|
Thyroid Dyshormonogenesis
Thyroid dyshormonogenesis is a rare condition due to genetic defects in the synthesis of thyroid hormones. It is due to either deficiency of thyroid enzymes, inability to concentrate, or ineffective binding. Signs and symptoms Patients develop hypothyroidism with a goiter. Cause This is due to inability to produce thyroid hormones due to congenital absence of peroxidase or dehalogenase enzymes Diagnosis Types One particular familial form is associated with sensorineural deafness ( Pendred's syndrome). OMIM Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM) is a continuously updated catalog of human genes and genetic disorders and traits, with a particular focus on the gene-phenotype relationship. , approximately 9,000 of the over 25,000 entries in OMIM ... includes the following: Treatment These patients respond well to levothyroxine (synthetic T4) and the goiter may decrease in size if any. They may not require surgery at any time. References External links Thyroid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyroid Hormones
File:Thyroid_system.svg, upright=1.5, The thyroid system of the thyroid hormones T3 and T4 rect 376 268 820 433 Thyroid-stimulating hormone rect 411 200 849 266 Thyrotropin-releasing hormone rect 297 168 502 200 Hypothalamus rect 66 216 386 256 Anterior pituitary gland rect 66 332 342 374 Negative feedback rect 308 436 510 475 Thyroid gland rect 256 539 563 635 Thyroid hormones rect 357 827 569 856 Catecholamine rect 399 716 591 750 Metabolism desc bottom-left Thyroid hormones are any hormones produced and released by the thyroid gland, namely triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4). They are tyrosine-based hormones that are primarily responsible for regulation of metabolism. T3 and T4 are partially composed of iodine. A deficiency of iodine leads to decreased production of T3 and T4, enlarges the thyroid tissue and will cause the disease known as simple goitre. The major form of thyroid hormone in the blood is thyroxine (T4), whose half-life of around one week is longer th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
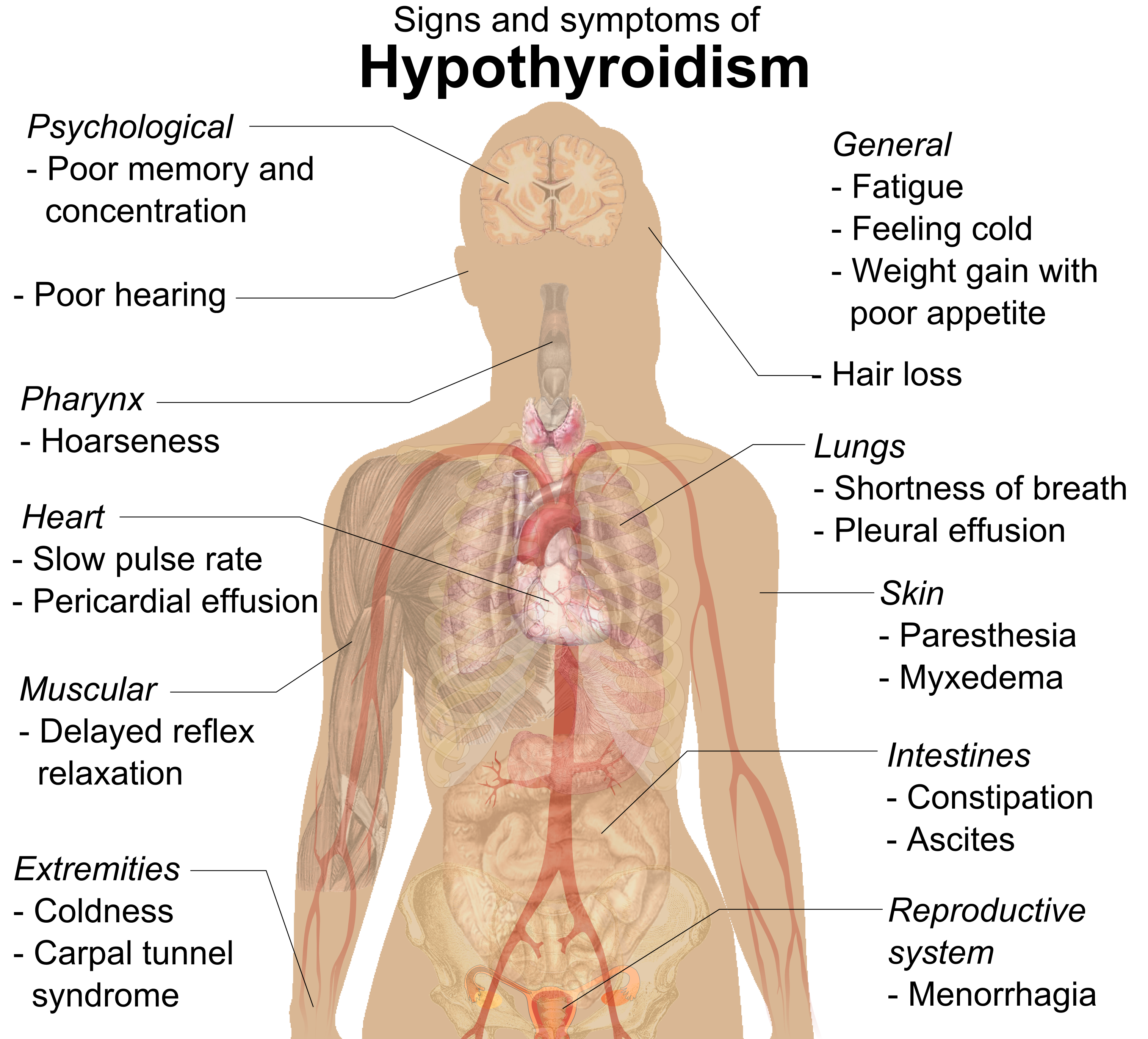
Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism (also called ''underactive thyroid'', ''low thyroid'' or ''hypothyreosis'') is a disorder of the endocrine system in which the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormone. It can cause a number of symptoms, such as poor ability to tolerate cold, a feeling of tiredness, constipation, slow heart rate, depression, and weight gain. Occasionally there may be swelling of the front part of the neck due to goiter. Untreated cases of hypothyroidism during pregnancy can lead to delays in growth and intellectual development in the baby or congenital iodine deficiency syndrome. Worldwide, too little iodine in the diet is the most common cause of hypothyroidism. Hashimoto's thyroiditis is the most common cause of hypothyroidism in countries with sufficient dietary iodine. Less common causes include previous treatment with radioactive iodine, injury to the hypothalamus or the anterior pituitary gland, certain medications, a lack of a functioning thyroid at bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sensorineural Deafness
Sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL) is a type of hearing loss in which the root cause lies in the inner ear or sensory organ (cochlea and associated structures) or the vestibulocochlear nerve (cranial nerve VIII). SNHL accounts for about 90% of reported hearing loss . SNHL is usually permanent and can be mild, moderate, severe, profound, or total. Various other descriptors can be used depending on the shape of the audiogram, such as high frequency, low frequency, U-shaped, notched, peaked, or flat. ''Sensory'' hearing loss often occurs as a consequence of damaged or deficient cochlear hair cells. Hair cells may be abnormal at birth or damaged during the lifetime of an individual. There are both external causes of damage, including infection, and ototoxic drugs, as well as intrinsic causes, including genetic mutations. A common cause or exacerbating factor in SNHL is prolonged exposure to environmental noise, or noise-induced hearing loss. Exposure to a single very loud noise such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pendred's Syndrome
Pendred syndrome is a genetic disorder leading to congenital bilateral (both sides) sensorineural hearing loss and goitre with euthyroid or mild hypothyroidism (decreased thyroid, thyroid gland function). There is no specific treatment, other than supportive measures for the hearing loss and thyroid hormone supplementation in case of hypothyroidism. It is named after Vaughan Pendred (1869–1946), the British people, British doctor who first described the condition in an Ireland, Irish family living in Durham, England, Durham in 1896. It accounts for 7.5% to 15% of all cases of congenital deafness. Signs and symptoms The hearing loss of Pendred syndrome is often, although not always, present from birth, and language acquisition may be a significant problem if deafness is severe in childhood. The hearing loss typically worsens over the years, and progression can be step-wise and related to minor head trauma. In some cases, language development worsens after head injury, demonstrating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OMIM
Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM) is a continuously updated catalog of human genes and genetic disorders and traits, with a particular focus on the gene-phenotype relationship. , approximately 9,000 of the over 25,000 entries in OMIM represented phenotypes; the rest represented genes, many of which were related to known phenotypes. Versions and history OMIM is the online continuation of Dr. Victor A. McKusick's ''Mendelian Inheritance in Man'' (MIM), which was published in 12 editions between 1966 and 1998.McKusick, V. A. ''Mendelian Inheritance in Man. Catalogs of Autosomal Dominant, Autosomal Recessive and X-Linked Phenotypes.'' Baltimore, MD: Johns Hopkins University Press, 1st ed, 1996; 2nd ed, 1969; 3rd ed, 1971; 4th ed, 1975; 5th ed, 1978; 6th ed, 1983; 7th ed, 1986; 8th ed, 1988; 9th ed, 1990; 10th ed, 1992. Nearly all of the 1,486 entries in the first edition of MIM discussed phenotypes. MIM/OMIM is produced and curated at the Johns Hopkins School of Medicine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
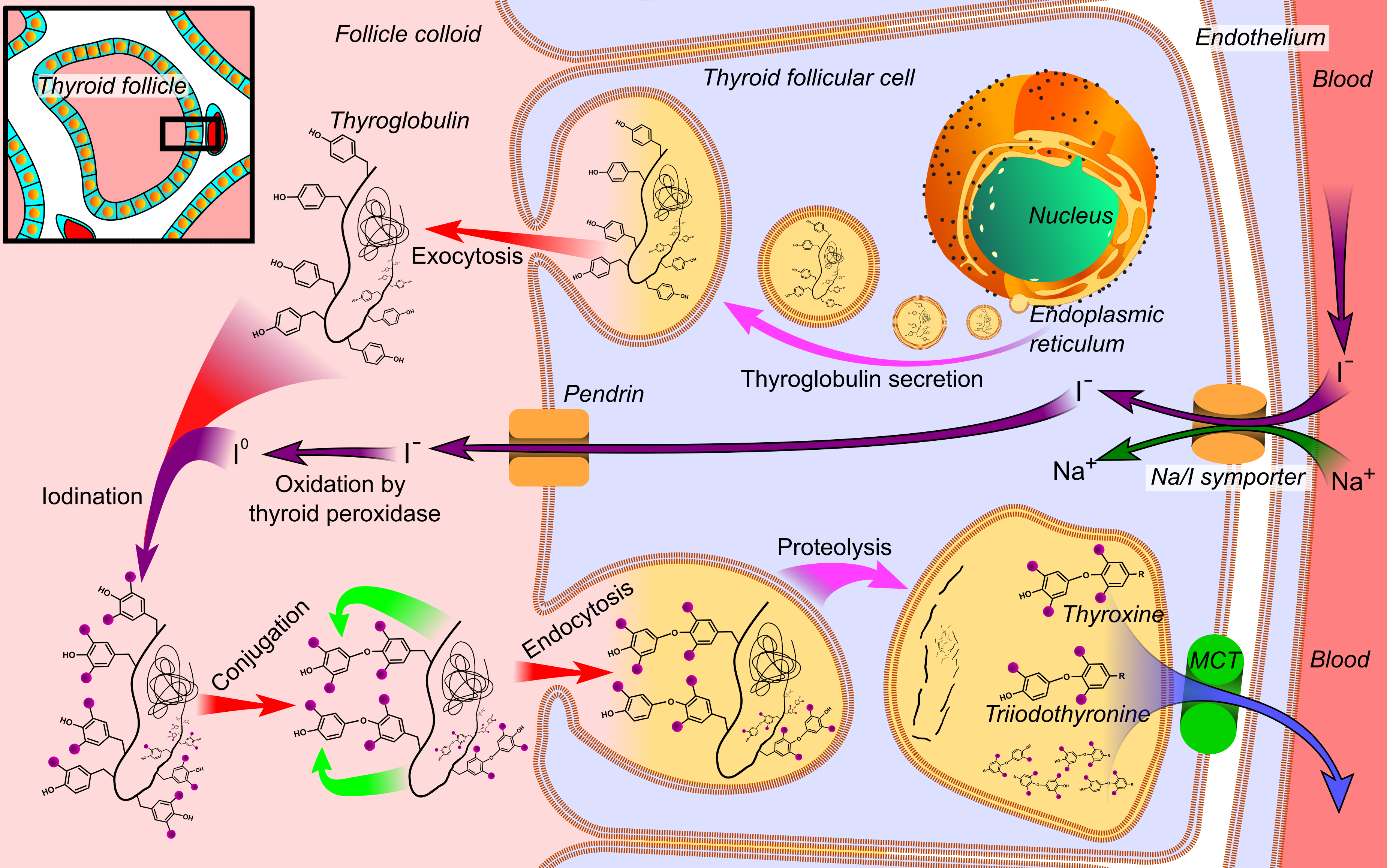
SLC5A5
The sodium/iodide cotransporter, also known as the sodium/iodide symporter (NIS), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SLC5A5'' gene. It is a transmembrane glycoprotein with a molecular weight of 87 k Da and 13 transmembrane domains, which transports two sodium cations (Na+) for each iodide anion (I−) into the cell. NIS mediated uptake of iodide into follicular cells of the thyroid gland is the first step in the synthesis of thyroid hormone. Iodine uptake Iodine uptake mediated by thyroid follicular cells from the blood plasma is the first step for the synthesis of thyroid hormones. This ingested iodine is bound to serum proteins, especially to albumins. The rest of the iodine which remains unlinked and free in bloodstream, is removed from the body through urine (the kidney is essential in the removal of iodine from extracellular space). Iodine uptake is a result of an active transport mechanism mediated by the NIS protein, which is found in the basolateral memb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyroid Peroxidase
Thyroid peroxidase, also called thyroperoxidase (TPO) or iodide peroxidase, is an enzyme expressed mainly in the thyroid where it is secreted into colloid. Thyroid peroxidase oxidizes iodide ions to form iodine atoms for addition onto tyrosine residues on thyroglobulin for the production of thyroxine (T4) or triiodothyronine (T3), the thyroid hormones. In humans, thyroperoxidase is encoded by the ''TPO'' gene. Catalyzed reaction + I− + H+ + H2O2 ⇒ + 2 H2O Iodide is oxidized to iodine radical which immediately reacts with tyrosine. + I− + H+ + H2O2 ⇒ + 2 H2O The second iodine atom is added in similar manner to the reaction intermediate 3-iodotyrosine. Function Inorganic iodine enters the body primarily as iodide, I−. After entering the thyroid follicle (or thyroid follicular cell) via a Na+/I− symporter (NIS) on the basolateral side, iodide is shuttled across the apical membrane into the colloid via pendrin, after which thyroid peroxidase oxidizes iodide t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SLC26A4
Pendrin is an anion exchange protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SLC26A4'' gene (solute carrier family 26, member 4). Pendrin was initially identified as a sodium-independent chloride-iodide exchanger with subsequent studies showing that it also accepts formate and bicarbonate as substrates. Pendrin is similar to the Band 3 transport protein found in red blood cells. Pendrin is the protein which is mutated in Pendred syndrome, which is an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by sensorineural hearing loss, goiter and a partial organification problem detectable by a positive perchlorate test. Pendrin is responsible for mediating the electroneutral exchange of chloride (Cl−) for bicarbonate (HCO3−) across a plasma membrane in the chloride cells of freshwater fish. By phylogenetic analysis, pendrin has been found to be a close relative of prestin present on the hair cells or organ of corti in the inner ear. Prestin is primarily an electromechanical transducer but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyroglobulin
Thyroglobulin (Tg) is a 660 kDa, dimeric glycoprotein produced by the follicular cells of the thyroid and used entirely within the thyroid gland. Tg is secreted and accumulated at hundreds of grams per litre in the extracellular compartment of the thyroid follicles, accounting for approximately half of the protein content of the thyroid gland. Human TG (hTG) is a homodimer of subunits each containing 2768 amino acids as synthesized (a short signal peptide of 19 aminoacids may be removed from the N-terminus in the mature protein). Thyroglobulin is in all vertebrates the main precursor to thyroid hormones, which are produced when thyroglobulin's tyrosine residues are combined with iodine and the protein is subsequently cleaved. Each thyroglobulin molecule contains approximately 100–120 tyrosine residues, but only a small number (20) of these are subject to iodination by thyroperoxidase in the follicular colloid. Therefore, each Tg molecule forms approximately 10 thyroid hormo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iodotyrosine Deiodinase
Iodotyrosine deiodinase, also known as iodotyrosine dehalogenase 1, is a type of deiodinase enzyme that scavenges iodide by removing it from iodinated tyrosine residues in the thyroid gland. These iodinated tyrosines are produced during thyroid hormone biosynthesis. The iodide that is scavenged by iodotyrosine deiodinase is necessary to again synthesize the thyroid hormones. After synthesis, the thyroid hormones circulate through the body to regulate metabolic rate, protein expression, and body temperature. Iodotyrosine deiodinase is thus necessary to keep levels of both iodide and thyroid hormones in balance. Dehalogenation in aerobic organisms is usually done through oxidation and hydrolysis; however, iodotyrosine deiodinase uses reductive dehalogenation. Iodotyrosine deiodinase and iodothyronine deiodinase have been determined as the only two known enzymes to catalyze reductive dehalogenation in mammals. Although these two enzymes perform similar functions, they are structural ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
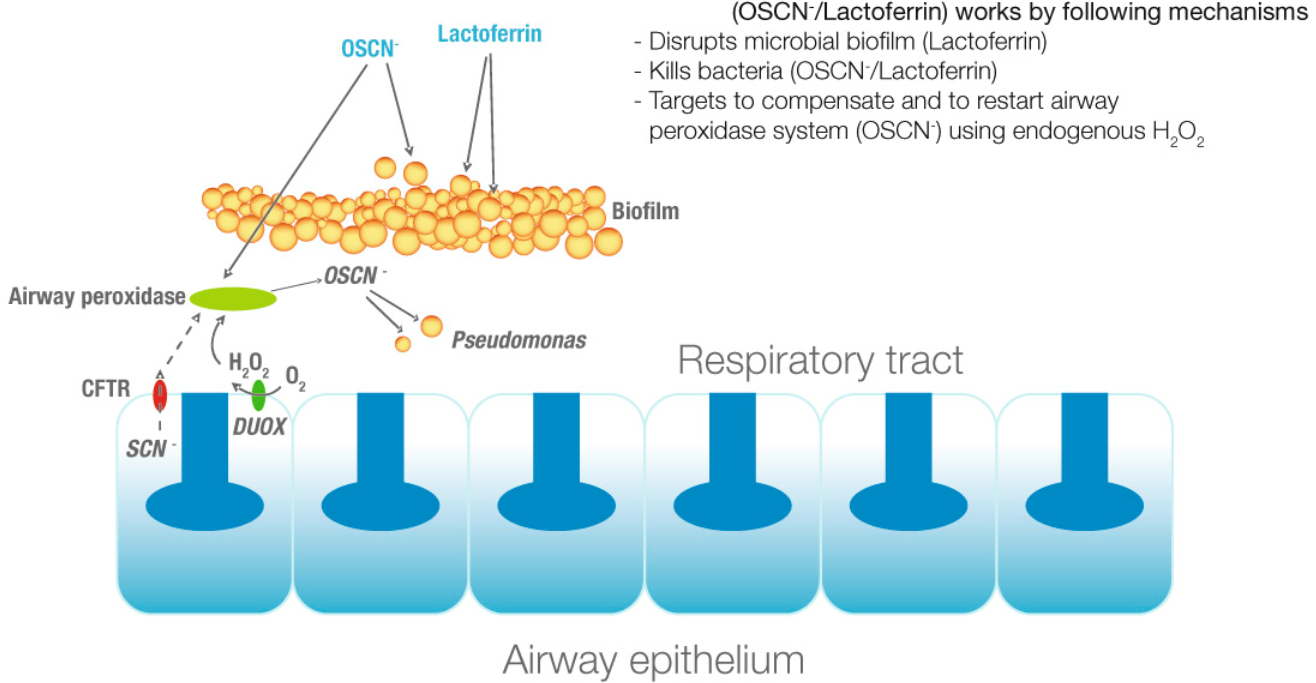
DUOX2
Dual oxidase 2, also known as DUOX2 or ThOX2 (for thyroid oxidase), is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''DUOX2'' gene. Dual oxidase is an enzyme that was first identified in the mammalian thyroid gland. In humans, two isoforms are found; hDUOX1 and hDUOX2 (this enzyme). The protein location is not exclusive to thyroid tissue; hDUOX1 is prominent in airway epithelial cells and hDUOX2 in the salivary glands and gastrointestinal tract. Function Investigations into reactive oxygen species ( ROS) in biological systems have, until recently, focused on characterization of phagocytic cell processes. It is now well accepted that production of such species is not restricted to phagocytic cells and can occur in eukaryotic non-phagocytic cell types via NADPH oxidase (NOX) or dual oxidase (DUOX). This new family of proteins, termed the NOX/DUOX family or NOX family of NADPH oxidases, consists of homologs to the catalytic moiety of phagocytic NADPH-oxidase, gp91phox. Members of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyroid Disease
Thyroid disease is a medical condition that affects the function of the thyroid gland. The thyroid gland is located at the front of the neck and produces thyroid hormones that travel through the blood to help regulate many other organs, meaning that it is an endocrine organ. These hormones normally act in the body to regulate energy use, infant development, and childhood development. There are five general types of thyroid disease, each with their own symptoms. A person may have one or several different types at the same time. The five groups are: # Hypothyroidism (low function) caused by not having enough free thyroid hormones # Hyperthyroidism (high function) caused by having too many free thyroid hormones # Structural abnormalities, most commonly a goiter (enlargement of the thyroid gland) # Tumors which can be benign (not cancerous) or cancerous # Abnormal thyroid function tests without any clinical symptoms (subclinical hypothyroidism or subclinical hyperthyroidism). In som ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |