|
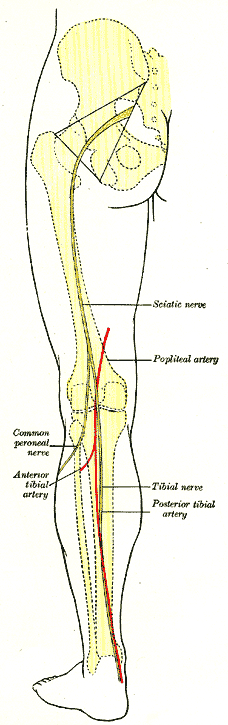
Tibial-fibular Trunk
Tibiofibular trunk (or tibioperoneal trunk) is an arterial trunk representing the direct continuation of the popliteal artery distal to where the anterior tibial artery (the first branch of the popliteal artery) branches off from it. The tibiofibular trunk terminates by bifurcating into two terminal branches: the posterior tibial artery, and the fibular artery In anatomy, the fibular artery, also known as the peroneal artery, supplies blood to the lateral compartment of the leg. It arises from the tibial-fibular trunk. Structure The fibular artery arises from the bifurcation of tibial-fibular trunk .... This is the most common configuration of the origins of these arteries, however, many other anatomical variations exist. The vessel here described as the tibiofibular trunk may alternately be regarded as the initial portion of the posterior tibial artery, with the fibular artery instead regarded as its branch. References External links * http://www.dartmouth.edu/~humananato ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posterior Tibial Artery
The posterior tibial artery of the lower limb is an artery that carries blood to the posterior compartment of the leg and plantar surface of the foot. It branches from the popliteal artery via the tibial-fibular trunk. Structure The posterior tibial artery arises from the popliteal artery in the popliteal fossa. It is accompanied by a deep vein, the posterior tibial vein, along its course. It passes just posterior to the medial malleolus of the tibia, but anterior to the Achilles tendon. It passes into the foot deep to the flexor retinaculum of the foot. It runs through the tarsal tunnel. Branches The posterior tibial artery gives rise to: * medial plantar artery. * lateral plantar artery. * fibular artery, which is said to rise from the bifurcation of the tibial-fibular trunk and the posterior tibial artery. * calcaneal branch to the medial aspect of the calcaneus. Function The posterior tibial artery supplies oxygenated blood to the posterior compartment of the leg and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Popliteal Artery
The popliteal artery is a deeply placed continuation of the femoral artery opening in the distal portion of the adductor magnus muscle. It courses through the popliteal fossa and ends at the lower border of the popliteus muscle, where it branches into the anterior tibial artery, anterior and Posterior tibial artery, posterior tibial arteries. The deepest (most anterior) structure in the fossa, the popliteal artery runs close to the joint capsule of the knee as it spans the Intercondylar fossa of femur, intercondylar fossa. Five genicular branches of the popliteal artery supply the capsule and ligaments of the knee joint. The genicular arteries are the superior lateral, superior medial, middle, inferior lateral, and inferior medial genicular arteries. They participate in the formation of the periarticular genicular anastomosis, a network of vessels surrounding the knee that provides collateral circulation capable of maintaining blood supply to the leg during full knee flexion, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anterior Tibial Artery
The anterior tibial artery is an artery of the leg. It carries blood to the anterior compartment of the leg and dorsum (biology), dorsal surface of the foot, from the popliteal artery. Structure Course The anterior tibial artery is a branch of the popliteal artery. It originates at the distal end of the popliteus muscle posterior to the tibia. The artery typically passes anterior to the popliteus muscle prior to passing between the tibia and fibula through an oval opening at the superior aspect of the interosseus membrane. The artery then descends between the tibialis anterior and extensor digitorum longus muscles. It is accompanied by the anterior tibial vein, and the deep peroneal nerve, along its course. It crosses the anterior aspect of the ankle joint, at which point it becomes the dorsalis pedis artery. Branches The branches of the anterior tibial artery are: *posterior tibial recurrent artery *anterior tibial recurrent artery *muscular branches *anterior medial malleo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibular Artery
In anatomy, the fibular artery, also known as the peroneal artery, supplies blood to the lateral compartment of the leg. It arises from the tibial-fibular trunk. Structure The fibular artery arises from the bifurcation of tibial-fibular trunk into the fibular and posterior tibial arteries in the upper part of the leg proper, just below the knee. It runs towards the foot in the deep posterior compartment of the leg, just medial to the fibula. It supplies a perforating branch to both the lateral and anterior compartments of the leg; it also provides a nutrient artery to the fibula. Some sources claim that the fibular artery arises directly from the posterior tibial artery, but vascular and plastic surgeons note the clinical significance of the tibial-fibular trunk. The fibular artery is accompanied by small veins (venae comitantes) known as fibular veins. Branches Communication branch to posterior tibial artery. Perforating branch to anterior lateral malleolar artery. A calcan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arteries
An artery (plural arteries) () is a blood vessel in humans and most animals that takes blood away from the heart to one or more parts of the body (tissues, lungs, brain etc.). Most arteries carry oxygenated blood; the two exceptions are the pulmonary and the umbilical arteries, which carry deoxygenated blood to the organs that oxygenate it (lungs and placenta, respectively). The effective arterial blood volume is that extracellular fluid which fills the arterial system. The arteries are part of the circulatory system, that is responsible for the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to all cells, as well as the removal of carbon dioxide and waste products, the maintenance of optimum blood pH, and the circulation of proteins and cells of the immune system. Arteries contrast with veins, which carry blood back towards the heart. Structure The anatomy of arteries can be separated into gross anatomy, at the macroscopic level, and microanatomy, which must be studied with a microscop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |