|
Trading Strategy
In finance, a trading strategy is a fixed plan that is designed to achieve a profitable return by going long or short in markets. The main reasons that a properly researched trading strategy helps are its verifiability, quantifiability, consistency, and objectivity. For every trading strategy one needs to define assets to trade, entry/exit points and money management rules. Bad money management can make a potentially profitable strategy unprofitable.Nekrasov, V. Knowledge rather than Hope: A Book for Retail Investors and Mathematical Finance Students''. 2014pages 24-26 Trading strategies are based on fundamental or technical analysis, or both. They are usually verified by backtesting, where the process should follow the scientific method, and by forward testing (a.k.a. 'paper trading') where they are tested in a simulated trading environment. Types of trading strategies The term trading strategy can in brief be used by any fixed plan of trading a financial instrument, but the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finance
Finance is the study and discipline of money, currency and capital assets. It is related to, but not synonymous with economics, the study of production, distribution, and consumption of money, assets, goods and services (the discipline of financial economics bridges the two). Finance activities take place in financial systems at various scopes, thus the field can be roughly divided into personal, corporate, and public finance. In a financial system, assets are bought, sold, or traded as financial instruments, such as currencies, loans, bonds, shares, stocks, options, futures, etc. Assets can also be banked, invested, and insured to maximize value and minimize loss. In practice, risks are always present in any financial action and entities. A broad range of subfields within finance exist due to its wide scope. Asset, money, risk and investment management aim to maximize value and minimize volatility. Financial analysis is viability, stability, and profitabili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trading The News
Trading the news is a technique to trade equities, currencies and other financial instruments on the financial markets. Trading news releases can be a significant tool for financial investors. Economic news reports often spur strong short-term moves in the markets, which may create trading opportunities for traders. Announcements about corporate profits, a change in management, rumors of a merger, are events that can cause a company's share price to move wildly up or down. Interest rates, unemployment and export rates, or the central bank's policy shifts, can cause a deep change of an exchange rate. Methods Manual Investors trading shares of a listed company know there are certain events that cause the share price to rise or fall — sudden changes in energy prices, a labor strike at a supplier, a poor month for the sales, for example. Trading the news is the technique of making a profit by trading financial instruments (stock, currency, etc.) just in time, and in accordance t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Investment Strategy
In finance, an investment strategy is a set of rules, behaviors or procedures, designed to guide an investor's selection of an investment portfolio. Individuals have different profit objectives, and their individual skills make different tactics and strategies appropriate. Some choices involve a tradeoff between risk and return. Most investors fall somewhere in between, accepting some risk for the expectation of higher returns. Investors frequently pick investments to hedge themselves against inflation. During periods of high inflation investments such as shares tend to perform less well in real terms. Time horizon of investments. Investments such as shares should be invested into with the time frame of a minimum of 5 years in mind. It is recommended in finance a minimum of 6 months to 12 months expenses in a rainy-day current account, giving instant access before investing in riskier investments than an instant access account. It is also recommended no more than 90% of your mon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Falsifiability
Falsifiability is a standard of evaluation of scientific theories and hypotheses that was introduced by the Philosophy of science, philosopher of science Karl Popper in his book ''The Logic of Scientific Discovery'' (1934). He proposed it as the cornerstone of a solution to both the problem of induction and the demarcation problem, problem of demarcation. A Scientific theory, theory or hypothesis is falsifiable (or refutable) if it can be ''logically'' contradicted by an empirical test that can potentially be executed with existing technologies. Popper insisted that, as a logical criterion, it is distinct from the related concept "capacity to be proven wrong" discussed in #Falsificationism, Lakatos' falsificationism. Even being a logical criterion, its purpose is to make the theory predictive power, predictive and Testability, testable, thus useful in practice. Popper opposed falsifiability to the intuitively similar concept of Verifiability (science), verifiability. Verifying ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Empirical Research
Empirical research is research using empirical evidence. It is also a way of gaining knowledge by means of direct and indirect observation or experience. Empiricism values some research more than other kinds. Empirical evidence (the record of one's direct observations or experiences) can be analyzed quantitatively or qualitatively. Quantifying the evidence or making sense of it in qualitative form, a researcher can answer empirical questions, which should be clearly defined and answerable with the evidence collected (usually called data). Research design varies by field and by the question being investigated. Many researchers combine qualitative and quantitative forms of analysis to better answer questions that cannot be studied in laboratory settings, particularly in the social sciences and in education. In some fields, quantitative research may begin with a research question (e.g., "Does listening to vocal music during the learning of a word list have an effect on later memor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Do-it-yourself Investing
Do-it-yourself (DIY) investing, self-directed investing or self-managed investing is an investment approach where the investor chooses to build and manage his or her own investment portfolio instead of hiring an agent, such as a stockbroker, investment adviser, private banker, or financial planner. Overview The DIY approach has pervaded many activities that were traditionally performed exclusively by institutions or trained professionals. A common approach to investing, for many investors, is to hire investment representation to build and manage their portfolios. The main duties of investment representatives are to provide ongoing advice, allocate money to asset classes and investment products, and to make portfolio management decisions. Individual investors will often choose to manage their own investments rather than hiring outside representation. Common reasons for doing so include the avoidance of agency fees, dissatisfaction with the quality of service or the investmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Samuelson
Paul Anthony Samuelson (May 15, 1915 – December 13, 2009) was an American economist who was the first American to win the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences. When awarding the prize in 1970, the Swedish Royal Academies stated that he "has done more than any other contemporary economist to raise the level of scientific analysis in economic theory". "In a career that spanned seven decades, he transformed his field, influenced millions of students and turned MIT into an economics powerhouse" Economic historian Randall E. Parker has called him the "Father of Modern Economics", and ''The New York Times'' considers him to be the "foremost academic economist of the 20th century". Samuelson was likely the most influential economist of the latter half of the 20th century."Paul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kelly Criterion
In probability theory, the Kelly criterion (or Kelly strategy or Kelly bet), is a formula that determines the optimal theoretical size for a bet. It is valid when the expected returns are known. The Kelly bet size is found by maximizing the expected value of the logarithm of wealth, which is equivalent to maximizing the expected geometric growth rate. J. L. Kelly Jr, a researcher at Bell Labs, described the criterion in 1956. Because the Kelly Criterion leads to higher wealth than any other strategy in the long run (i.e., the theoretical maximum return as the number of bets goes to infinity), it is a scientific gambling method. The practical use of the formula has been demonstrated for gambling and the same idea was used to explain diversification in investment management., page 184f. In the 2000s, Kelly-style analysis became a part of mainstream investment theory and the claim has been made that well-known successful investors including Warren Buffett and Bill Gross use Kelly m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
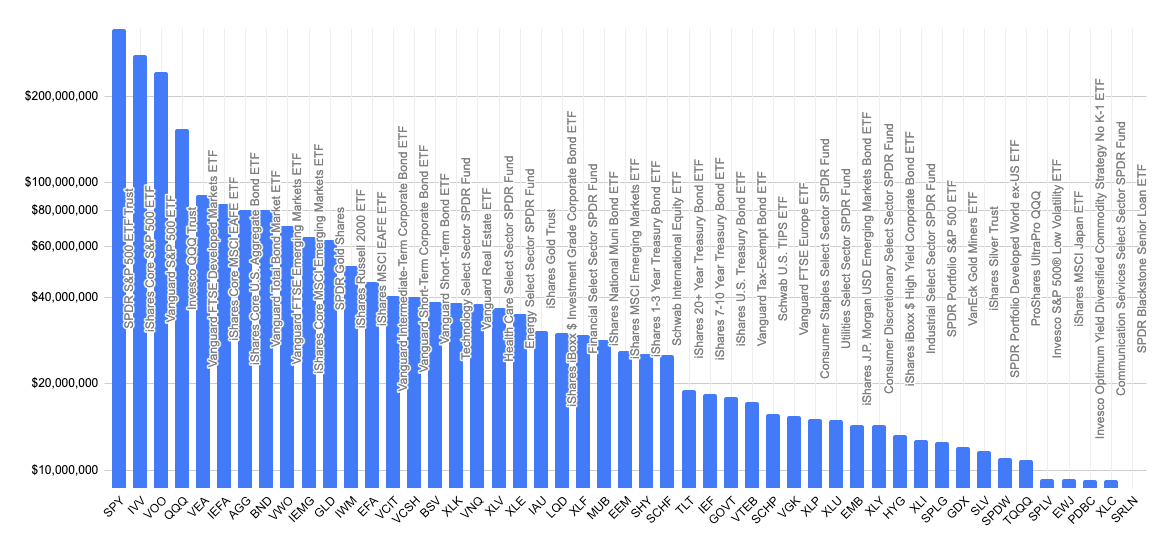
Exchange-traded Fund
An exchange-traded fund (ETF) is a type of investment fund and exchange-traded product, i.e. they are traded on stock exchanges. ETFs are similar in many ways to mutual funds, except that ETFs are bought and sold from other owners throughout the day on stock exchanges whereas mutual funds are bought and sold from the issuer based on their price at day's end. An ETF holds assets such as stocks, bonds, currencies, futures contracts, and/or commodities such as gold bars, and generally operates with an arbitrage mechanism designed to keep it trading close to its net asset value, although deviations can occasionally occur. Most ETFs are index funds: that is, they hold the same securities in the same proportions as a certain stock market index or bond market index. The most popular ETFs in the U.S. replicate the S&P 500, the total market index, the NASDAQ-100 index, the price of gold, the "growth" stocks in the Russell 1000 Index, or the index of the largest technology compan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maximum Drawdown
The drawdown is the measure of the decline from a historical peak in some variable (typically the cumulative profit or total open equity of a financial trading strategy). Somewhat more formally, if X(t), \; t \ge 0 is a stochastic process with X(0) = 0, the drawdown at time T, denoted D(T), is defined as: D(T) = \max\left max_X(t)-X(T),0 \right \equiv \left \max_X(t)-X(T) \right The average drawdown (AvDD) up to time T is the time average of drawdowns that have occurred up to time T:\operatorname(T) = \int_0^T D(t) \, dtThe maximum drawdown (MDD) up to time T is the maximum of the drawdown over the history of the variable. More formally, the MDD is defined as: \operatorname(T)=\max_D(\tau)=\max_\left max_ X(t)- X(\tau) \right/math> Pseudocode The following pseudocode computes the Drawdown ("DD") and Max Drawdown ("MDD") of the variable "NAV", the Net Asset Value of an investment. Drawdown and Max Drawdown are calculated as percentages: MDD = 0 peak = -99999 for i = 1 to N step ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sharpe Ratio
In finance, the Sharpe ratio (also known as the Sharpe index, the Sharpe measure, and the reward-to-variability ratio) measures the performance of an investment such as a security or portfolio compared to a risk-free asset, after adjusting for its risk. It is defined as the difference between the returns of the investment and the risk-free return, divided by the standard deviation of the investment returns. It represents the additional amount of return that an investor receives per unit of increase in risk. It was named after William F. Sharpe, who developed it in 1966. Definition Since its revision by the original author, William Sharpe, in 1994, the ''ex-ante'' Sharpe ratio is defined as: : S_a = \frac = \frac, where R_a is the asset return, R_b is the risk-free return (such as a U.S. Treasury security). E_a-R_b/math> is the expected value of the excess of the asset return over the benchmark return, and is the standard deviation of the asset excess return. The ''ex-p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |