|
Thyristors
A thyristor () is a solid-state semiconductor device with four layers of alternating P- and N-type materials used for high-power applications. It acts exclusively as a bistable switch (or a latch), conducting when the gate receives a current trigger, and continuing to conduct until the voltage across the device is reversed biased, or until the voltage is removed (by some other means). There are two designs, differing in what triggers the conducting state. In a three-lead thyristor, a small current on its Gate lead controls the larger current of the Anode to Cathode path. In a two-lead thyristor, conduction begins when the potential difference between the Anode and Cathode themselves is sufficiently large (breakdown voltage). Some sources define silicon-controlled rectifier (SCR) and thyristor as synonymous. Other sources define thyristors as more complex devices that incorporate at least four layers of alternating N-type and P-type substrate. The first thyristor devices were r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gate Turn-off Thyristor
A gate turn-off thyristor (GTO) is a special type of thyristor, which is a high-power (.e.g. 1200V AC) semiconductor device. It was invented by General Electric. GTOs, as opposed to normal thyristors, are fully controllable switches which can be turned on and off by their gate lead. Device description Normal thyristors ( silicon-controlled rectifiers) are not fully controllable switches (a "fully controllable switch" can be turned on and off at will). Thyristors can only be turned on using the gate lead, but cannot be turned off using the gate lead. Thyristors are switched on by a gate signal, but even after the gate signal is de-asserted (removed, reverse biased), the thyristor remains in the on state until a turn-off condition occurs (which can be the application of a reverse voltage to the terminals or a decrease of the forward current below a certain threshold value known as the "holding current"). Thus, a thyristor behaves like a normal semiconductor diode after it is t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High-voltage Direct-current
A high-voltage direct current (HVDC) electric power transmission system (also called a power superhighway or an electrical superhighway) uses direct current (DC) for electric power transmission, in contrast with the more common alternating current (AC) transmission systems. Most HVDC links use voltages between 100 kV and 800 kV. However, a 1,100 kV link in China was completed in 2019 over a distance of with a power capacity of 12 GW. With this dimension, intercontinental connections become possible which could help to deal with the fluctuations of wind power and photovoltaics. HVDC allows power transmission between AC transmission systems that are not synchronized. Since the power flow through an HVDC link can be controlled independently of the phase angle between source and load, it can stabilize a network against disturbances due to rapid changes in power. HVDC also allows the transfer of power between grid systems running at different frequencies, such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silicon-controlled Rectifier
A silicon controlled rectifier or semiconductor controlled rectifier is a four-layer solid-state current-controlling device. The name "silicon controlled rectifier" is General Electric's trade name for a type of thyristor. The principle of four-layer p–n–p–n switching was developed by Moll, Tanenbaum, Goldey, and Holonyak of Bell Laboratories in 1956. The practical demonstration of silicon controlled switching and detailed theoretical behavior of a device in agreement with the experimental results was presented by Dr Ian M. Mackintosh of Bell Laboratories in January 1958. The SCR was developed by a team of power engineers led by Gordon Hall and commercialized by Frank W. "Bill" Gutzwiller in 1957. Some sources define silicon-controlled rectifiers and thyristors as synonymous while other sources define silicon-controlled rectifiers as a proper subset of the set of thyristors; the latter being devices with at least four layers of alternating n- and p-type material. Acco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Relaxation Oscillator
In electronics a relaxation oscillator is a nonlinear electronic oscillator circuit that produces a nonsinusoidal repetitive output signal, such as a triangle wave or square wave. on Peter Millet'Tubebookswebsite The circuit consists of a feedback loop containing a switching device such as a transistor, comparator, relay, op amp, or a negative resistance device like a tunnel diode, that repetitively charges a capacitor or inductor through a resistance until it reaches a threshold level, then discharges it again. The period of the oscillator depends on the time constant of the capacitor or inductor circuit. The active device switches abruptly between charging and discharging modes, and thus produces a discontinuously changing repetitive waveform. This contrasts with the other type of electronic oscillator, the harmonic or linear oscillator, which uses an amplifier with feedback to excite resonant oscillations in a resonator, producing a sine wave. Relaxation oscillators ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Charge
Electric charge is the physical property of matter that causes charged matter to experience a force when placed in an electromagnetic field. Electric charge can be ''positive'' or ''negative'' (commonly carried by protons and electrons respectively). Like charges repel each other and unlike charges attract each other. An object with an absence of net charge is referred to as neutral. Early knowledge of how charged substances interact is now called classical electrodynamics, and is still accurate for problems that do not require consideration of quantum effects. Electric charge is a conserved property; the net charge of an isolated system, the amount of positive charge minus the amount of negative charge, cannot change. Electric charge is carried by subatomic particles. In ordinary matter, negative charge is carried by electrons, and positive charge is carried by the protons in the nuclei of atoms. If there are more electrons than protons in a piece of matter, it will have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron
The electron (, or in nuclear reactions) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary electric charge. Electrons belong to the first generation of the lepton particle family, and are generally thought to be elementary particles because they have no known components or substructure. The electron's mass is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton. Quantum mechanical properties of the electron include an intrinsic angular momentum ( spin) of a half-integer value, expressed in units of the reduced Planck constant, . Being fermions, no two electrons can occupy the same quantum state, per the Pauli exclusion principle. Like all elementary particles, electrons exhibit properties of both particles and waves: They can collide with other particles and can be diffracted like light. The wave properties of electrons are easier to observe with experiments than those of other particles like neutrons and protons because electrons have a lower mass and hence a longer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron Hole
In physics, chemistry, and electronic engineering, an electron hole (often simply called a hole) is a quasiparticle which is the lack of an electron at a position where one could exist in an atom or atomic lattice. Since in a normal atom or crystal lattice the negative charge of the electrons is balanced by the positive charge of the atomic nuclei, the absence of an electron leaves a net positive charge at the hole's location. Holes in a metal or semiconductor crystal lattice can move through the lattice as electrons can, and act similarly to positively-charged particles. They play an important role in the operation of semiconductor devices such as transistors, diodes and integrated circuits. If an electron is excited into a higher state it leaves a hole in its old state. This meaning is used in Auger electron spectroscopy (and other x-ray techniques), in computational chemistry, and to explain the low electron-electron scattering-rate in crystals (metals, semiconductor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
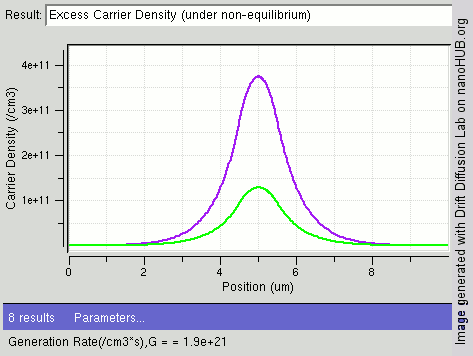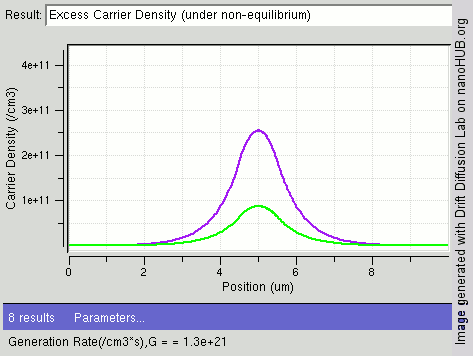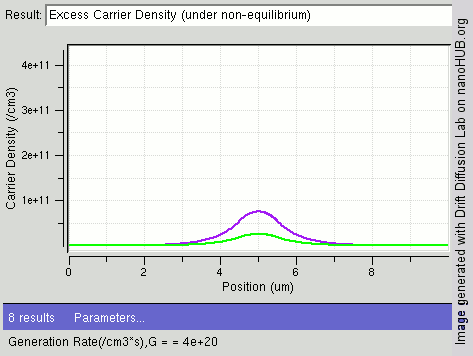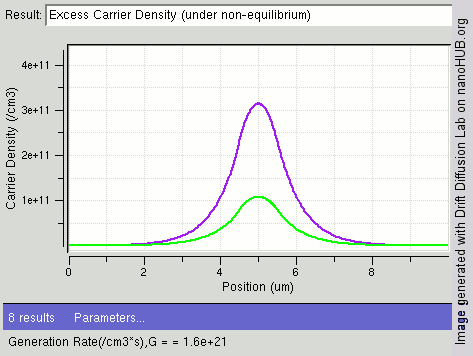
Carrier Generation And Recombination
In the solid-state physics of semiconductors, carrier generation and carrier recombination are processes by which mobile charge carriers (electrons and electron holes) are created and eliminated. Carrier generation and recombination processes are fundamental to the operation of many optoelectronic semiconductor devices, such as photodiodes, light-emitting diodes and laser diodes. They are also critical to a full analysis of p-n junction devices such as bipolar junction transistors and p-n junction diodes. The electron–hole pair is the fundamental unit of generation and recombination in inorganic semiconductors, corresponding to an electron transitioning between the valence band and the conduction band where generation of electron is a transition from the valence band to the conduction band and recombination leads to a reverse transition. Overview Like other solids, semiconductor materials have an electronic band structure determined by the crystal properties of the mate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heavy Metal (chemistry)
upright=1.2, Crystals of lead.html" ;"title="osmium, a heavy metal nearly twice as dense as lead">osmium, a heavy metal nearly twice as dense as lead Heavy metals are generally defined as metals with relatively high density, densities, atomic weights, or atomic numbers. The criteria used, and whether metalloids are included, vary depending on the author and context. In metallurgy, for example, a heavy metal may be defined on the basis of density, whereas in physics the distinguishing criterion might be atomic number, while a chemist would likely be more concerned with chemical property, chemical behaviour. More specific definitions have been published, but none of these have been widely accepted. The definitions surveyed in this article encompass up to 96 out of the 118 known chemical elements; only mercury, lead and bismuth meet all of them. Despite this lack of agreement, the term (plural or singular) is widely used in science. A density of more than 5 g/cm3 is somet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |