to see service during World War II. Versions with a turbocharger gave excellent performance at high altitude in the twin-engined Lockheed P-38 Lightning, and turbo-superchargers were fitted to experimental single-engined fighters with similar results. The United States Army Air Corps (USAAC) preference for turbochargers early in the V-1710's development program meant that less effort was spent on developing suitable mechanically driven centrifugal superchargers for the Allison V-12 design, as other V-12 designs from friendly nations like the British Rolls-Royce Merlin were already using. When smaller-dimensioned or lower-cost versions of the V-1710 were desired, they generally had poor performance at higher altitudes. The V-1710 nevertheless gave excellent service when turbocharged, notably in the P-38 Lightning, which accounted for m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rolls-Royce Griffon
The Rolls-Royce Griffon is a British 37-litre (2,240 cu in) capacity, 60-degree V-12, liquid-cooled aero engine designed and built by Rolls-Royce Limited. In keeping with company convention, the Griffon was named after a bird of prey, in this case the griffon vulture. Design work on the Griffon started in 1938 at the request of the Fleet Air Arm, for use in new aircraft designs such as the Fairey Firefly. In 1939 it was also decided that the engine could be adapted for use in the Spitfire. Development was stopped temporarily to concentrate efforts on the smaller Merlin and the 24-cylinder Vulture; the engine did not go into production until the early 1940s. The Griffon was the last in the line of V-12 aero engines to be produced by Rolls-Royce with production ceasing in 1955. Griffon engines remain in Royal Air Force service today with the Battle of Britain Memorial Flight and power the last remaining airworthy Avro Shackleton. Design and development Origins Accor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Napier & Son
D. Napier & Son Limited was a British engineering company best known for its luxury motor cars in the Edwardian era and for its aero engines throughout the early to mid-20th century. Napier was founded as a precision engineering company in 1808 and for nearly a century produced machinery for the financial, print, and munitions industries. In the early 20th century it moved for a time into internal combustion engines and road vehicles before turning to aero engines. Its powerful Lion dominated the UK market in the 1920s and the Second World War era Sabre produced 3500 hp (2,600 kW) in its later versions. Many world speed records on land and water, as well as the Hawker Typhoon and Tempest fighter planes, were powered by Napier engines. During the Second World War the company was taken over by English Electric, and engine manufacture eventually ceased. Today, Napier Turbochargers is a subsidiary of the American company Wabtec. History Early years and precision engin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Specific Fuel Consumption (shaft Engine)
Brake-specific fuel consumption (BSFC) is a measure of the fuel efficiency of any prime mover that burns fuel and produces rotational, or shaft power. It is typically used for comparing the efficiency of internal combustion engines with a shaft output. It is the rate of fuel consumption divided by the power produced. In traditional units, it measures fuel consumption in pounds per hour divided by the brake horsepower, lb/(hp⋅h); in SI units, this corresponds to the inverse of the units of specific energy, kg/J = s2/m2. It may also be thought of as power-specific fuel consumption, for this reason. BSFC allows the fuel efficiency of different engines to be directly compared. The term "brake" here as in "brake horsepower" refers to a historical method of measuring torque (see Prony brake). The BSFC calculation (in metric units) To calculate BSFC, use the formula : BSFC = \frac where: :'' r '' is the fuel consumption rate in grams per second (g/s) :'' P '' is the power produced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turbojet
The turbojet is an airbreathing jet engine which is typically used in aircraft. It consists of a gas turbine with a propelling nozzle. The gas turbine has an air inlet which includes inlet guide vanes, a compressor, a combustion chamber, and a turbine (that drives the compressor). The compressed air from the compressor is heated by burning fuel in the combustion chamber and then allowed to expand through the turbine. The turbine exhaust is then expanded in the propelling nozzle where it is accelerated to high speed to provide thrust. Two engineers, Frank Whittle in the United Kingdom and Hans von Ohain in Germany, developed the concept independently into practical engines during the late 1930s. Turbojets have poor efficiency at low vehicle speeds, which limits their usefulness in vehicles other than aircraft. Turbojet engines have been used in isolated cases to power vehicles other than aircraft, typically for attempts on land speed records. Where vehicles are "turbine-powere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daimler Trucks North America
Daimler Truck North America LLC (formerly Freightliner Corporation) is an automotive industry manufacturer of commercial vehicles headquartered in Portland, Oregon, and LLC of the German multinational Daimler Truck AG. On October 1, 2021, Daimler AG stockholders approved a spinoff of the truck division. Brands * Alliance Parts * Detroit Diesel *Freightliner Trucks *Freightliner Custom Chassis Corporation *Freightliner SelecTrucks *Thomas Built Buses *Western Star Trucks *Demand Detroit *Sterling Trucks Fuso Trucks America, while mostly owned by Daimler Truck, currently operates separately from Daimler Trucks North America. History Early years *1896- Gottlieb Daimler creates the first truck. *1923- First diesel truck: Benz *1926- Daimler and Benz merge. *1942- Leland James founds the Freightliner Corporation. *1947- Freightliner opens its first truck plant in Portland, Oregon. *1950- Hyster Company is the first private carrier to order a Freightliner truck. *1951- Freight ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |