|
Transmembrane Channels
Transmembrane channels, also called membrane channels, are pores within a lipid bilayer. The channels can be formed by protein complexes that run across the membrane or by peptides. They may cross the cell membrane, connecting the cytosol, or cytoplasm, to the extracellular matrix. Transmembrane channels are also found in the membranes of organelles including the nucleus, the endoplasmic reticulum, the Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, chloroplasts, and lysosomes. Transmembrane channels differ from transporters and pumps in several ways. Some channels are less selective than typical transporters and pumps, differentiating solutes primarily by size and ionic charge. Channels perform passive transport of materials also known as facilitated diffusion. Transporters can carry out either passive or active transfer of materials while pumps require energy to act. There are several modes by which membrane channels operate. The most common is the gated channel which requires a trigger, such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Membrane Channels
Membrane channels are a family of biological membrane proteins which allow the passive movement of ions (ion channels), water (aquaporins) or other solutes to passively pass through the membrane down their electrochemical gradient. They are studied using a range of channelomics experimental and mathematical techniques. Insights have suggested endocannabinoids (eCBs) as Molecules and Cells, molecules that can regulate the opening of these channels during diverse conditions. Properties Hemichannels A hemichannel is a membrane channel made up of six subunits. A hemichannel is defined as one-half of a gap junction channel. Hemichannels consist of connexins. Pannexin Pannexins are involved in the process of purinergic signalling. They release adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which activate purinergic receptors. On the other hand, purinergic receptor activation can also lead to the opening of the channel, via a positive feedback loop. In addition, P2Y receptors activate inositol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Facilitated Diffusion
Facilitated diffusion (also known as facilitated transport or passive-mediated transport) is the process of spontaneous passive transport (as opposed to active transport) of molecules or ions across a biological membrane via specific transmembrane integral proteins. Being passive, facilitated transport does not directly require chemical energy from ATP hydrolysis in the transport step itself; rather, molecules and ions move down their concentration gradient reflecting its diffusive nature. Facilitated diffusion differs from simple diffusion in several ways. # the transport relies on molecular binding between the cargo and the membrane-embedded channel or carrier protein. # the rate of facilitated diffusion is saturable with respect to the concentration difference between the two phases; unlike free diffusion which is linear in the concentration difference. # the temperature dependence of facilitated transport is substantially different due to the presence of an activated bin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ataxia
Ataxia is a neurological sign consisting of lack of voluntary coordination of muscle movements that can include gait abnormality, speech changes, and abnormalities in eye movements. Ataxia is a clinical manifestation indicating dysfunction of the parts of the nervous system that coordinate movement, such as the cerebellum. Ataxia can be limited to one side of the body, which is referred to as hemiataxia. Several possible causes exist for these patterns of neurological dysfunction. Dystaxia is a mild degree of ataxia. Friedreich's ataxia has gait abnormality as the most commonly presented symptom. The word is from Greek α- negative prefix+ -τάξις rder= "lack of order". Types Cerebellar The term cerebellar ataxia is used to indicate ataxia due to dysfunction of the cerebellum. The cerebellum is responsible for integrating a significant amount of neural information that is used to coordinate smoothly ongoing movements and to participate in motor planning. Although a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paralysis
Paralysis (also known as plegia) is a loss of motor function in one or more muscles. Paralysis can also be accompanied by a loss of feeling (sensory loss) in the affected area if there is sensory damage. In the United States, roughly 1 in 50 people have been diagnosed with some form of permanent or transient paralysis. The word "paralysis" derives from the Greek παράλυσις, meaning "disabling of the nerves" from παρά (''para'') meaning "beside, by" and λύσις (''lysis'') meaning "making loose". A paralysis accompanied by involuntary tremors is usually called "palsy". Causes Paralysis is most often caused by damage in the nervous system, especially the spinal cord. Other major causes are stroke, trauma with nerve injury, poliomyelitis, cerebral palsy, peripheral neuropathy, Parkinson's disease, ALS, botulism, spina bifida, multiple sclerosis, and Guillain–Barré syndrome. Temporary paralysis occurs during REM sleep, and dysregulation of this system can lead ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiac Arrhythmia
Arrhythmias, also known as cardiac arrhythmias, heart arrhythmias, or dysrhythmias, are irregularities in the heartbeat, including when it is too fast or too slow. A resting heart rate that is too fast – above 100 beats per minute in adults – is called tachycardia, and a resting heart rate that is too slow – below 60 beats per minute – is called bradycardia. Some types of arrhythmias have no symptoms. Symptoms, when present, may include palpitations or feeling a pause between heartbeats. In more serious cases, there may be lightheadedness, passing out, shortness of breath or chest pain. While most cases of arrhythmia are not serious, some predispose a person to complications such as stroke or heart failure. Others may result in sudden death. Arrhythmias are often categorized into four groups: extra beats, supraventricular tachycardias, ventricular arrhythmias and bradyarrhythmias. Extra beats include premature atrial contractions, premature ventricular contra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epilepsy
Epilepsy is a group of non-communicable neurological disorders characterized by recurrent epileptic seizures. Epileptic seizures can vary from brief and nearly undetectable periods to long periods of vigorous shaking due to abnormal electrical activity in the brain. These episodes can result in physical injuries, either directly such as broken bones or through causing accidents. In epilepsy, seizures tend to recur and may have no immediate underlying cause. Isolated seizures that are provoked by a specific cause such as poisoning are not deemed to represent epilepsy. People with epilepsy may be treated differently in various areas of the world and experience varying degrees of social stigma due to the alarming nature of their symptoms. The underlying mechanism of epileptic seizures is excessive and abnormal neuronal activity in the cortex of the brain which can be observed in the electroencephalogram (EEG) of an individual. The reason this occurs in most cases of epilepsy is u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cystic Fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a rare genetic disorder that affects mostly the lungs, but also the pancreas, liver, kidneys, and intestine. Long-term issues include difficulty breathing and coughing up mucus as a result of frequent lung infections. Other signs and symptoms may include sinus infections, poor growth, fatty stool, clubbing of the fingers and toes, and infertility in most males. Different people may have different degrees of symptoms. Cystic fibrosis is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner. It is caused by the presence of mutations in both copies of the gene for the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) protein. Those with a single working copy are carriers and otherwise mostly healthy. CFTR is involved in the production of sweat, digestive fluids, and mucus. When the CFTR is not functional, secretions which are usually thin instead become thick. The condition is diagnosed by a sweat test and genetic testing. Screening of infants at bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cation
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge. The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convention. The net charge of an ion is not zero because its total number of electrons is unequal to its total number of protons. A cation is a positively charged ion with fewer electrons than protons while an anion is a negatively charged ion with more electrons than protons. Opposite electric charges are pulled towards one another by electrostatic force, so cations and anions attract each other and readily form ionic compounds. Ions consisting of only a single atom are termed atomic or monatomic ions, while two or more atoms form molecular ions or polyatomic ions. In the case of physical ionization in a fluid (gas or liquid), "ion pairs" are created by spontaneous molecule collisions, where each generated pair consists of a free electron and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
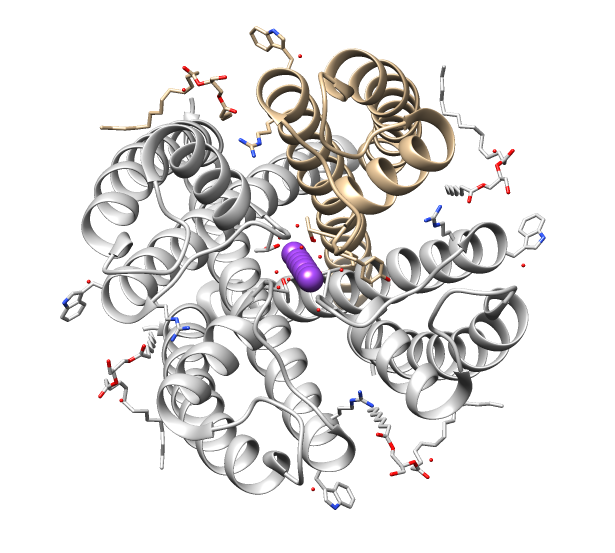
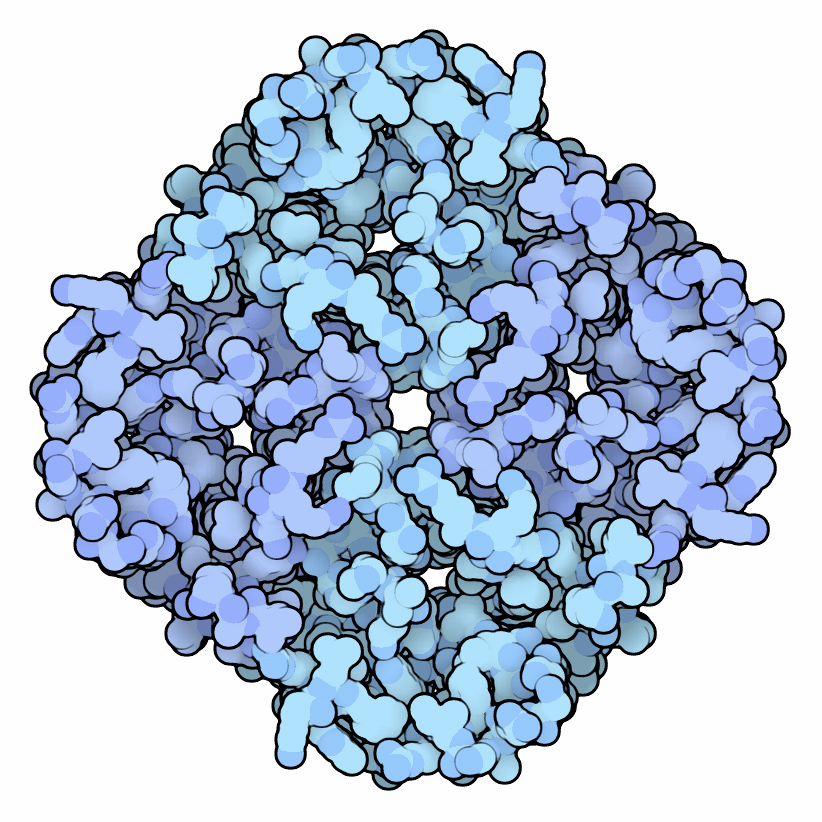
Potassium Ion Channel
Potassium channels are the most widely distributed type of ion channel found in virtually all organisms. They form potassium-selective pores that span cell membranes. Potassium channels are found in most cell types and control a wide variety of cell functions. Function Potassium channels function to conduct potassium ions down their electrochemical gradient, doing so both rapidly (up to the diffusion rate of K+ ions in bulk water) and selectively (excluding, most notably, sodium despite the sub-angstrom difference in ionic radius). Biologically, these channels act to set or reset the resting potential in many cells. In excitable cells, such as neurons, the delayed counterflow of potassium ions shapes the action potential. By contributing to the regulation of the cardiac action potential duration in cardiac muscle, malfunction of potassium channels may cause life-threatening arrhythmias. Potassium channels may also be involved in maintaining vascular tone. They also regulate ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ion Channels
Ion channels are pore-forming membrane proteins that allow ions to pass through the channel pore. Their functions include establishing a resting membrane potential, shaping action potentials and other electrical signals by gating the flow of ions across the cell membrane, controlling the flow of ions across secretory and epithelial cells, and regulating cell volume. Ion channels are present in the membranes of all cells. Ion channels are one of the two classes of ionophoric proteins, the other being ion transporters. The study of ion channels often involves biophysics, electrophysiology, and pharmacology, while using techniques including voltage clamp, patch clamp, immunohistochemistry, X-ray crystallography, fluoroscopy, and RT-PCR. Their classification as molecules is referred to as channelomics. Basic features There are two distinctive features of ion channels that differentiate them from other types of ion transporter proteins: #The rate of ion transport through the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aquaporins
Aquaporins, also called water channels, are channel proteins from a larger family of major intrinsic proteins that form pores in the membrane of biological cells, mainly facilitating transport of water between cells. The cell membranes of a variety of different bacteria, fungi, animal and plant cells contain aquaporins through which water can flow more rapidly into and out of the cell than by diffusing through the phospholipid bilayer. Aquaporins have six membrane-spanning alpha helical domains with both carboxylic and amino terminals on the cytoplasmic side. Two hydrophobic loops contain conserved asparagine-proline-alanine ("NPA motif") which form a barrel surrounding a central pore-like region that contains additional protein density. Because aquaporins are usually always open and are prevalent in just about every cell type, this leads to a misconception that water readily passes through the cell membrane down its concentration gradient. Water can pass through the cell membr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurotransmitter
A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a synapse. The cell receiving the signal, any main body part or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell. Neurotransmitters are released from synaptic vesicles into the synaptic cleft where they are able to interact with neurotransmitter receptors on the target cell. The neurotransmitter's effect on the target cell is determined by the receptor it binds. Many neurotransmitters are synthesized from simple and plentiful precursors such as amino acids, which are readily available and often require a small number of biosynthetic steps for conversion. Neurotransmitters are essential to the function of complex neural systems. The exact number of unique neurotransmitters in humans is unknown, but more than 100 have been identified. Common neurotransmitters include glutamate, GABA, acetylcholine, glycine and norepinephrine. Mechanism and cycle Synthes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)