|
Transmembrane Proteins
A transmembrane protein (TP) is a type of integral membrane protein that spans the entirety of the cell membrane. Many transmembrane proteins function as gateways to permit the transport of specific substances across the membrane. They frequently undergo significant conformational changes to move a substance through the membrane. They are usually highly hydrophobic and aggregate and precipitate in water. They require detergents or nonpolar solvents for extraction, although some of them ( beta-barrels) can be also extracted using denaturing agents. The peptide sequence that spans the membrane, or the transmembrane segment, is largely hydrophobic and can be visualized using the hydropathy plot. Depending on the number of transmembrane segments, transmembrane proteins can be classified as single-span (or bitopic) or multi-span (polytopic). Some other integral membrane proteins are called monotopic, meaning that they are also permanently attached to the membrane, but do not pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stannin
Stannins are small proteins that consist of a single transmembrane helix, an unstructured linker domain, and a cytoplasmic domain. The transmembrane region contains a conserved cysteine residue (Cys32) that, together with Cys34 found in the stannin unstructured linker domain, constitutes the putative trimethyltin-binding site, close to the lipid/solvent interface. The unstructured protein region connects two adjacent helical domains. It contains a conserved CXC metal-binding motif and a putative 14-3-3-zeta binding domain. Upon coordinating dimethytin, considerable structural or dynamic changes in the flexible loop region of SNN may take place, recruiting other binding partners such as 14-3-3-zeta, and thereby initiating the apoptotic cascade. The cytoplasmic domain forms a distorted helix that is partially absorbed into the plane of the lipid bilayer. It interacts with the surface of the lipid bilayer, and contributes to the initiation of the apoptotic Apoptosis (from grc, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lipid Bilayer
The lipid bilayer (or phospholipid bilayer) is a thin polar membrane made of two layers of lipid molecules. These membranes are flat sheets that form a continuous barrier around all cells. The cell membranes of almost all organisms and many viruses are made of a lipid bilayer, as are the nuclear membrane surrounding the cell nucleus, and membranes of the membrane-bound organelles in the cell. The lipid bilayer is the barrier that keeps ions, proteins and other molecules where they are needed and prevents them from diffusing into areas where they should not be. Lipid bilayers are ideally suited to this role, even though they are only a few nanometers in width, because they are impermeable to most water-soluble ( hydrophilic) molecules. Bilayers are particularly impermeable to ions, which allows cells to regulate salt concentrations and pH by transporting ions across their membranes using proteins called ion pumps. Biological bilayers are usually composed of amphiphilic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Topology
Protein topology is a property of protein molecule that does not change under deformation (without cutting or breaking a bond). Frameworks Two main topology frameworks have been developed and applied to protein molecules. Knot Theory Knot theory which categorises chain entanglements. The usage of knot theory is limited to a small percentage of proteins as most of them are unknot. Circuit topology Circuit topology categorises intra-chain contacts based on their arrangements. Other Uses In biology literature, the term topology is also used to refer to mutual orientation of regular secondary structures, such as alpha-helices and beta strands in protein structure For example, two adjacent interacting alpha-helices or beta-strands can go in the same or in opposite directions. Topology diagrams of di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyproline Helix
A polyproline helix is a type of protein secondary structure which occurs in proteins comprising repeating proline residues. A left-handed polyproline II helix (PPII, poly-Pro II) is formed when sequential residues all adopt (φ,ψ) backbone dihedral angles of roughly (-75°, 150°) and have ''trans'' isomers of their peptide bonds. This PPII conformation is also common in proteins and polypeptides with other amino acids apart from proline. Similarly, a more compact right-handed polyproline I helix (PPI, poly-Pro I) is formed when sequential residues all adopt (φ,ψ) backbone dihedral angles of roughly (-75°, 160°) and have '' cis'' isomers of their peptide bonds. Of the twenty common naturally occurring amino acids, only proline is likely to adopt the ''cis'' isomer of the peptide bond, specifically the X-Pro peptide bond; steric and electronic factors heavily favor the ''trans'' isomer in most other peptide bonds. However, peptide bonds that replace proline with another ''N' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
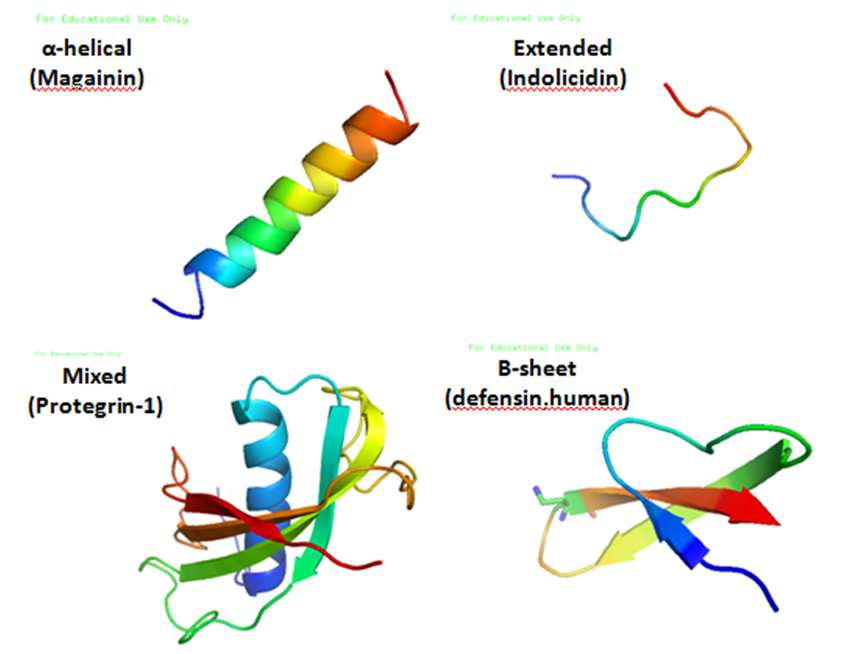
Antimicrobial Peptides
Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs), also called host defence peptides (HDPs) are part of the innate immune response found among all classes of life. Fundamental differences exist between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells that may represent targets for antimicrobial peptides. These peptides are potent, broad spectrum antibiotics which demonstrate potential as novel therapeutic agents. Antimicrobial peptides have been demonstrated to kill Gram negative and Gram positive bacteria, enveloped viruses, fungi and even transformed or cancerous cells. Unlike the majority of conventional antibiotics it appears that antimicrobial peptides frequently destabilize biological membranes, can form transmembrane channels, and may also have the ability to enhance immunity by functioning as immunomodulators. Structure Antimicrobial peptides are a unique and diverse group of molecules, which are divided into subgroups on the basis of their amino acid composition and structure. Antimicrobial peptides a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gramicidin A
Gramicidin, also called gramicidin D, is a mix of ionophoric antibiotics, gramicidin A, B and C, which make up about 80%, 5%, and 15% of the mix, respectively. Each has 2 isoforms, so the mix has 6 different types of gramicidin molecules. They can be extracted from ''Brevibacillus brevis'' soil bacteria. Gramicidins are linear peptides with 15 amino acids. This is in contrast to unrelated gramicidin S, which is a cyclic peptide. Medical uses Gramicidins work as antibiotics against gram-positive bacteria like ''Bacillus subtilis'' and ''Staphylococcus aureus'', but not well against gram-negative ones like ''E. coli''. Gramicidins are used in medicinal lozenges for sore throat and in topical medicines to treat infected wounds. Gramicidins are often mixed with other antibiotics like tyrocidine and antiseptics. Gramicidins are also used in eye drops for bacterial eye infections. In drops, they are often mixed with other antibiotics like polymyxin B or neomycin. Multiple antibiotic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pore-forming Toxin
Pore-forming proteins (PFTs, also known as pore-forming toxins) are usually produced by bacteria, and include a number of protein exotoxins but may also be produced by other organisms such as apple snails that produce perivitellin-2 or earthworms, who produce lysenin. They are frequently cytotoxic (i.e., they kill cells), as they create unregulated pores in the membrane of targeted cells. Types PFTs can be divided into two categories, depending on the alpha-helical or beta-barrel architecture of their transmembrane channel that can consist either of * Alpha-pore-forming toxins ** e.g., Haemolysin E family, actinoporins, Corynebacterial porin B, Cytolysin A of ''E. coli''. * Beta-barrel pore-forming toxins ** e.g. α-hemolysin (Fig 1), PVL – Panton-Valentine leukocidin, various insecticidal toxins. Other categories: * Large beta-barrel pore-forming toxins ** MACPF and Cholesterol-dependent cytolysins (CDCs), gasdermin * Binary toxins ** e.g., Anthrax toxin, Pleur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloroplasts
A chloroplast () is a type of membrane-bound organelle known as a plastid that conducts photosynthesis mostly in plant and algal cells. The photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll captures the energy from sunlight, converts it, and stores it in the energy-storage molecules ATP and NADPH while freeing oxygen from water in the cells. The ATP and NADPH is then used to make organic molecules from carbon dioxide in a process known as the Calvin cycle. Chloroplasts carry out a number of other functions, including fatty acid synthesis, amino acid synthesis, and the immune response in plants. The number of chloroplasts per cell varies from one, in unicellular algae, up to 100 in plants like '' Arabidopsis'' and wheat. A chloroplast is characterized by its two membranes and a high concentration of chlorophyll. Other plastid types, such as the leucoplast and the chromoplast, contain little chlorophyll and do not carry out photosynthesis. Chloroplasts are highly dynamic—they cir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitochondria
A mitochondrion (; ) is an organelle found in the cells of most Eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi. Mitochondria have a double membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is used throughout the cell as a source of chemical energy. They were discovered by Albert von Kölliker in 1857 in the voluntary muscles of insects. The term ''mitochondrion'' was coined by Carl Benda in 1898. The mitochondrion is popularly nicknamed the "powerhouse of the cell", a phrase coined by Philip Siekevitz in a 1957 article of the same name. Some cells in some multicellular organisms lack mitochondria (for example, mature mammalian red blood cells). A large number of unicellular organisms, such as microsporidia, parabasalids and diplomonads, have reduced or transformed their mitochondria into other structures. One eukaryote, '' Monocercomonoides'', is known to have completely lost its mitochondria, and one multicellular orga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outer Mitochondrial Membrane
A mitochondrion (; ) is an organelle found in the cells of most Eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi. Mitochondria have a double membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is used throughout the cell as a source of chemical energy. They were discovered by Albert von Kölliker in 1857 in the voluntary muscles of insects. The term ''mitochondrion'' was coined by Carl Benda in 1898. The mitochondrion is popularly nicknamed the "powerhouse of the cell", a phrase coined by Philip Siekevitz in a 1957 article of the same name. Some cells in some multicellular organisms lack mitochondria (for example, mature mammalian red blood cells). A large number of unicellular organisms, such as microsporidia, parabasalids and diplomonads, have reduced or transformed their mitochondria into other structures. One eukaryote, ''Monocercomonoides'', is known to have completely lost its mitochondria, and one multicellular organism, ''Henn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gram-positive Bacteria
In bacteriology, gram-positive bacteria are bacteria that give a positive result in the Gram stain test, which is traditionally used to quickly classify bacteria into two broad categories according to their type of cell wall. Gram-positive bacteria take up the crystal violet stain used in the test, and then appear to be purple-coloured when seen through an optical microscope. This is because the thick peptidoglycan layer in the bacterial cell wall retains the stain after it is washed away from the rest of the sample, in the decolorization stage of the test. Conversely, gram-negative bacteria cannot retain the violet stain after the decolorization step; alcohol used in this stage degrades the outer membrane of gram-negative cells, making the cell wall more porous and incapable of retaining the crystal violet stain. Their peptidoglycan layer is much thinner and sandwiched between an inner cell membrane and a bacterial outer membrane, causing them to take up the counterstain ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |