|
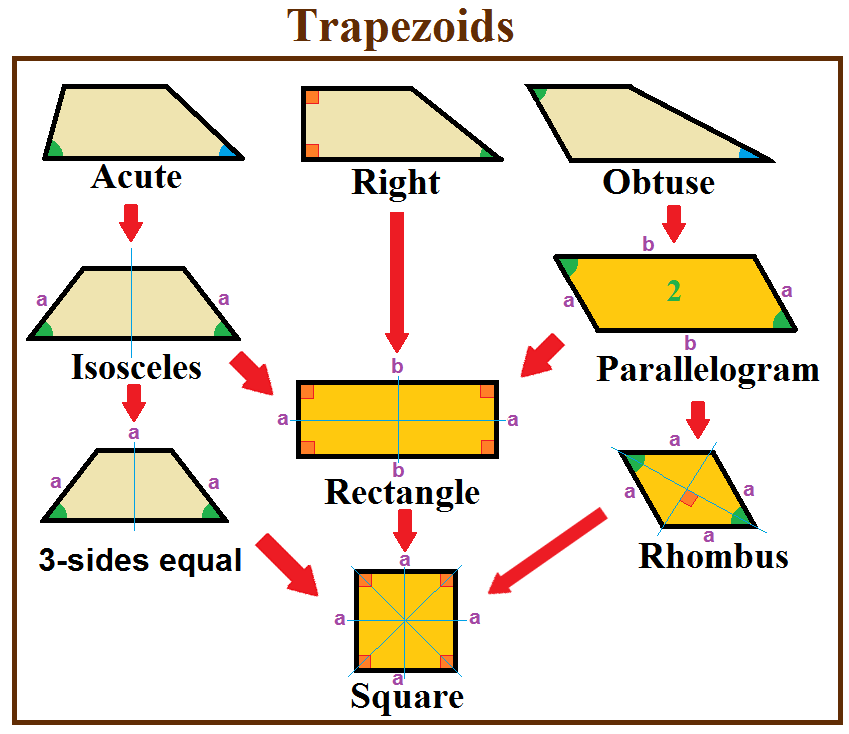
Trapezoid
In geometry, a trapezoid () in North American English, or trapezium () in British English, is a quadrilateral that has at least one pair of parallel sides. The parallel sides are called the ''bases'' of the trapezoid. The other two sides are called the ''legs'' or ''lateral sides''. (If the trapezoid is a parallelogram, then the choice of bases and legs is arbitrary.) A trapezoid is usually considered to be a convex quadrilateral in Euclidean geometry, but there are also crossed cases. If ''ABCD'' is a convex trapezoid, then ''ABDC'' is a crossed trapezoid. The metric formulas in this article apply in convex trapezoids. Definitions ''Trapezoid'' can be defined exclusively or inclusively. Under an exclusive definition a trapezoid is a quadrilateral having pair of parallel sides, with the other pair of opposite sides non-parallel. Parallelograms including rhombi, rectangles, and squares are then not considered to be trapezoids. Under an inclusive definition, a trapezoid is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Isosceles Trapezoid
In Euclidean geometry, an isosceles trapezoid is a convex quadrilateral with a line of symmetry bisecting one pair of opposite sides. It is a special case of a trapezoid. Alternatively, it can be defined as a trapezoid in which both legs and both base angles are of equal measure, or as a trapezoid whose diagonals have equal length. Note that a non-rectangular parallelogram is not an isosceles trapezoid because of the second condition, or because it has no line of symmetry. In any isosceles trapezoid, two opposite sides (the bases) are parallel, and the two other sides (the legs) are of equal length (properties shared with the parallelogram), and the diagonals have equal length. The base angles of an isosceles trapezoid are equal in measure (there are in fact two pairs of equal base angles, where one base angle is the supplementary angle of a base angle at the other base). Special cases Trapezoid is defined as a quadrilateral having exactly one pair of parallel sides, with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Quadrilateral
In Euclidean geometry, geometry a quadrilateral is a four-sided polygon, having four Edge (geometry), edges (sides) and four Vertex (geometry), corners (vertices). The word is derived from the Latin words ''quadri'', a variant of four, and ''latus'', meaning "side". It is also called a tetragon, derived from Greek "tetra" meaning "four" and "gon" meaning "corner" or "angle", in analogy to other polygons (e.g. pentagon). Since "gon" means "angle", it is analogously called a quadrangle, or 4-angle. A quadrilateral with vertices A, B, C and D is sometimes denoted as \square ABCD. Quadrilaterals are either simple polygon, simple (not self-intersecting), or complex polygon, complex (self-intersecting, or crossed). Simple quadrilaterals are either convex polygon, convex or concave polygon, concave. The Internal and external angle, interior angles of a simple (and Plane (geometry), planar) quadrilateral ''ABCD'' add up to 360 Degree (angle), degrees, that is :\angle A+\angle B+\angle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Crossed Quadrilateral
In geometry a quadrilateral is a four-sided polygon, having four edges (sides) and four corners (vertices). The word is derived from the Latin words ''quadri'', a variant of four, and ''latus'', meaning "side". It is also called a tetragon, derived from Greek "tetra" meaning "four" and "gon" meaning "corner" or "angle", in analogy to other polygons (e.g. pentagon). Since "gon" means "angle", it is analogously called a quadrangle, or 4-angle. A quadrilateral with vertices A, B, C and D is sometimes denoted as \square ABCD. Quadrilaterals are either simple (not self-intersecting), or complex (self-intersecting, or crossed). Simple quadrilaterals are either convex or concave. The interior angles of a simple (and planar) quadrilateral ''ABCD'' add up to 360 degrees, that is :\angle A+\angle B+\angle C+\angle D=360^. This is a special case of the ''n''-gon interior angle sum formula: ''S'' = (''n'' − 2) × 180° (here, n=4). All non-self-crossing quadrilaterals tile the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Antiparallelogram
In geometry, an antiparallelogram is a type of list of self-intersecting polygons, self-crossing quadrilateral. Like a parallelogram, an antiparallelogram has two opposite pairs of equal-length sides, but these pairs of sides are not in general parallel (geometry), parallel. Instead, each pair of sides is antiparallel lines, antiparallel with respect to the other, with sides in the longer pair crossing each other as in a scissors mechanism. Whereas a parallelogram's opposite angles are equal and oriented the same way, an antiparallelogram's are equal but oppositely oriented. Antiparallelograms are also called contraparallelograms or crossed parallelograms. Antiparallelograms occur as the vertex figures of certain nonconvex uniform polyhedron, nonconvex uniform polyhedra. In the theory of four-bar linkages, the linkages with the form of an antiparallelogram are also called butterfly linkages or bow-tie linkages, and are used in the design of non-circular gears. In celestial mechan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
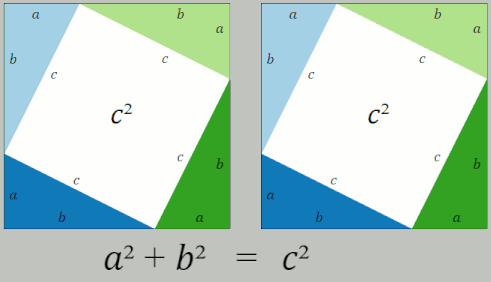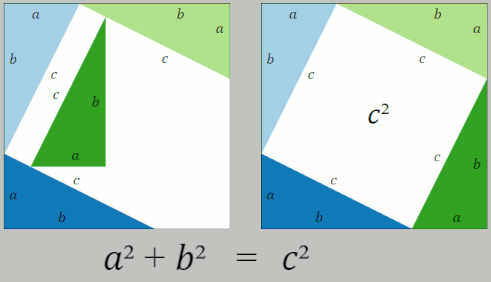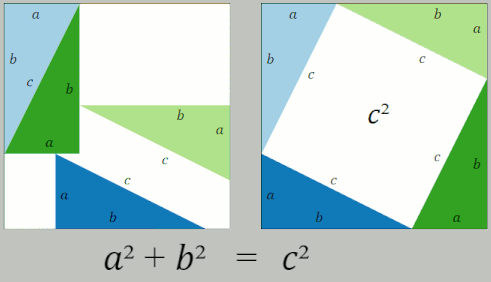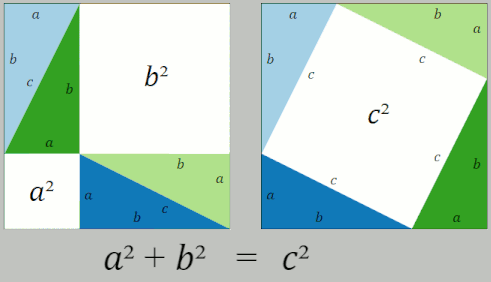
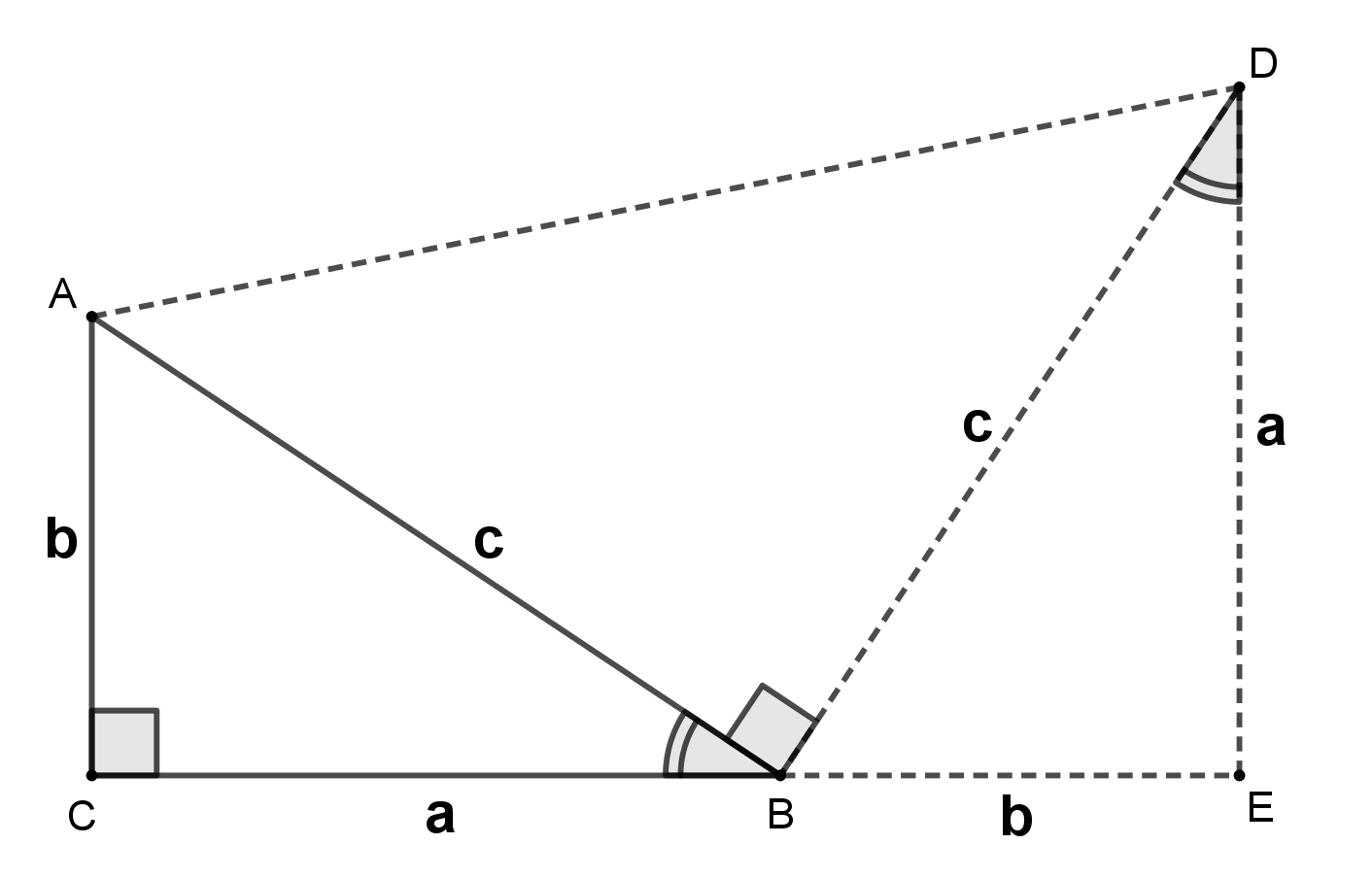
Pythagorean Theorem
In mathematics, the Pythagorean theorem or Pythagoras' theorem is a fundamental relation in Euclidean geometry between the three sides of a right triangle. It states that the area of the square whose side is the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the areas of the squares on the other two sides. The theorem can be written as an equation relating the lengths of the sides , and the hypotenuse , sometimes called the Pythagorean equation: :a^2 + b^2 = c^2 . The theorem is named for the Ancient Greece, Greek philosopher Pythagoras, born around 570 BC. The theorem has been Mathematical proof, proved numerous times by many different methods – possibly the most for any mathematical theorem. The proofs are diverse, including both Geometry, geometric proofs and Algebra, algebraic proofs, with some dating back thousands of years. When Euclidean space is represented by a Cartesian coordinate system in analytic geometry, Euclidean distance satisfies th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Garfield's Proof Of The Pythagorean Theorem
Garfield's proof of the Pythagorean theorem is an original proof of the Pythagorean theorem discovered by James A. Garfield (November 19, 1831 – September 19, 1881), the 20th president of the United States. The proof appeared in print in the ''Journal of Education, New-England Journal of Education'' (Vol. 3, No.14, April 1, 1876). At the time of the publication of the proof Garfield was a Congressman from Ohio. He assumed the office of President on March 4, 1881, and served in that position only for a brief period up to September 19, 1881 when he died following his assassination in July. Garfield was the only President of the United States to have contributed anything original to mathematics. The proof is nontrivial and, according to the historian of mathematics William Dunham (mathematician), William Dunham, "Garfield's is really a very clever proof." The proof appears as the 231st proof in ''The Pythagorean Proposition'', a compendium of 370 different proofs of the Pythagorean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Reflection Symmetry
In mathematics, reflection symmetry, line symmetry, mirror symmetry, or mirror-image symmetry is symmetry with respect to a Reflection (mathematics), reflection. That is, a figure which does not change upon undergoing a reflection has reflectional symmetry. In Two-dimensional space, two-dimensional space, there is a line/axis of symmetry, in Three-dimensional space, three-dimensional space, there is a plane (mathematics), plane of symmetry. An object or figure which is indistinguishable from its transformed image is called mirror image, mirror symmetric. Symmetric function In formal terms, a mathematical object is symmetric with respect to a given mathematical operation, operation such as reflection, Rotational symmetry, rotation, or Translational symmetry, translation, if, when applied to the object, this operation preserves some property of the object. The set of operations that preserve a given property of the object form a group (algebra), group. Two objects are symmetr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Rectangle
In Euclidean geometry, Euclidean plane geometry, a rectangle is a Rectilinear polygon, rectilinear convex polygon or a quadrilateral with four right angles. It can also be defined as: an equiangular quadrilateral, since equiangular means that all of its angles are equal (360°/4 = 90°); or a parallelogram containing a right angle. A rectangle with four sides of equal length is a ''square''. The term "wikt:oblong, oblong" is used to refer to a non-square rectangle. A rectangle with Vertex (geometry), vertices ''ABCD'' would be denoted as . The word rectangle comes from the Latin ''rectangulus'', which is a combination of ''rectus'' (as an adjective, right, proper) and ''angulus'' (angle). A #Crossed rectangles, crossed rectangle is a crossed (self-intersecting) quadrilateral which consists of two opposite sides of a rectangle along with the two diagonals (therefore only two sides are parallel). It is a special case of an antiparallelogram, and its angles are not right angles an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Crossed Polygon
A crossed polygon is a polygon in the plane with a turning number or Density (polygon), density of zero, with the appearance of a figure 8, infinity symbol, or lemniscate curve. ''Crossed polygons'' are related to star polygons which have turning numbers greater than 1. The vertices with clockwise turning angles equal the vertices with counterclockwise turning angles. A ''crossed polygon'' will always have at least 2 edges or vertices intersecting or coinciding. Any convex polygon with 4 or more sides can be remade into a crossed polygon by swapping the positions of two adjacent vertices. ''Crossed polygons'' are common as vertex figures of List_of_uniform_polyhedra#Uniform_star_polyhedra, uniform star polyhedra.Coxeter, Coxeter, H.S.M., Michael S. Longuet-Higgins, M. S. Longuet-Higgins and J.C.P Miller, Uniform Polyhedra, ''Phil. Trans.'' 246 A (1954) pp. 401–450. Crossed quadrilateral Crossed quadrilaterals are most common, including: *''crossed parallelogram'' or ant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Square
In geometry, a square is a regular polygon, regular quadrilateral. It has four straight sides of equal length and four equal angles. Squares are special cases of rectangles, which have four equal angles, and of rhombuses, which have four equal sides. As with all rectangles, a square's angles are right angles (90 degree (angle), degrees, or Pi, /2 radians), making adjacent sides perpendicular. The area of a square is the side length multiplied by itself, and so in algebra, multiplying a number by itself is called square (algebra), squaring. Equal squares can tile the plane edge-to-edge in the square tiling. Square tilings are ubiquitous in tiled floors and walls, graph paper, image pixels, and game boards. Square shapes are also often seen in building floor plans, origami paper, food servings, in graphic design and heraldry, and in instant photos and fine art. The formula for the area of a square forms the basis of the calculation of area and motivates the search for methods for s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Parallelogram
In Euclidean geometry, a parallelogram is a simple polygon, simple (non-list of self-intersecting polygons, self-intersecting) quadrilateral with two pairs of Parallel (geometry), parallel sides. The opposite or facing sides of a parallelogram are of equal length and the opposite angles of a parallelogram are of equal measure. The congruence (geometry), congruence of opposite sides and opposite angles is a direct consequence of the Euclidean parallel postulate and neither condition can be proven without appealing to the Euclidean parallel postulate or one of its equivalent formulations. By comparison, a quadrilateral with at least one pair of parallel sides is a trapezoid in American English or a trapezium in British English. The three-dimensional counterpart of a parallelogram is a parallelepiped. The word "parallelogram" comes from the Greek παραλληλό-γραμμον, ''parallēló-grammon'', which means "a shape of parallel lines". Special cases *Rectangle – A par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |