|
Tire Model
In vehicle dynamics, a tire model is a type of multibody simulation used to simulate the behavior of tires. In current vehicle simulator models, the tire model is the weakest and most difficult part to simulate.Yukio Nakajima (2019) Advanced Tire Mechanics', ch.11 pp.707-710 Tire models can be classified on their accuracy and complexity, in a spectrum that goes from more simple empirical models to more complex physical models that are theoretically grounded.Monsma, Saskia (2015Feel the Tire - Tire Influence on Driver’s Handling Assessmen phd thesis at Aalto University , pp.19-20 Empirical models include Hans B. Pacejka's ''Magic Formula'', while physically based models include brush models (although they are still quite simplified), and more complex and detailed physical models include RMOD-K, FTire and Hankook. Theoretically-based models can be in turn classified from more approximative to more complex ones, going for example from the solid model, to the rigid ring model, to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magic Formula Curve
Magic or Magick most commonly refers to: * Magic (supernatural), beliefs and actions employed to influence supernatural beings and forces * Ceremonial magic, encompasses a wide variety of rituals of magic * Magical thinking, the belief that unrelated events are causally connected, particularly as a result of supernatural effects * Magic (illusion), the art of appearing to perform supernatural feats Magic(k) may also refer to: Art and entertainment Film and television * ''Magic'' (1917 film), a silent Hungarian drama * ''Magic'' (1978 film), an American horror film * ''Magic'' (soap opera), 2013 Indonesian soap opera * Magic (TV channel), a British music television station Literature * Magic in fiction, the genre of fiction that uses supernatural elements as a theme * ''Magic'' (Chesterton play), 1913 * ''Magic'' (short story collection), 1996 short story collection by Isaac Asimov * ''Magic'' (novel), 1976 novel by William Goldman * ''The Magic Comic'', a 1939–1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slip (vehicle Dynamics)
In (automotive) vehicle dynamics, slip is the relative motion between a tire and the road surface it is moving on. This slip can be generated either by the tire's rotational speed being greater or less than the free-rolling speed (usually described as ''percent'' slip), or by the tire's plane of rotation being at an angle to its direction of motion (referred to as slip angle). In rail vehicle dynamics, this overall slip of the wheel relative to the rail is called ''creepage''. It is distinguished from the local sliding velocity of surface particles of wheel and rail, which is called ''micro-slip''. Longitudinal slip The longitudinal slip is generally given as a percentage of the difference between the surface speed of the wheel compared to the speed between axle and road surface, as: : \text=-\frac where \Omega is the longitudinal component of the rotational speed of the wheel, r is wheel radius at the point of contact and v_x is vehicle speed in the plane of the tire. A positi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dynamical Systems
In mathematics, a dynamical system is a system in which a function describes the time dependence of a point in an ambient space. Examples include the mathematical models that describe the swinging of a clock pendulum, the flow of water in a pipe, the random motion of particles in the air, and the number of fish each springtime in a lake. The most general definition unifies several concepts in mathematics such as ordinary differential equations and ergodic theory by allowing different choices of the space and how time is measured. Time can be measured by integers, by real or complex numbers or can be a more general algebraic object, losing the memory of its physical origin, and the space may be a manifold or simply a set, without the need of a smooth space-time structure defined on it. At any given time, a dynamical system has a state representing a point in an appropriate state space. This state is often given by a tuple of real numbers or by a vector in a geometrical manif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computational Physics
Computational physics is the study and implementation of numerical analysis to solve problems in physics for which a quantitative theory already exists. Historically, computational physics was the first application of modern computers in science, and is now a subset of computational science. It is sometimes regarded as a subdiscipline (or offshoot) of theoretical physics, but others consider it an intermediate branch between theoretical and experimental physics - an area of study which supplements both theory and experiment. Overview In physics, different theories based on mathematical models provide very precise predictions on how systems behave. Unfortunately, it is often the case that solving the mathematical model for a particular system in order to produce a useful prediction is not feasible. This can occur, for instance, when the solution does not have a closed-form expression, or is too complicated. In such cases, numerical approximations are required. Computational phys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vehicle Dynamics
For motorized vehicles, such as automobiles, aircraft, and watercraft, vehicle dynamics is the study of vehicle motion, e.g., how a vehicle's forward movement changes in response to driver inputs, propulsion system outputs, ambient conditions, air/surface/water conditions, etc. Vehicle dynamics is a part of engineering primarily based on classical mechanics. Factors affecting vehicle dynamics The aspects of a vehicle's design which affect the dynamics can be grouped into drivetrain and braking, suspension and steering, distribution of mass, aerodynamics and tires. Drivetrain and braking * Automobile layout (i.e. location of engine and driven wheels) * Powertrain * Braking system Suspension and steering Some attributes relate to the geometry of the suspension, steering and chassis. These include: * Ackermann steering geometry * Axle track * Camber angle * Caster angle * Ride height * Roll center * Scrub radius * Steering ratio * Toe * Wheel alignment * Wheelbase Distribut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simulation Software
Simulation software is based on the process of modeling a real phenomenon with a set of mathematical formulas. It is, essentially, a program that allows the user to observe an operation through simulation without actually performing that operation. Simulation software is used widely to design equipment so that the final product will be as close to design specs as possible without expensive in process modification. Simulation software with real-time response is often used in gaming, but it also has important industrial applications. When the penalty for improper operation is costly, such as airplane pilots, nuclear power plant operators, or chemical plant operators, a mock up of the actual control panel is connected to a real-time simulation of the physical response, giving valuable training experience without fear of a disastrous outcome. Advanced computer programs can simulate power system behavior, weather conditions, electronic circuits, chemical reactions, mechatronics, heat pum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Racing Simulators
Simulated racing or racing simulation, commonly known as simply sim racing, are the collective terms for racing game software that attempts to accurately simulate auto racing, complete with real-world variables such as fuel usage, damage, tire wear and grip, and suspension settings. To be competitive in sim racing, a driver must understand all aspects of car handling that make real-world racing so difficult, such as threshold braking, how to maintain control of a car as the tires lose traction, and how properly to enter and exit a turn without sacrificing speed. It is this level of difficulty that distinguishes sim racing from arcade racing-style driving games where real-world variables are taken out of the equation and the principal objective is to create a sense of speed as opposed to a sense of realism. In general, sim racing applications, such as ''rFactor'', ''Grand Prix Legends'', '' NASCAR Racing'', ''Race 07'', '' F1 Career Challenge'', ''F1 2021'', ''Assetto Corsa'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Driving Simulators
Driving simulators are used for entertainment as well as in training of driver's education courses taught in educational institutions and private businesses. They are also used for research purposes in the area of human factors and medical research, to monitor driver behavior, performance, and attention and in the car industry to design and evaluate new vehicles or new advanced driver assistance systems. Training Driving simulators are being increasingly used for training drivers. Versions exist for cars, trucks, buses, etc. Uses * Novice driver training and testing * Professional driver training and testing * Training in critical driving conditions * Testing the effects of impairment on driver performance * Analysis of the driver behaviours * Analysis of driver responses * Evaluating user performances in different conditions (handling of controls) * Assessing fitness to drive for aging drivers * Testing future in-vehicle technologies on drivers or passengers (Human -Machine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Project Chrono
Project Chrono is a physics engine developed by University of Wisconsin-Madison and University of Parma and members of its open source community. It supports simulating rigid and soft body dynamics, collision detection, vehicle dynamics, fluid-solid interaction, deformable terrain, and granular dynamics, among other physical systems. The latest developments are in the area of sensor simulation, robotics simulation, human-autonomous agent interaction (real-time simulation), and autonomous vehicle simulation, where the emphasis is on off-road scenarios. Parts of the code run on the GPU, multi-core CPUs, and distributed memory architectures via MPI. It is used at tens of universities, in industry, and federal research labs. History Project Chrono was initially developed for use as a multibody simulation tool for robotics and biomechanics applications by Alessandro Tasora while a student at the Polytechnic University of Milan. This became a joint University of Wisconsin-Universi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hans Pacejka
Hans Bastiaan Pacejka (12 September 1934 – 17 September 2017) was an expert in vehicle system dynamics and particularly in tire dynamics, fields in which his works are now standard references. He was Professor emeritus at Delft University of Technology in Delft, Netherlands. Magic Formula tire models Pacejka developed a series of tire design models over the last 20 years. They were named the "Magic Formula" because there is no particular physical basis for the structure of the equations chosen, but they fit a wide variety of tire constructions and operating conditions. Each tire is characterized by 10–20 coefficients for each important force that it can produce at the contact patch, typically lateral and longitudinal force, and self-aligning torque, as a best fit between experimental data and the model. These coefficients are then used to generate equations showing how much force is generated for a given vertical load on the tire, camber angle and slip angle. The Pacejka ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
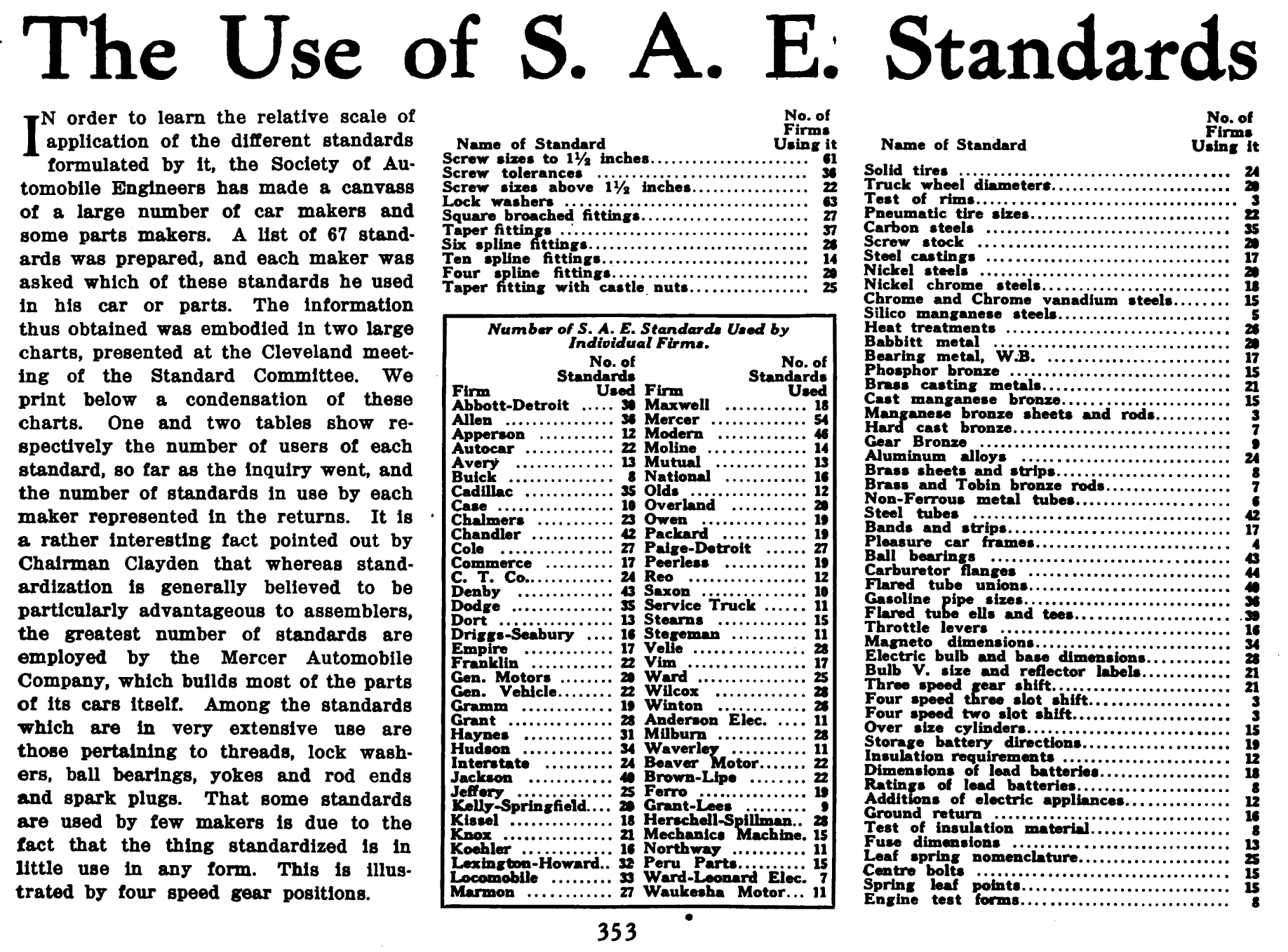
Society Of Automotive Engineers
SAE International, formerly named the Society of Automotive Engineers, is a United States-based, globally active professional association and standards developing organization for engineering professionals in various industries. SAE International's world headquarters is in Warrendale, Pennsylvania, 20 miles north of Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. Principal emphasis is placed on global transport industries such as aerospace, automotive, and commercial vehicles. The organization adopted the name SAE International to reflect the broader emphasis on mobility. SAE International has over 138,000 global members. Membership is granted to individuals, rather than companies. Aside from its standardization efforts, SAE International also devotes resources to projects and programs in STEM education, professional certification, and collegiate design competitions. For historical legacy reasons, the label "SAE" is commonly used on tools and hardware in North America to indicate United States ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |