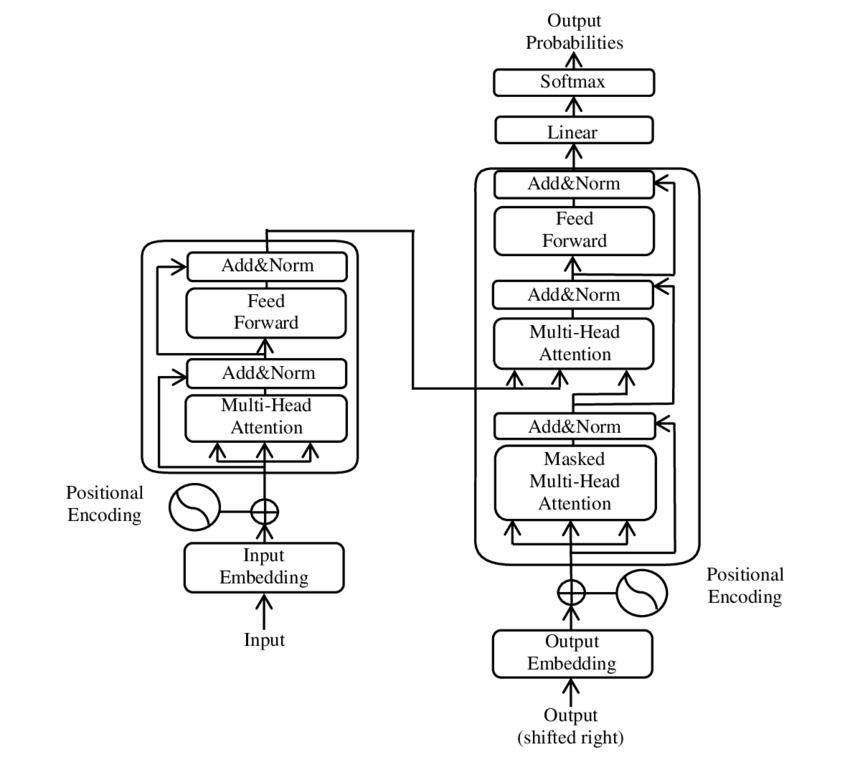
|
Tokenizer
Lexical tokenization is conversion of a text into (semantically or syntactically) meaningful ''lexical tokens'' belonging to categories defined by a "lexer" program. In case of a natural language, those categories include nouns, verbs, adjectives, punctuations etc. In case of a programming language, the categories include identifiers, operators, grouping symbols, data types and language keywords. Lexical tokenization is related to the type of tokenization used in large language models (LLMs) but with two differences. First, lexical tokenization is usually based on a lexical grammar, whereas LLM tokenizers are usually probability-based. Second, LLM tokenizers perform a second step that converts the tokens into numerical values. Rule-based programs A rule-based program, performing lexical tokenization, is called ''tokenizer'', or ''scanner'', although ''scanner'' is also a term for the first stage of a lexer. A lexer forms the first phase of a compiler frontend in processing. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Large Language Model
A large language model (LLM) is a language model trained with self-supervised machine learning on a vast amount of text, designed for natural language processing tasks, especially language generation. The largest and most capable LLMs are generative pretrained transformers (GPTs), which are largely used in generative chatbots such as ChatGPT or Gemini. LLMs can be fine-tuned for specific tasks or guided by prompt engineering. These models acquire predictive power regarding syntax, semantics, and ontologies inherent in human language corpora, but they also inherit inaccuracies and biases present in the data they are trained in. History Before the emergence of transformer-based models in 2017, some language models were considered large relative to the computational and data constraints of their time. In the early 1990s, IBM's statistical models pioneered word alignment techniques for machine translation, laying the groundwork for corpus-based language modeling. A sm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokenize
Lexical tokenization is conversion of a text into (semantically or syntactically) meaningful ''lexical tokens'' belonging to categories defined by a "lexer" program. In case of a natural language, those categories include nouns, verbs, adjectives, punctuations etc. In case of a programming language, the categories include identifiers, operators, grouping symbols, data types and language keywords. Lexical tokenization is related to the type of tokenization used in large language models (LLMs) but with two differences. First, lexical tokenization is usually based on a lexical grammar, whereas LLM tokenizers are usually probability-based. Second, LLM tokenizers perform a second step that converts the tokens into numerical values. Rule-based programs A rule-based program, performing lexical tokenization, is called ''tokenizer'', or ''scanner'', although ''scanner'' is also a term for the first stage of a lexer. A lexer forms the first phase of a compiler frontend in processing. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Identifier (computer Languages)
In computer programming languages, an identifier is a Lexical analysis#Token, lexical token (also called a symbol, but not to be confused with the symbol (programming), symbol primitive data type) that names the language's entities. Some of the kinds of entities an identifier might denote include Variable (computer science), variables, data types, Label (computer science), labels, subroutines, and Modular programming, modules. Lexical form Which character sequences constitute identifiers depends on the lexical grammar of the language. A common rule is alphanumeric sequences, with underscore also allowed (in some languages, _ is not allowed), and with the condition that it can not begin with a numerical digit (to simplify Lexical analysis, lexing by avoiding confusing with integer literals) – so foo, foo1, foo_bar, _foo are allowed, but 1foo is not – this is the definition used in earlier versions of C (programming language), C and C++, Python (programming language), Python ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synthetic Language
A synthetic language is a language that is characterized by denoting syntactic relationships between words via inflection or agglutination. Synthetic languages are statistically characterized by a higher morpheme-to-word ratio relative to analytic languages. Fusional languages favor inflection and agglutinative languages favor agglutination. Further divisions include polysynthetic languages (most belonging to an agglutinative-polysynthetic subtype, although Navajo and other Athabaskan languages are often classified as belonging to a fusional subtype) and oligosynthetic languages (only found in constructed languages). In contrast, rule-wise, the analytic languages rely more on auxiliary verbs and word order to denote syntactic relationship between words. Adding morphemes to a root word is used in inflection to convey a grammatical property of the word, such as denoting a subject or an object. Combining two or more morphemes into one word is used in agglutinating l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delimiter
A delimiter is a sequence of one or more Character (computing), characters for specifying the boundary between separate, independent regions in plain text, Expression (mathematics), mathematical expressions or other Data stream, data streams. An example of a delimiter is the comma character, which acts as a ''field delimiter'' in a sequence of comma-separated values. Another example of a delimiter is the time gap used to separate letters and words in the transmission of Morse code. In mathematics, delimiters are often used to specify the scope of an Operation (mathematics), operation, and can occur both as isolated symbols (e.g., Colon (punctuation), colon in "1 : 4") and as a pair of opposing-looking symbols (e.g., Angled bracket, angled brackets in \langle a, b \rangle). Delimiters represent one of various means of specifying boundaries in a data stream. String literal#Declarative notation, Declarative notation, for example, is an alternate method (without the use of delimiter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reserved Word
In a programming language, a reserved word (sometimes known as a reserved identifier) is a word that cannot be used by a programmer as an identifier, such as the name of a variable, function, or label – it is "reserved from use". In brief, an ''identifier'' starts with a letter, which is followed by any sequence of letters and digits (in some languages, the underscore '_' is treated as a letter). In an imperative programming language and in many object-oriented programming languages, apart from assignments and subroutine calls, keywords are often used to identify a particular statement, e.g. if, while, do, for, etc. Many languages treat keywords as reserved words, including Ada, C, C++, COBOL, Java, and Pascal. The number of reserved words varies widely from one language to another: C has about 30 while COBOL has about 400. A few languages do not have any reserved words; Fortran and PL/I identify keywords by context, while Algol 60 and Algol 68 generally use stroppin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
String (computer Science)
In computer programming, a string is traditionally a sequence of character (computing), characters, either as a literal (computer programming), literal constant or as some kind of Variable (computer science), variable. The latter may allow its elements to be Immutable object, mutated and the length changed, or it may be fixed (after creation). A string is often implemented as an array data structure of bytes (or word (computer architecture), words) that stores a sequence of elements, typically characters, using some character encoding. More general, ''string'' may also denote a sequence (or List (abstract data type), list) of data other than just characters. Depending on the programming language and precise data type used, a variable (programming), variable declared to be a string may either cause storage in memory to be statically allocated for a predetermined maximum length or employ dynamic allocation to allow it to hold a variable number of elements. When a string appears lit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HEAD
A head is the part of an organism which usually includes the ears, brain, forehead, cheeks, chin, eyes, nose, and mouth, each of which aid in various sensory functions such as sight, hearing, smell, and taste. Some very simple animals may not have a head, but many bilaterally symmetric forms do, regardless of size. Heads develop in animals by an evolutionary trend known as cephalization. In bilaterally symmetrical animals, nervous tissue concentrate at the anterior region, forming structures responsible for information processing. Through biological evolution, sense organs and feeding structures also concentrate into the anterior region; these collectively form the head. Human head The human head is an anatomical unit that consists of the skull, hyoid bone and cervical vertebrae. The skull consists of the brain case which encloses the cranial cavity, and the facial skeleton, which includes the mandible. There are eight bones in the brain case ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokenizing
Tokenization may refer to: * Tokenization (lexical analysis) in language processing * Tokenization in search engine indexing * Tokenization (data security) in the field of data security * Word segmentation * A procedure during the Transformer In electrical engineering, a transformer is a passive component that transfers electrical energy from one electrical circuit to another circuit, or multiple Electrical network, circuits. A varying current in any coil of the transformer produces ... architecture See also * Tokenism of minorities {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |