|
Titanosuchid
Titanosuchidae is an extinct family of dinocephalians. The titanosuchids were carnivorous to omnivorous (herbivorous?) tapinocephalians. As with other tapinocephalians, they had thick skulls probably for head-butting. They had large canine teeth, and their incisors were very strong. They are related to other dinocephalians, such as the Tapinocephalidae - a group that includes ''Moschops''. The most famous titanosuchids are '' Jonkeria'' and ''Titanosuchus ''Titanosuchus ferox'' ("Fierce titan crocodile") is an extinct species of dinocephalian therapsids that lived in the Middle Permian epoch in South Africa. Along with its close relatives, ''Jonkeria'' and ''Moschops'', ''Titanosuchus'' inhabited ...''. References *L. D. Boonstra, "The Fauna of the Tapinocephalus Zone (Beaufort Beds of the Karoo)", Annals of the South African Museum, 56 (1) 1969, pp. 1–73 *Carroll, R. L. Vertebrate paleontology and evolution. -W. H. Freeman and company, New York, 1988 *Edwin H. Colb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeosuchus
''Anteosaurus'' (meaning "Antaeus reptile") is an extinct genus of large carnivorous dinocephalian synapsid. It lived at the end of the Guadalupian (= Middle Permian) during the Capitanian stage, about 265 to 260 million years ago in what is now South Africa. It is mainly known by cranial remains and few postcranial bones. With its skull reaching in length and a body size estimated at more than in length, and in weight, ''Anteosaurus'' was the largest known carnivorous non-mammalian synapsid and the largest terrestrial predator of the Permian period. Occupying the top of the food chain in the Middle Permian, its skull, jaws and teeth show adaptations to capture large prey like the giants titanosuchids and tapinocephalids dinocephalians and large pareiasaurs. As in many other dinocephalians the cranial bones of ''Anteosaurus'' are pachyostosed, but to a lesser extent than in tapinocephalid dinocephalians. In ''Anteosaurus'', pachyostosis mainly occurs in the form of horn-s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
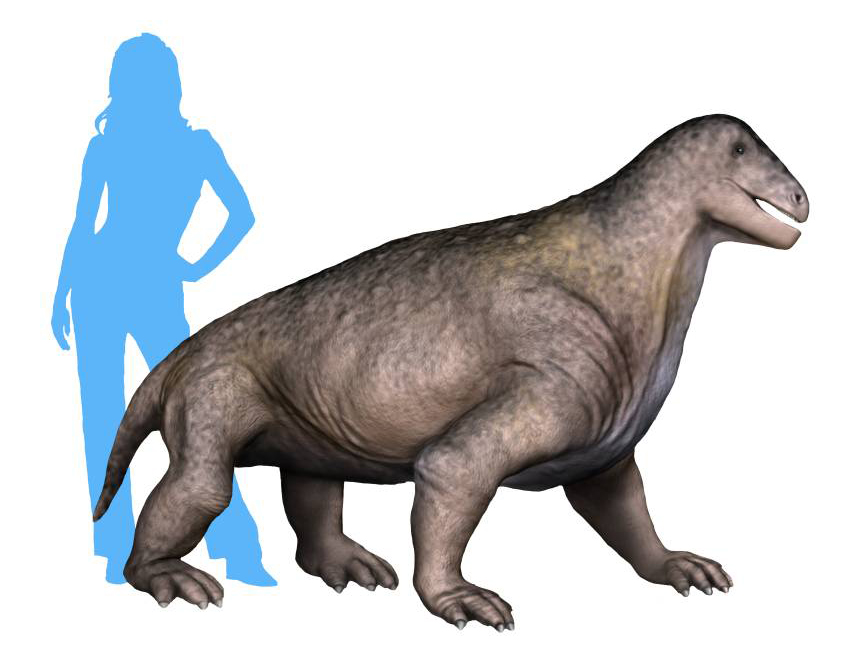
Moschops
''Moschops'' (Greek for "calf face") is an extinct genus of therapsids that lived in the Guadalupian epoch, around 265–260 million years ago. They were heavily built plant eaters, and they may have lived partly in water, as hippopotamuses do. They had short, thick heads and might have competed by head-butting each other. Their elbow joints allowed them to walk with a more mammal-like gait rather than crawling. Their remains were found in the Karoo region of South Africa, belonging to the ''Tapinocephalus'' Assemblage Zone. Therapsids, such as ''Moschops'', are synapsids, the dominant land animals in the Permian period, which ended 252 million years ago. Description ''Moschops'' were heavy set dinocephalian synapsids, measuring in length, and weighing on average and in maximum body mass. They had small heads with broad orbits and heavily-built short necks. Like other members of Tapinocephalidae, the skull had a tiny opening for the pineal organ. The occiput was broa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
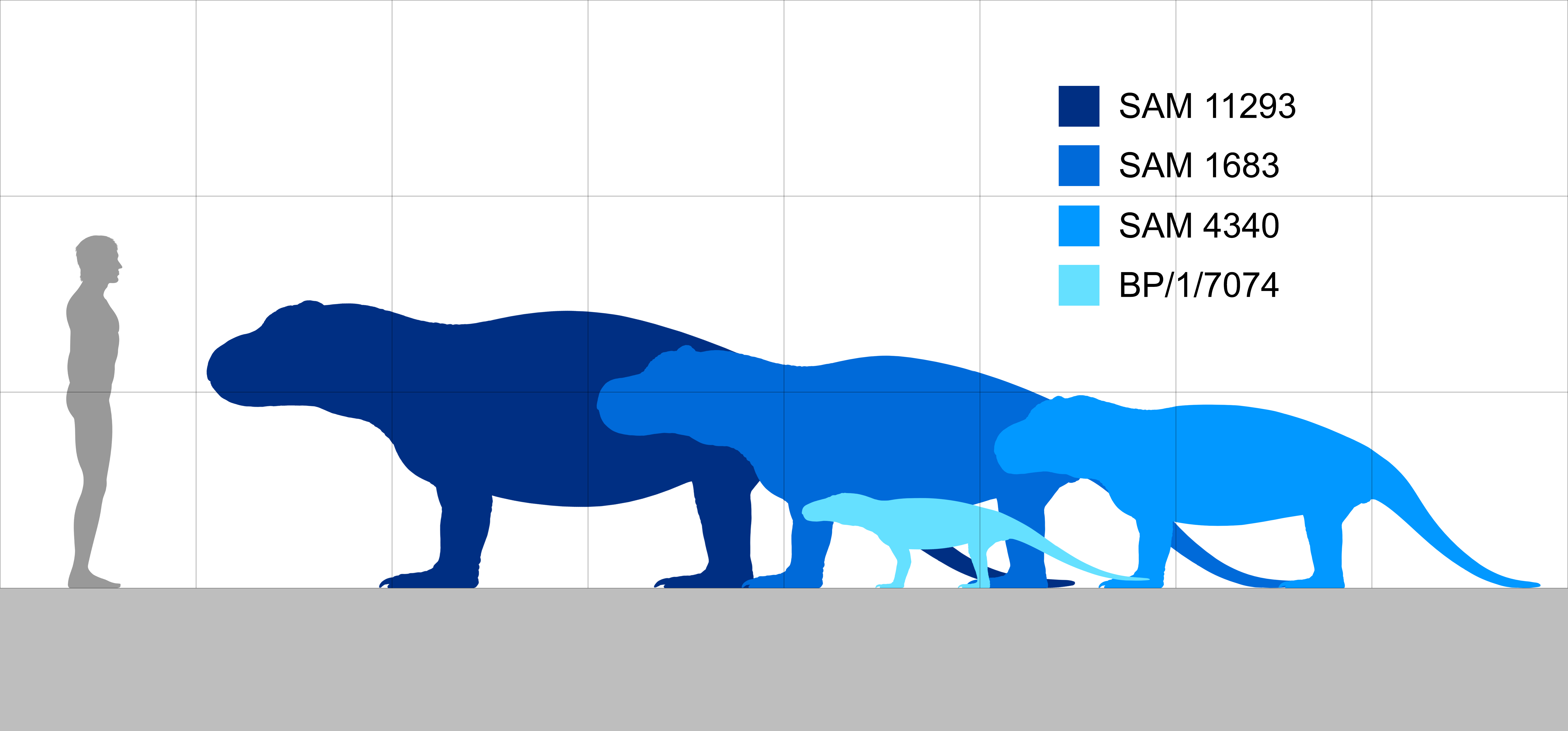
Jonkeria
''Jonkeria'' is an extinct genus of dinocephalians. Species were very large and omnivorous (although there is some dispute to this, e.g. Colbert 1969 p. 136), from the Tapinocephalus Assemblage Zone, Lower Beaufort Group, of the South African Karoo. Description The overall length was or more (up to ), the skull about 55 cm long. The skull is nearly twice as long as wide, and the snout is elongated and provided with sharp incisors and large canines. The cheek teeth were small. The body is robustly built, and the limbs stout. According to Boonstra 1969 p. 38, ''Jonkeria'' cannot be distinguished from its relative ''Titanosuchus'' on cranial grounds, but only in limb length; ''Jonkeria'' having short and squat limbs, and ''Titanosuchus'' long ones. Evidence of femoral osteomyelitis has been described in a fossilised specimen of ''J. parva''. The authors attributed the cause of the pathology, characterised by bony spicules growing perpendicular to nonpathological ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lamiasaurus
''Lamiasaurus'' is an extinct genus of therapsids from the Tapinocephalus Assemblage Zone of the Karoo. It is known from an indeterminate jaw fragment that may be either titanosuchid or anteosaur Anteosaurs are a group of large, primitive carnivorous dinocephalian therapsids with large canines and incisors and short limbs, that are known from the Middle Permian of South Africa, Russia, China, and Brazil. Some grew very large, with skulls ...id.L.D. Boonstra, 1969, "The Fauna of the Tapinocephalus Zone", pg 36 References Tapinocephalians Prehistoric therapsid genera Prehistoric synapsids of Africa Fossil taxa described in 1914 Taxa named by D. M. S. Watson {{paleo-Therapsid-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Permian
The Guadalupian is the second and middle series/ epoch of the Permian. The Guadalupian was preceded by the Cisuralian and followed by the Lopingian. It is named after the Guadalupe Mountains of New Mexico and Texas, and dates between 272.95 ± 0.5 – 259.1 ± 0.4 Mya. The series saw the rise of the therapsids, a minor extinction event called Olson's Extinction and a significant mass extinction called the end-Capitanian extinction event. The Guadalupian was previously known as the Middle Permian. Name and background The Guadalupian is the second and middle series or epoch of the Permian. Previously called Middle Permian, the name of this epoch is part of a revision of Permian stratigraphy for standard global correlation. The name "Guadalupian" was first proposed in the early 1900s, and approved by the International Subcommission on Permian Stratigraphy in 1996. References to the Middle Permian still exist. The Guadalupian was preceded by the Cisuralian and followed by t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carnivorous
A carnivore , or meat-eater (Latin, ''caro'', genitive ''carnis'', meaning meat or "flesh" and ''vorare'' meaning "to devour"), is an animal or plant whose food and energy requirements derive from animal tissues (mainly muscle, fat and other soft tissues) whether through hunting or scavenging. Nomenclature Mammal order The technical term for mammals in the order Carnivora is ''carnivoran'', and they are so-named because most member species in the group have a carnivorous diet, but the similarity of the name of the order and the name of the diet causes confusion. Many but not all carnivorans are meat eaters; a few, such as the large and small cats ( felidae) are ''obligate'' carnivores (see below). Other classes of carnivore are highly variable. The Ursids, for example: While the Arctic polar bear eats meat almost exclusively (more than 90% of its diet is meat), almost all other bear species are omnivorous, and one species, the giant panda, is nearly exclusively herbivo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guadalupian First Appearances
The Guadalupian is the second and middle series/epoch of the Permian. The Guadalupian was preceded by the Cisuralian and followed by the Lopingian. It is named after the Guadalupe Mountains of New Mexico and Texas, and dates between 272.95 ± 0.5 – 259.1 ± 0.4 Mya. The series saw the rise of the therapsids, a minor extinction event called Olson's Extinction and a significant mass extinction called the end-Capitanian extinction event. The Guadalupian was previously known as the Middle Permian. Name and background The Guadalupian is the second and middle series or epoch of the Permian. Previously called Middle Permian, the name of this epoch is part of a revision of Permian stratigraphy for standard global correlation. The name "Guadalupian" was first proposed in the early 1900s, and approved by the International Subcommission on Permian Stratigraphy in 1996. References to the Middle Permian still exist. The Guadalupian was preceded by the Cisuralian and followed by the Lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tapinocephalians
The Tapinocephalia are one of the major groups of dinocephalian therapsids and the major herbivorous group. Tapinocephalia has been found to consist of three clades: Styracocephalidae, Titanosuchidae, and the very successful Tapinocephalidae. Notable tapinocephalians include ''Moschops'', ''Tapinocephalus'', and ''Titanosuchus''. Description Unlike anteosaurs and estemmenosuchids, tapinocephalians are primarily an African group. The estemmenosuchids and pareiasaurs may have occupied this paleo-bovine niche in the north. Only one tapinocephalian, '' Ulemosaurus'', is known from Russia. Earlier tapinocephalians were carnivorous or omnivorous. One such group was Titanosuchidae, which consisted of long-tailed predators that hunted herbivorous therapsids Therapsida is a major group of eupelycosaurian synapsids that includes mammals, their ancestors and relatives. Many of the traits today seen as unique to mammals had their origin within early therapsids, including limbs that we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tapinocephalidae
Tapinocephalidae was an advanced family of tapinocephalians. It is defined as the clade containing '' Ulemosaurus'', ''Tapinocaninus'', and the Tapinocephalinae. They are known from both Russia and South Africa. In all probability, the Tapinocephalidae had a worldwide (Pangean) distribution. They flourished briefly during the Wordian and Capitanian ages, radiating into several lineages, existing simultaneously, and differing mainly in details of the skull and, to an even lesser degree, the skeleton. It is not clear how such similar animals could each find their own ecological niche, but such was obviously the case. There is a parallel here with the hadrosaur and ceratopsian dinosaurs of the Late Cretaceous. The cause of their abrupt extinction is not clear, since other smaller animals, and even the pareiasaurs, were not affected. Quite probably, like the extinction of the late Pleistocene megafauna, a number of factors were involved. Description The body is deep and capacious, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tapinocephalia
The Tapinocephalia are one of the major groups of dinocephalian therapsids and the major herbivorous group. Tapinocephalia has been found to consist of three clades: Styracocephalidae, Titanosuchidae, and the very successful Tapinocephalidae. Notable tapinocephalians include ''Moschops'', '' Tapinocephalus'', and ''Titanosuchus''. Description Unlike anteosaurs and estemmenosuchids, tapinocephalians are primarily an African group. The estemmenosuchids and pareiasaurs may have occupied this paleo-bovine niche in the north. Only one tapinocephalian, '' Ulemosaurus'', is known from Russia. Earlier tapinocephalians were carnivorous or omnivorous. One such group was Titanosuchidae, which consisted of long-tailed predators that hunted herbivorous therapsids Therapsida is a major group of eupelycosaurian synapsids that includes mammals, their ancestors and relatives. Many of the traits today seen as unique to mammals had their origin within early therapsids, including limbs that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herbivorous
A herbivore is an animal anatomically and physiologically adapted to eating plant material, for example foliage or marine algae, for the main component of its diet. As a result of their plant diet, herbivorous animals typically have mouthparts adapted to rasping or grinding. Horses and other herbivores have wide flat teeth that are adapted to grinding grass, tree bark, and other tough plant material. A large percentage of herbivores have mutualistic gut flora that help them digest plant matter, which is more difficult to digest than animal prey. This flora is made up of cellulose-digesting protozoans or bacteria. Etymology Herbivore is the anglicized form of a modern Latin coinage, ''herbivora'', cited in Charles Lyell's 1830 '' Principles of Geology''.J.A. Simpson and E.S.C. Weiner, eds. (2000) ''The Oxford English Dictionary'', vol. 8, p. 155. Richard Owen employed the anglicized term in an 1854 work on fossil teeth and skeletons. ''Herbivora'' is derived from Latin ''herb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Omnivorous
An omnivore () is an animal that has the ability to eat and survive on both plant and animal matter. Obtaining energy and nutrients from plant and animal matter, omnivores digest carbohydrates, protein, fat, and fiber, and metabolize the nutrients and energy of the sources absorbed. Often, they have the ability to incorporate food sources such as algae, fungi, and bacteria into their diet. Omnivores come from diverse backgrounds that often independently evolved sophisticated consumption capabilities. For instance, dogs evolved from primarily carnivorous organisms (Carnivora) while pigs evolved from primarily herbivorous organisms ( Artiodactyla). Despite this, physical characteristics such as tooth morphology may be reliable indicators of diet in mammals, with such morphological adaptation having been observed in bears. The variety of different animals that are classified as omnivores can be placed into further sub-categories depending on their feeding behaviors. Frugivore ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_grazing_-_20050809.jpg)
