|
Tube Sound
Tube sound (or valve sound) is the characteristic sound associated with a vacuum tube amplifier (valve amplifier in British English), a vacuum tube-based audio amplifier. At first, the concept of ''tube sound'' did not exist, because practically all electronic amplification of audio signals was done with vacuum tubes and other comparable methods were not known or used. After introduction of solid state amplifiers, tube sound appeared as the logical complement of transistor sound, which had some negative connotations due to crossover distortion in early transistor amplifiers. However, solid state amplifiers have been developed to be flawless and the sound is later regarded neutral compared to tube amplifiers. Thus the tube sound now means 'euphonic distortion.' The audible significance of tube amplification on audio signals is a subject of continuing debate among audio enthusiasts. (also found in ) Many electric guitar, electric bass, and keyboard players in several genres also pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tubes
Tube or tubes may refer to: * ''Tube'' (2003 film), a 2003 Korean film * ''The Tube'' (TV series), a music related TV series by Channel 4 in the United Kingdom * "Tubes" (Peter Dale), performer on the Soccer AM television show * Tube (band), a Japanese rock band * Tube & Berger, the alias of dance/electronica producers Arndt Rörig and Marco Vidovic from Germany * The Tube Music Network, a music video network that operated between 2006 and 2007 * The Tubes, a San Francisco-based band, popular in the 1970s and 1980s Other media * Tube, a freeware game for MS-DOS computers from Bullfrog Productions * ''TUBE.'', an online magazine about visual and performing arts, founded in 2012 in Sacramento, California * Series of tubes, an analogy for the Internet used by United States Senator Ted Stevens * Picture tube, term in Paint Shop Pro software for a small digital image with no background * YouTube, a video sharing website Science, technology, and mathematics Construction and mechani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distortion (guitar)
Distortion and overdrive are forms of audio signal processing used to alter the sound of amplified electric musical instruments, usually by increasing their gain, producing a "fuzzy", "growling", or "gritty" tone. Distortion is most commonly used with the electric guitar, but may also be used with other electric instruments such as electric bass, electric piano, synthesizer and Hammond organ. Guitarists playing electric blues originally obtained an overdriven sound by turning up their vacuum tube-powered guitar amplifiers to high volumes, which caused the signal to distort. While overdriven tube amps are still used to obtain overdrive, especially in genres like blues and rockabilly, a number of other ways to produce distortion have been developed since the 1960s, such as distortion effect pedals. The growling tone of a distorted electric guitar is a key part of many genres, including blues and many rock music genres, notably hard rock, punk rock, hardcore punk, acid rock, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Power Amplifier Classes
In electronics, power amplifier classes are letter symbols applied to different power amplifier types. The class gives a broad indication of an amplifier's characteristics and performance. The classes are related to the time period that the active amplifier device is passing current, expressed as a fraction of the period of a signal waveform applied to the input. A class A amplifier is conducting through all the period of the signal; Class B only for one-half the input period, class C for much less than half the input period. A Class D amplifier operates its output device in a switching manner; the fraction of the time that the device is conducting is adjusted so a pulse-width modulation output is obtained from the stage. Additional letter classes are defined for special-purpose amplifiers, with additional active elements or particular power supply improvements; sometimes a new letter symbol is used by a manufacturer to promote its proprietary design. Power amplifier classes Pow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transfer Characteristic
In engineering, a transfer function (also known as system function or network function) of a system, sub-system, or component is a mathematical function that theoretically models the system's output for each possible input. They are widely used in electronics and control systems. In some simple cases, this function is a two-dimensional graph of an independent scalar input versus the dependent scalar output, called a transfer curve or characteristic curve. Transfer functions for components are used to design and analyze systems assembled from components, particularly using the block diagram technique, in electronics and control theory. The dimensions and units of the transfer function model the output response of the device for a range of possible inputs. For example, the transfer function of a two-port electronic circuit like an amplifier might be a two-dimensional graph of the scalar voltage at the output as a function of the scalar voltage applied to the input; the transfer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Even And Odd Functions
In mathematics, even functions and odd functions are functions which satisfy particular symmetry relations, with respect to taking additive inverses. They are important in many areas of mathematical analysis, especially the theory of power series and Fourier series. They are named for the parity of the powers of the power functions which satisfy each condition: the function f(x) = x^n is an even function if ''n'' is an even integer, and it is an odd function if ''n'' is an odd integer. Definition and examples Evenness and oddness are generally considered for real functions, that is real-valued functions of a real variable. However, the concepts may be more generally defined for functions whose domain and codomain both have a notion of additive inverse. This includes abelian groups, all rings, all fields, and all vector spaces. Thus, for example, a real function could be odd or even (or neither), as could a complex-valued function of a vector variable, and so on. The gi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Number
In mathematics, the natural numbers are those numbers used for counting (as in "there are ''six'' coins on the table") and ordering (as in "this is the ''third'' largest city in the country"). Numbers used for counting are called '' cardinal numbers'', and numbers used for ordering are called '' ordinal numbers''. Natural numbers are sometimes used as labels, known as ''nominal numbers'', having none of the properties of numbers in a mathematical sense (e.g. sports jersey numbers). Some definitions, including the standard ISO 80000-2, begin the natural numbers with , corresponding to the non-negative integers , whereas others start with , corresponding to the positive integers Texts that exclude zero from the natural numbers sometimes refer to the natural numbers together with zero as the whole numbers, while in other writings, that term is used instead for the integers (including negative integers). The natural numbers form a set. Many other number sets are built by succ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Impedance
In electrical engineering, impedance is the opposition to alternating current presented by the combined effect of resistance and reactance in a circuit. Quantitatively, the impedance of a two-terminal circuit element is the ratio of the complex representation of the sinusoidal voltage between its terminals, to the complex representation of the current flowing through it. In general, it depends upon the frequency of the sinusoidal voltage. Impedance extends the concept of resistance to alternating current (AC) circuits, and possesses both magnitude and phase, unlike resistance, which has only magnitude. Impedance can be represented as a complex number, with the same units as resistance, for which the SI unit is the ohm (). Its symbol is usually , and it may be represented by writing its magnitude and phase in the polar form . However, Cartesian complex number representation is often more powerful for circuit analysis purposes. The notion of impedance is useful for pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IGBT
An insulated-gate bipolar transistor (IGBT) is a three-terminal power semiconductor device primarily used as an electronic switch, which, as it was developed, came to combine high efficiency and fast switching. It consists of four alternating layers (P–N–P–N) that are controlled by a metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) gate structure. Although the structure of the IGBT is topologically the same as a thyristor with a "MOS" gate ( MOS-gate thyristor), the thyristor action is completely suppressed, and only the transistor action is permitted in the entire device operation range. It is used in switching power supplies in high-power applications: variable-frequency drives (VFDs), electric cars, trains, variable-speed refrigerators, lamp ballasts, arc-welding machines, induction hobs, and air conditioners. Since it is designed to turn on and off rapidly, the IGBT can synthesize complex waveforms with pulse-width modulation and low-pass filters, so it is also used in switching amp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bipolar Transistor
A bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is a type of transistor that uses both electrons and electron holes as charge carriers. In contrast, a unipolar transistor, such as a field-effect transistor, uses only one kind of charge carrier. A bipolar transistor allows a small current injected at one of its terminals to control a much larger current flowing between the terminals, making the device capable of amplification or switching. BJTs use two p–n junctions between two semiconductor types, n-type and p-type, which are regions in a single crystal of material. The junctions can be made in several different ways, such as changing the doping of the semiconductor material as it is grown, by depositing metal pellets to form alloy junctions, or by such methods as diffusion of n-type and p-type doping substances into the crystal. The superior predictability and performance of junction transistors quickly displaced the original point-contact transistor. Diffused transistors, alon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
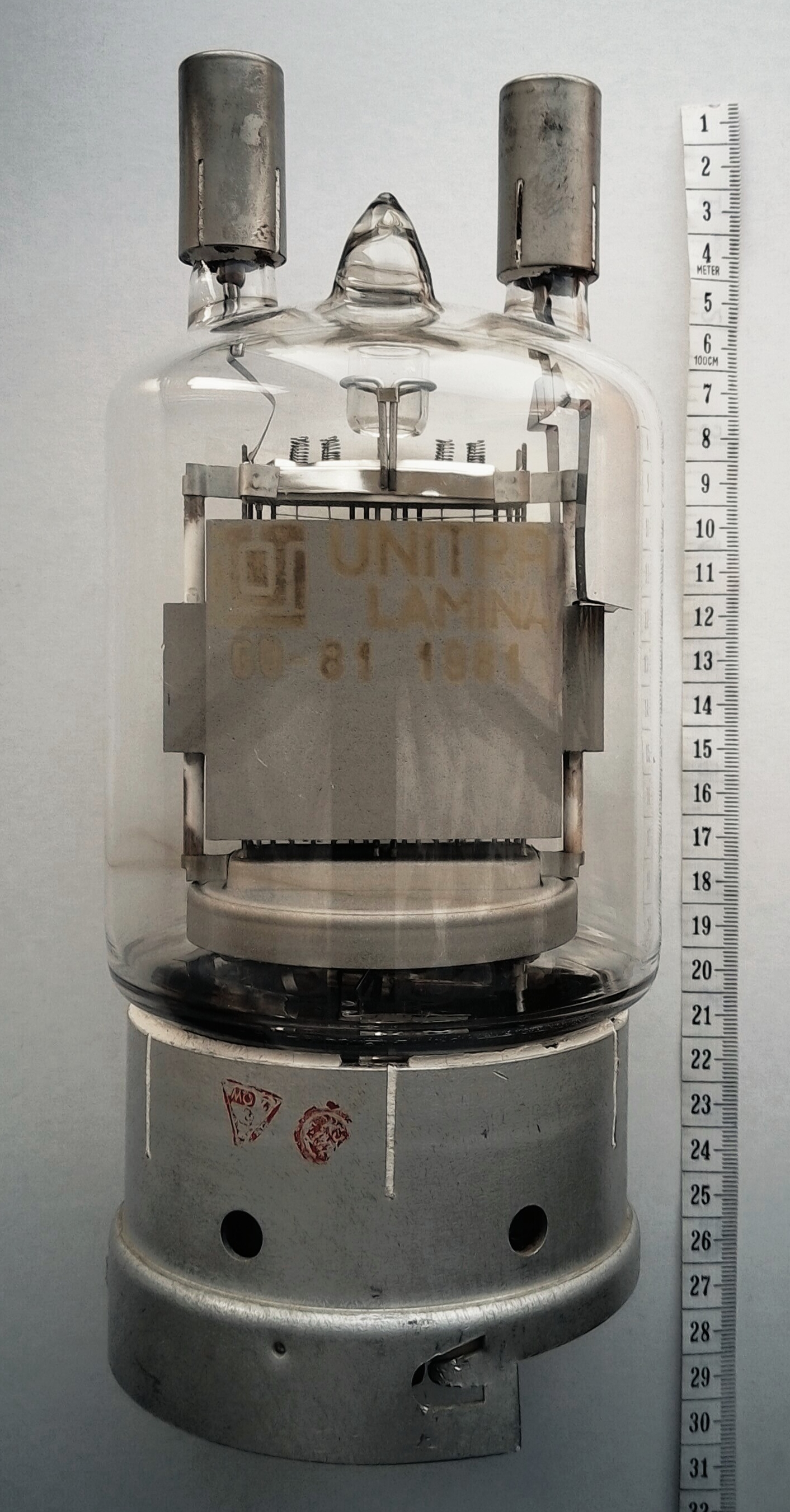
Pentode
A pentode is an electronic device having five electrodes. The term most commonly applies to a three-grid amplifying vacuum tube or thermionic valve that was invented by Gilles Holst and Bernhard D.H. Tellegen in 1926. The pentode (called a ''triple-grid amplifier'' in some literature) was developed from the ''screen-grid tube'' or ''shield-grid tube'' (a type of tetrode tube) by the addition of a grid between the screen grid and the plate. The screen-grid tube was limited in performance as an amplifier due to secondary emission of electrons from the plate. The additional grid is called the ''suppressor grid''. The suppressor grid is usually operated at or near the potential of the cathode and prevents secondary emission electrons from the plate from reaching the screen grid. The addition of the suppressor grid permits much greater output signal amplitude to be obtained from the plate of the pentode in amplifier operation than from the plate of the screen-grid tube at the same plate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrode
A tetrode is a vacuum tube (called ''valve'' in British English) having four active electrodes. The four electrodes in order from the centre are: a thermionic cathode, first and second grids and a plate (called ''anode'' in British English). There are several varieties of tetrodes, the most common being the screen-grid tube and the beam tetrode. In screen-grid tubes and beam tetrodes, the first grid is the control grid and the second grid is the screen grid. In other tetrodes one of the grids is a control grid, while the other may have a variety of functions. The tetrode was developed in the 1920s by adding an additional grid to the first amplifying vacuum tube, the triode, to correct limitations of the triode. During the period 1913 to 1927, three distinct types of tetrode valves appeared. All had a normal control grid whose function was to act as a primary control for current passing through the tube, but they differed according to the intended function of the other gri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
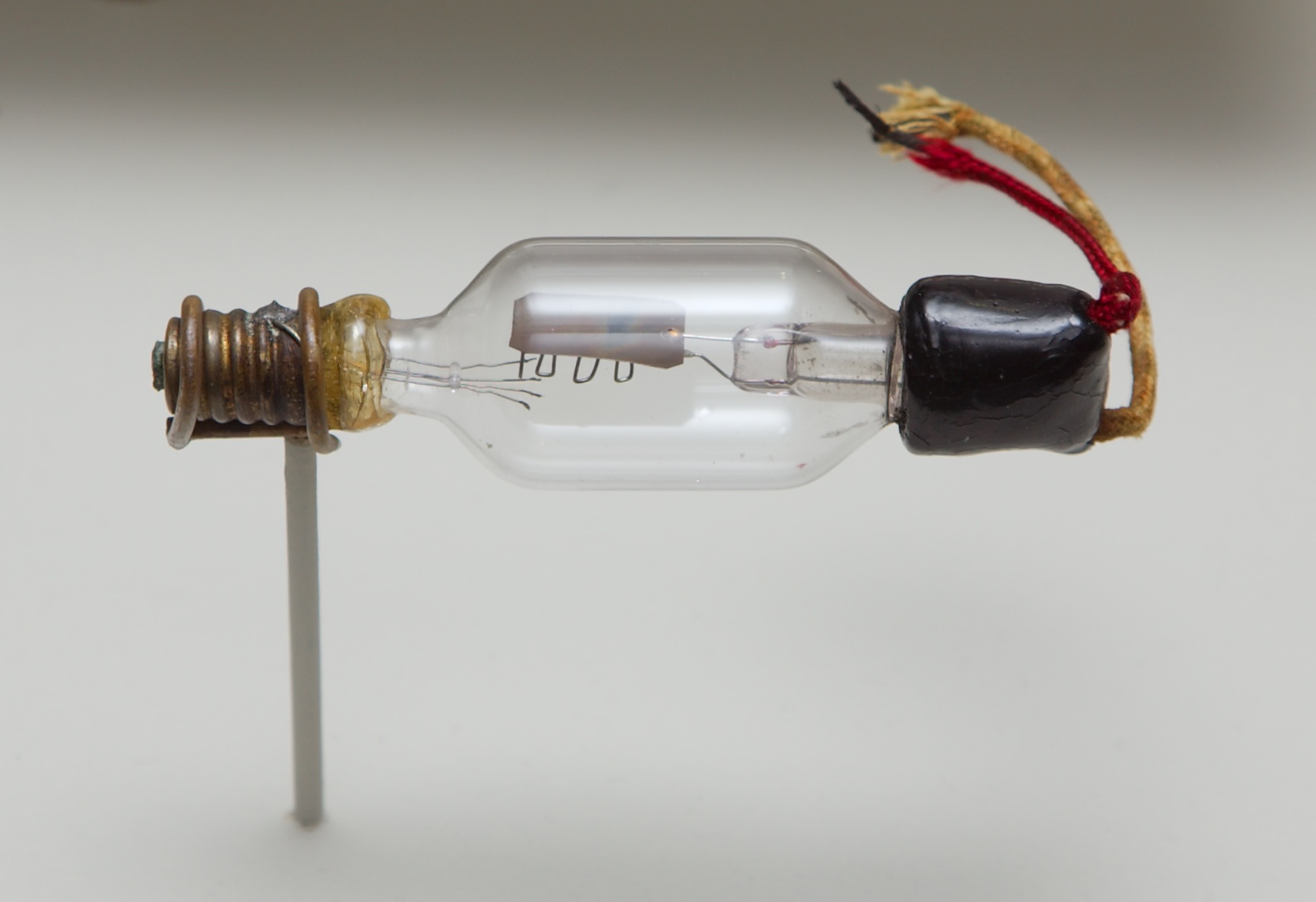
Triode
A triode is an electronic amplifying vacuum tube (or ''valve'' in British English) consisting of three electrodes inside an evacuated glass envelope: a heated filament or cathode, a grid, and a plate (anode). Developed from Lee De Forest's 1906 Audion, a partial vacuum tube that added a grid electrode to the thermionic diode ( Fleming valve), the triode was the first practical electronic amplifier and the ancestor of other types of vacuum tubes such as the tetrode and pentode. Its invention founded the electronics age, making possible amplified radio technology and long-distance telephony. Triodes were widely used in consumer electronics devices such as radios and televisions until the 1970s, when transistors replaced them. Today, their main remaining use is in high-power RF amplifiers in radio transmitters and industrial RF heating devices. In recent years there has been a resurgence in demand for low power triodes due to renewed interest in tube-type audio systems by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |