|
Troponin C
Troponin C is a protein which is part of the troponin complex. It contains four calcium-binding EF hands, although different isoforms may have fewer than four functional calcium-binding subdomains. It is a component of thin filaments, along with actin and tropomyosin. It contains an N lobe and a C lobe. The C lobe serves a structural purpose and binds to the N domain of troponin I (TnI). The C lobe can bind either Ca2+ or Mg2+. The N lobe, which binds only Ca2+, is the regulatory lobe and binds to the C domain of troponin I after calcium binding. Isoforms The tissue specific subtypes are: * Slow troponin C, TNNC1 (3p21.1 ) * Fast troponin C, TNNC2 (20q12-q13.11, ) Mutations Point mutations can occur in troponin C inducing alterations to Ca2+ and Mg2+ binding and protein structure, leading to abnormalities in muscle contraction. In cardiac muscle, they are related to dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM). These known point mutations ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiac Sarcomere Structure
The heart is a muscular organ found in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon dioxide to the lungs. In humans, the heart is approximately the size of a closed fist and is located between the lungs, in the middle compartment of the chest, called the mediastinum. In humans, other mammals, and birds, the heart is divided into four chambers: upper left and right atria and lower left and right ventricles. Commonly, the right atrium and ventricle are referred together as the right heart and their left counterparts as the left heart. Fish, in contrast, have two chambers, an atrium and a ventricle, while most reptiles have three chambers. In a healthy heart, blood flows one way through the heart due to heart valves, which prevent backflow. The heart is enclosed in a protective sac, the pericardium, which also contains a sma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TNNC2
Troponin C, skeletal muscle is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TNNC2'' gene. Troponin (Tn), is a key protein complex in the regulation of striated muscle contraction, composed of three subunits. The TnI subunit inhibits actomyosin ATPase, the TnT subunit binds tropomyosin and TnC, while the TnC subunit binds calcium Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar t ... and overcomes the inhibitory action of the troponin complex on actin thin filaments. The protein encoded by the ''TNNC2'' gene is the TnC subunit. References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * {{gene-20-stub EF-hand-containing proteins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcium-binding Protein
Calcium-binding proteins are proteins that participate in calcium cell signalling pathways by binding to Ca2+, the calcium ion that plays an important role in many cellular processes. Calcium-binding proteins have specific domains that bind to calcium and are known to be heterogeneous. One of the functions of calcium binding proteins is to regulate the amount of free (unbound) Ca2+ in the cytosol of the cell. The cellular regulation of calcium is known as calcium homeostasis. Types Many different calcium-binding proteins exist, with different cellular and tissue distribution and involvement in specific functions. Calcium binding proteins also serve an important physiological role for cells. The most ubiquitous Ca2+-sensing protein, found in all eukaryotic organisms including yeasts, is calmodulin. Intracellular storage and release of Ca2+ from the sarcoplasmic reticulum is associated with the high-capacity, low-affinity calcium-binding protein calsequestrin. Calretinin is anoth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Troponin I
Troponin I is a cardiac and skeletal muscle protein family. It is a part of the troponin protein complex, where it binds to actin in thin myofilaments to hold the actin-tropomyosin complex in place. Troponin I prevents myosin from binding to actin in relaxed muscle. When calcium binds to the troponin C, it causes conformational changes which lead to dislocation of troponin I. Afterwards, tropomyosin leaves the binding site for myosin on actin leading to contraction of muscle. The letter ''I'' is given due to its inhibitory character. It is a useful marker in the laboratory diagnosis of heart attack. It occurs in different plasma concentration but the same circumstances as troponin T - either test can be performed for confirmation of cardiac muscle damage and laboratories usually offer one test or the other. Three paralogs with unique tissue-specific expression patterns are expressed in humans, listed below with their locations and OMIM accessions: * Slow-twitch skeletal muscle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Troponin T
Troponin T (shortened TnT or TropT) is a part of the troponin complex, which are proteins integral to the contraction of skeletal and heart muscles. They are expressed in skeletal and cardiac myocytes. Troponin T binds to tropomyosin and helps position it on actin, and together with the rest of the troponin complex, modulates contraction of striated muscle. The cardiac subtype of troponin T is especially useful in the laboratory diagnosis of heart attack because it is released into the blood-stream when damage to heart muscle occurs. It was discovered by the German physician Hugo A. Katus at the University of Heidelberg, who also developed the troponin T assay. Subtypes * Slow skeletal troponin T1, TNNT1 (19q13.4, ) * Cardiac troponin T2, TNNT2 (1q32, ) * Fast skeletal troponin T3, TNNT3 (11p15.5, ) Reference values The 99th percentile cutoff for cardiac troponin T (cTnT) is 0.01 ng/mL. The reference range for the high sensitivity troponin T is a normal 52 ng/L. Backgroun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
D145E
D145E is a point mutation on troponin C that leads to hypertrophic cardiomyopathy disease. This mutation is caused by the change of nucleotide C to A at nucleotide 435, switching the amino acid aspartic acid to glutamic acid, which is located at the C-terminal tail. Patients with this mutation have different structure on the thin filament and alter the binding of Ca2+ at the troponin C site IV. Further, D145E causes increase in development of force and activation of ATPase ATPases (, Adenosine 5'-TriPhosphatase, adenylpyrophosphatase, ATP monophosphatase, triphosphatase, SV40 T-antigen, ATP hydrolase, complex V (mitochondrial electron transport), (Ca2+ + Mg2+)-ATPase, HCO3−-ATPase, adenosine triphosphatase) are ... in the presence of Ca2+. References Mutation Troponin {{Gene-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM, or HOCM when obstructive) is a condition in which the heart becomes thickened without an obvious cause. The parts of the heart most commonly affected are the interventricular septum and the ventricles. This results in the heart being less able to pump blood effectively and also may cause electrical conduction problems. People who have HCM may have a range of symptoms. People may be asymptomatic, or may have fatigue, leg swelling, and shortness of breath. It may also result in chest pain or fainting. Symptoms may be worse when the person is dehydrated. Complications may include heart failure, an irregular heartbeat, and sudden cardiac death. HCM is most commonly inherited from a person's parents in an autosomal dominant pattern. It is often due to mutations in certain genes involved with making heart muscle proteins. Other inherited causes of left ventricular hypertrophy may include Fabry disease, Friedreich's ataxia, and certain m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
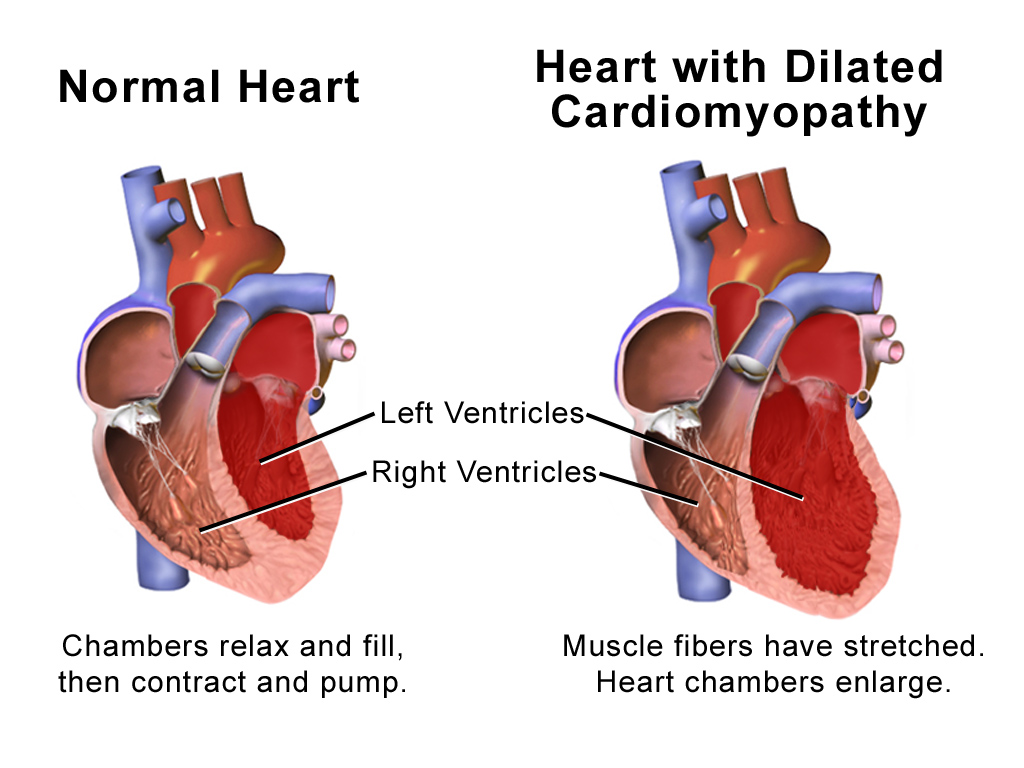
Dilated Cardiomyopathy
Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) is a condition in which the heart becomes enlarged and cannot pump blood effectively. Symptoms vary from none to feeling tired, leg swelling, and shortness of breath. It may also result in chest pain or fainting. Complications can include heart failure, heart valve disease, or an irregular heartbeat. Causes include genetics, alcohol, cocaine, certain toxins, complications of pregnancy, and certain infections. Coronary artery disease and high blood pressure may play a role, but are not the primary cause. In many cases the cause remains unclear. It is a type of cardiomyopathy, a group of diseases that primarily affects the heart muscle. The diagnosis may be supported by an electrocardiogram, chest X-ray, or echocardiogram. In those with heart failure, treatment may include medications in the ACE inhibitor, beta blocker, and diuretic families. A low salt diet may also be helpful. In those with certain types of irregular heartbeat, blood thinners ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TNNC1
Troponin C, also known as TN-C or TnC, is a protein that resides in the troponin complex on actin thin filaments of striated muscle (cardiac, fast-twitch skeletal, or slow-twitch skeletal) and is responsible for binding calcium to activate muscle contraction. Troponin C is encoded by the ''TNNC1'' gene in humans for both cardiac and slow skeletal muscle. Structure Cardiac troponin C (cTnC) is a 161-amino acid protein organized into two domains: the regulatory N-terminal domain (cNTnC, residues 1-86), the structural C-terminal domain (cCTnC, residues 93-161), and a flexible linker connecting the two domains (residues 87-92). Each domain contains two EF-hands, Ca2+-binding helix-loop-helix motifs exemplified by proteins like parvalbumin and calmodulin. In cCTnC the two EF-hand motifs constitute two high affinity Ca2+-binding sites. that are occupied at all physiologically relevant calcium concentrations. In contrast, only the second EF-hand in cNTnC binds Ca2+ with low affinity, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Troponin
image:Troponin Ribbon Diagram.png, 400px, Ribbon representation of the human cardiac troponin core complex (52 kDa core) in the calcium-saturated form. Blue = troponin C; green = troponin I; magenta = troponin T.; ; rendered with PyMOL Troponin, or the troponin complex, is a complex of three regulatory proteins (troponin C, troponin I, and troponin T) that are integral to muscle contraction in skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle, but not smooth muscle. Measurements of cardiac-specific troponins I and T are extensively used as diagnostic and prognostic indicators in the management of myocardial infarction and acute coronary syndrome. Blood troponin levels may be used as a diagnostic marker for stroke or other myocardial injury that is ongoing, although the sensitivity of this measurement is low. Function Troponin is attached to the protein tropomyosin and lies within the groove between actin filaments in muscle tissue. In a relaxed muscle, tropomyosin blocks the attachment site ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Troponin I
Troponin I is a cardiac and skeletal muscle protein family. It is a part of the troponin protein complex, where it binds to actin in thin myofilaments to hold the actin-tropomyosin complex in place. Troponin I prevents myosin from binding to actin in relaxed muscle. When calcium binds to the troponin C, it causes conformational changes which lead to dislocation of troponin I. Afterwards, tropomyosin leaves the binding site for myosin on actin leading to contraction of muscle. The letter ''I'' is given due to its inhibitory character. It is a useful marker in the laboratory diagnosis of heart attack. It occurs in different plasma concentration but the same circumstances as troponin T - either test can be performed for confirmation of cardiac muscle damage and laboratories usually offer one test or the other. Three paralogs with unique tissue-specific expression patterns are expressed in humans, listed below with their locations and OMIM accessions: * Slow-twitch skeletal muscle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropomyosin
Tropomyosin is a two-stranded alpha-helical, coiled coil protein found in actin-based cytoskeletons. Tropomyosin and the actin skeleton All organisms contain organelles that provide physical integrity to their cells. These type of organelles are collectively known as the cytoskeleton, and one of the most ancient systems is based on filamentous polymers of the protein actin. A polymer of a second protein, tropomyosin, is an integral part of most actin filaments in animals. Tropomyosins are a large family of integral components of actin filaments that play a critical role in regulating the function of actin filaments in both muscle and nonmuscle cells. These proteins consist of rod-shaped coiled-coil hetero- or homo- dimers that lie along the α-helical groove of most actin filaments. Interaction occurs along the length of the actin filament, with dimers aligning in a head-to-tail fashion. Tropomyosins are often categorised into two groups, muscle tropomyosin isoforms and nonmu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)