|
Tibric Acid
Tibric acid is a sulfamylbenzoic acid that acts as a hypolipidemic agent. Although it was found to be more powerful than clofibrate in lowering lipid levels, it was found to cause liver cancer in mice and rats, and so was not introduced as a human drug. In rats it causes an increase in peroxisomes, and liver enlargement, and then liver cancer. However the peroxisome changes do not occur in humans, and it is not likely to cause liver cancer in humans. Synthesis Tibric acid can be made in a multi-step process. Firstly 2-chlorobenzoic acid is reacted with chlorosulfonic acid Chlorosulfuric acid (IUPAC name: sulfurochloridic acid) is the inorganic compound with the formula HSO3Cl. It is also known as chlorosulfonic acid, being the sulfonic acid of chlorine. It is a distillable, colorless liquid which is hygroscopic and ... to add chlorosulfonate group in the 5- position. This reacts with 3,5-dimethylpiperidine to yield tibric acid. References {{Reflist Hypolipidemic agents Sulfon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypolipidemic
Lipid-lowering agents, also sometimes referred to as hypolipidemic agents, cholesterol-lowering drugs, or antihyperlipidemic agents are a diverse group of pharmaceuticals that are used to lower the level of lipids and lipoproteins such as cholesterol, in the blood (hyperlipidemia). The American Heart Association recommends the descriptor 'lipid lowering agent' be used for this class of drugs rather than the term 'hypolipidemic'. Classes The several classes of lipid lowering drugs may differ in both their impact on the cholesterol profile and adverse effects. For example, some may lower low density lipoprotein (LDL) levels more so than others, while others may preferentially increase high density lipoprotein (HDL). Clinically, the choice of an agent depends on the patient's cholesterol profilecardiovascular risk and the liver and kidney functions of the patient, evaluated against the balancing of risks and benefits of the medications. In the United States, this is guided by the ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clofibrate
Clofibrate (trade name Atromid-S) is a lipid-lowering agent used for controlling the high cholesterol and triacylglyceride level in the blood. It belongs to the class of fibrates. It increases lipoprotein lipase activity to promote the conversion of VLDL to LDL, and hence reduce the level of VLDL. It can increase the level of HDL as well. It was patented in 1958 by Imperial Chemical Industries and approved for medical use in 1963. Clofibrate was discontinued in 2002 due to adverse effects. Complications and controversies It can induce SIADH, syndrome of inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone ADH (vasopressin). Clofibrate can also result in formation of cholesterol stones in the gallbladder. The World Health Organization Cooperative Trial on Primary Prevention of Ischaemic Heart Disease using clofibrate to lower serum cholesterol Cholesterol is any of a class of certain organic molecules called lipids. It is a sterol (or modified steroid), a type of lipid. Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peroxisome
A peroxisome () is a membrane-bound organelle, a type of microbody, found in the cytoplasm of virtually all eukaryotic cells. Peroxisomes are oxidative organelles. Frequently, molecular oxygen serves as a co-substrate, from which hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) is then formed. Peroxisomes owe their name to hydrogen peroxide generating and scavenging activities. They perform key roles in lipid metabolism and the conversion of reactive oxygen species. Peroxisomes are involved in the catabolism of very long chain fatty acids, branched chain fatty acids, bile acid intermediates (in the liver), D-amino acids, and polyamines, the reduction of reactive oxygen species – specifically hydrogen peroxide – and the biosynthesis of plasmalogens, i.e., ether phospholipids critical for the normal function of mammalian brains and lungs. They also contain approximately 10% of the total activity of two enzymes (Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase and 6-Phosphogluconate dehydrogenase) in the pentose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2-chlorobenzoic Acid
2-Chlorobenzoic acid is an organic compound with the formula ClC6H4CO2H. It is one of three isomeric chlorobenzoic acids, the one that is the strongest acid. This white solid is used as a precursor to a variety of drugs, food additives, and dyes.Takao Maki, Kazuo Takeda "Benzoic Acid and Derivatives" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2002, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. . Synthesis and reactions It is prepared by the oxidation of 2-chlorotoluene. The laboratory scale reaction employs potassium permanganate Potassium permanganate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula KMnO4. It is a purplish-black crystalline salt, that dissolves in water as K+ and , an intensely pink to purple solution. Potassium permanganate is widely used in the c .... Alternatively it arises by the hydrolysis of α,α,α-trichloro-2-toluene. The chloride is readily replaced by ammonia to 2-aminobenzoic acid. Similarly, the chloride is displaced by diphenylphosphide, leading to 2- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlorosulfonic Acid
Chlorosulfuric acid (IUPAC name: sulfurochloridic acid) is the inorganic compound with the formula HSO3Cl. It is also known as chlorosulfonic acid, being the sulfonic acid of chlorine. It is a distillable, colorless liquid which is hygroscopic and a powerful lachrymator. Commercial samples usually are pale brown or straw colored. Salts and esters of chlorosulfuric acid are known as chlorosulfates. Structure and properties Chlorosulfuric acid is a tetrahedral molecule. The formula is more descriptively written SO2(OH)Cl, but HSO3Cl is traditional. It is an intermediate, chemically and conceptually, between sulfuryl chloride (SO2Cl2) and sulfuric acid (H2SO4). The compound is rarely obtained pure. Upon standing with excess sulfur trioxide, it decomposes to pyrosulfuryl chlorides: :2 ClSO3H + SO3 → H2SO4 + S2O5Cl2 Synthesis The industrial synthesis entails the reaction of hydrogen chloride with a solution of sulfur trioxide in sulfuric acid: :HCl + SO3 → ClSO3H It can als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypolipidemic Agents
Lipid-lowering agents, also sometimes referred to as hypolipidemic agents, cholesterol-lowering drugs, or antihyperlipidemic agents are a diverse group of pharmaceuticals that are used to lower the level of lipids and lipoproteins such as cholesterol, in the blood (hyperlipidemia). The American Heart Association recommends the descriptor 'lipid lowering agent' be used for this class of drugs rather than the term 'hypolipidemic'. Classes The several classes of lipid lowering drugs may differ in both their impact on the cholesterol profile and adverse effects. For example, some may lower low density lipoprotein (LDL) levels more so than others, while others may preferentially increase high density lipoprotein (HDL). Clinically, the choice of an agent depends on the patient's cholesterol profilecardiovascular risk and the liver and kidney functions of the patient, evaluated against the balancing of risks and benefits of the medications. In the United States, this is guided by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
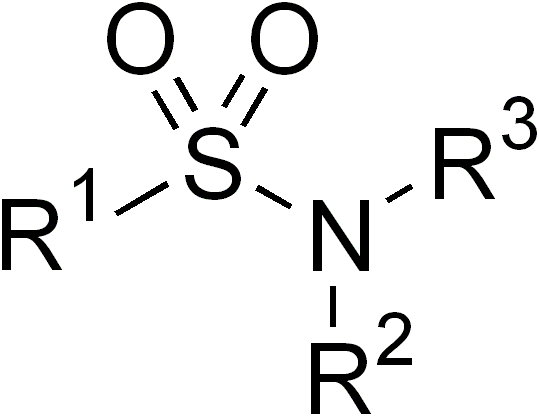
Sulfonamides
In organic chemistry, the sulfonamide functional group (also spelled sulphonamide) is an organosulfur group with the structure . It consists of a sulfonyl group () connected to an amine group (). Relatively speaking this group is unreactive. Because of the rigidity of the functional group, sulfonamides are typically crystalline; for this reason, the formation of a sulfonamide is a classic method to convert an amine into a crystalline derivative which can be identified by its melting point. Many important drugs contain the sulfonamide group. A sulfonamide (compound) is a chemical compound that contains this group. The general formula is or , where each R is some organic group; for example, "methanesulfonamide" (where R = methane, R' = R" = hydrogen) is . Any sulfonamide can be considered as derived from a sulfonic acid by replacing a hydroxyl group () with an amine group. In medicine, the term "sulfonamide" is sometimes used as a synonym for sulfa drug, a derivative or var ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abandoned Drugs
Abandon, abandoned, or abandonment may refer to: Common uses * Abandonment (emotional), a subjective emotional state in which people feel undesired, left behind, insecure, or discarded * Abandonment (legal), a legal term regarding property ** Child abandonment, the extralegal abandonment of children ** Lost, mislaid, and abandoned property, legal status of property after abandonment and rediscovery * Abandonment (mysticism) Art, entertainment, and media Film * ''Abandon'' (film), a 2002 film starring Katie Holmes * ''Abandoned'' (1949 film), starring Dennis O'Keefe * ''Abandoned'' (1955 film), the English language title of the Italian war film ''Gli Sbandati'' * ''Abandoned'' (2001 film), a Hungarian film * ''Abandoned'' (2010 film), starring Brittany Murphy * ''Abandoned'' (2015 film), a television movie about the shipwreck of the ''Rose-Noëlle'' in 1989 * ''Abandoned'' (2022 film), starring Emma Roberts * ''The Abandoned'' (1945 film), a 1945 Mexican film * ''The Aban ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |