|
Thoracic Breathing
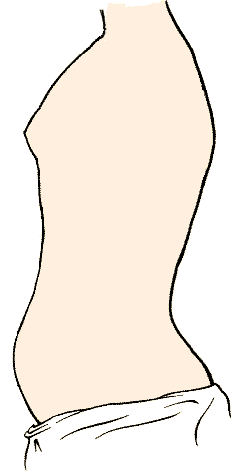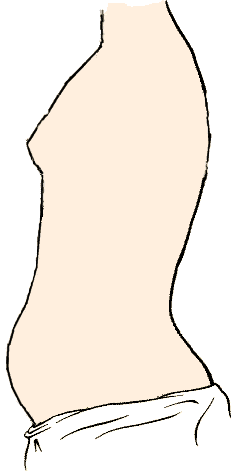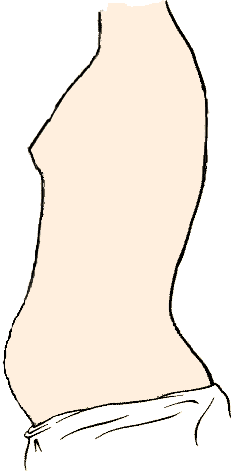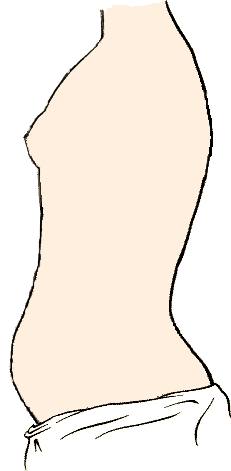
Shallow breathing, thoracic breathing, costal breathing or chest breathing is the drawing of minimal breath into the lungs, usually by drawing air into the chest area using the intercostal muscles rather than throughout the lungs via the diaphragm. Shallow breathing can result in or be symptomatic of rapid breathing and hypoventilation. Most people who breathe shallowly do it throughout the day and they are almost always unaware of the condition. In upper lobar breathing, clavicular breathing, or clavicle breathing, air is drawn predominantly into the chest by the raising of the shoulders and collarbone (clavicles), and simultaneous contracting of the abdomen during inhalation. A maximum amount of air can be drawn this way only for short periods of time, since it requires persistent effort. Conditions Several conditions are marked by, or are symptomatic of, shallow breathing. The more common of these conditions include: various anxiety disorders, asthma, hyperventilation, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shallow Breathing
Shallow breathing, thoracic breathing, costal breathing or chest breathing is the drawing of minimal Breathing, breath into the lungs, usually by drawing air into the Thoracic cavity, chest area using the intercostal muscles rather than throughout the lungs via the diaphragm (anatomy), diaphragm. Shallow breathing can result in or be symptomatic of rapid breathing and hypoventilation. Most people who breathe shallowly do it throughout the day and they are almost always unaware of the condition. In upper lobar breathing, clavicular breathing, or clavicle breathing, air is drawn predominantly into the chest by the raising of the shoulders and collarbone (clavicles), and simultaneous contracting of the abdomen during inhalation. A maximum amount of air can be drawn this way only for short periods of time, since it requires persistent effort. Conditions Several conditions are marked by, or are symptomatic of, shallow breathing. The more common of these conditions include: variou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panic Attack
Panic attacks are sudden periods of intense fear and discomfort that may include palpitations, sweating, chest pain or chest discomfort, shortness of breath, trembling, dizziness, numbness, confusion, or a feeling of impending doom or of losing control. Typically, symptoms reach a peak within ten minutes of onset, and last for roughly 30 minutes, but the duration can vary from seconds to hours. Although they can be extremely frightening and distressing, panic attacks themselves are not physically dangerous. The essential features of panic attacks remain unchanged, although the complicated DSM-IV terminology for describing different types of panic attacks (i.e., situationally bound/cued, situationally predisposed, and unexpected/uncued) is replaced with the terms unexpected and expected panic attacks. Panic attacks function as a marker and prognostic factor for severity of diagnosis, course, and comorbidity across an array of disorders, including but not limited to anxiety disord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brain Damage
Neurotrauma, brain damage or brain injury (BI) is the destruction or degeneration of brain cells. Brain injuries occur due to a wide range of internal and external factors. In general, brain damage refers to significant, undiscriminating trauma-induced damage. A common category with the greatest number of injuries is traumatic brain injury (TBI) following physical trauma or head injury from an outside source, and the term acquired brain injury (ABI) is used in appropriate circles to differentiate brain injuries occurring after birth from injury, from a genetic disorder (GBI), or from a congenital disorder (CBI). Primary and secondary brain injuries identify the processes involved, while focal and diffuse brain injury describe the severity and localization. Recent research has demonstrated that neuroplasticity, which allows the brain to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections throughout life, provides for rearrangement of its workings. This allows the brain to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as well as with other compounds. Oxygen is Earth's most abundant element, and after hydrogen and helium, it is the third-most abundant element in the universe. At standard temperature and pressure, two atoms of the element bind to form dioxygen, a colorless and odorless diatomic gas with the formula . Diatomic oxygen gas currently constitutes 20.95% of the Earth's atmosphere, though this has changed considerably over long periods of time. Oxygen makes up almost half of the Earth's crust in the form of oxides.Atkins, P.; Jones, L.; Laverman, L. (2016).''Chemical Principles'', 7th edition. Freeman. Many major classes of organic molecules in living organisms contain oxygen atoms, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and fats, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxygen Saturation
Oxygen saturation (symbol SO2) is a relative measure of the concentration of oxygen that is dissolved or carried in a given medium as a proportion of the maximal concentration that can be dissolved in that medium at the given temperature. It can be measured with a dissolved oxygen probe such as an oxygen sensor or an optode in liquid media, usually water. The standard unit of oxygen saturation is percent (%). Oxygen saturation can be measured regionally and noninvasively. Arterial oxygen saturation (SaO2) is commonly measured using pulse oximetry. Tissue saturation at peripheral scale can be measured using NIRS. This technique can be applied on both muscle and brain. In medicine In medicine, oxygen saturation refers to ''oxygenation'', or when oxygen molecules () enter the tissues of the body. In this case blood is oxygenated in the lungs, where oxygen molecules travel from the air into the blood. Oxygen saturation (() sats) measures the percentage of hemoglobin binding s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Positive Airway Pressure
Positive airway pressure (PAP) is a mode of respiratory ventilation used in the treatment of sleep apnea. PAP ventilation is also commonly used for those who are critically ill in hospital with respiratory failure, in newborn infants (neonates), and for the prevention and treatment of atelectasis in patients with difficulty taking deep breaths. In these patients, PAP ventilation can prevent the need for tracheal intubation, or allow earlier extubation. Sometimes patients with neuromuscular diseases use this variety of ventilation as well. CPAP is an acronym for "continuous positive airway pressure", which was developed by Dr. George Gregory and colleagues in the neonatal intensive care unit at the University of California, San Francisco. A variation of the PAP system was developed by Professor Colin Sullivan at Royal Prince Alfred Hospital in Sydney, Australia, in 1981. The main difference between BiPAP and CPAP machines is that BiPAP machines have two pressure settings: the pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sleep Disorder
A sleep disorder, or somnipathy, is a medical disorder of an individual's sleep patterns. Some sleep disorders are severe enough to interfere with normal physical, mental, social and emotional functioning. Polysomnography and actigraphy are tests commonly ordered for diagnosing sleep disorders. Sleep disorders are broadly classified into dyssomnias, parasomnias, circadian rhythm sleep disorders involving the timing of sleep, and other disorders including ones caused by medical or psychological conditions. When a person struggles to fall asleep and/or stay asleep with no obvious cause, it is referred to as insomnia, the most common sleep disorder. Others include sleep apnea, narcolepsy and hypersomnia (excessive sleepiness at inappropriate times), sleeping sickness (disruption of sleep cycle due to infection), sleepwalking, and night terrors. Sleep disruptions can be caused by various issues, including teeth grinding ( bruxism) and night terrors. Management of sleep disturbances ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
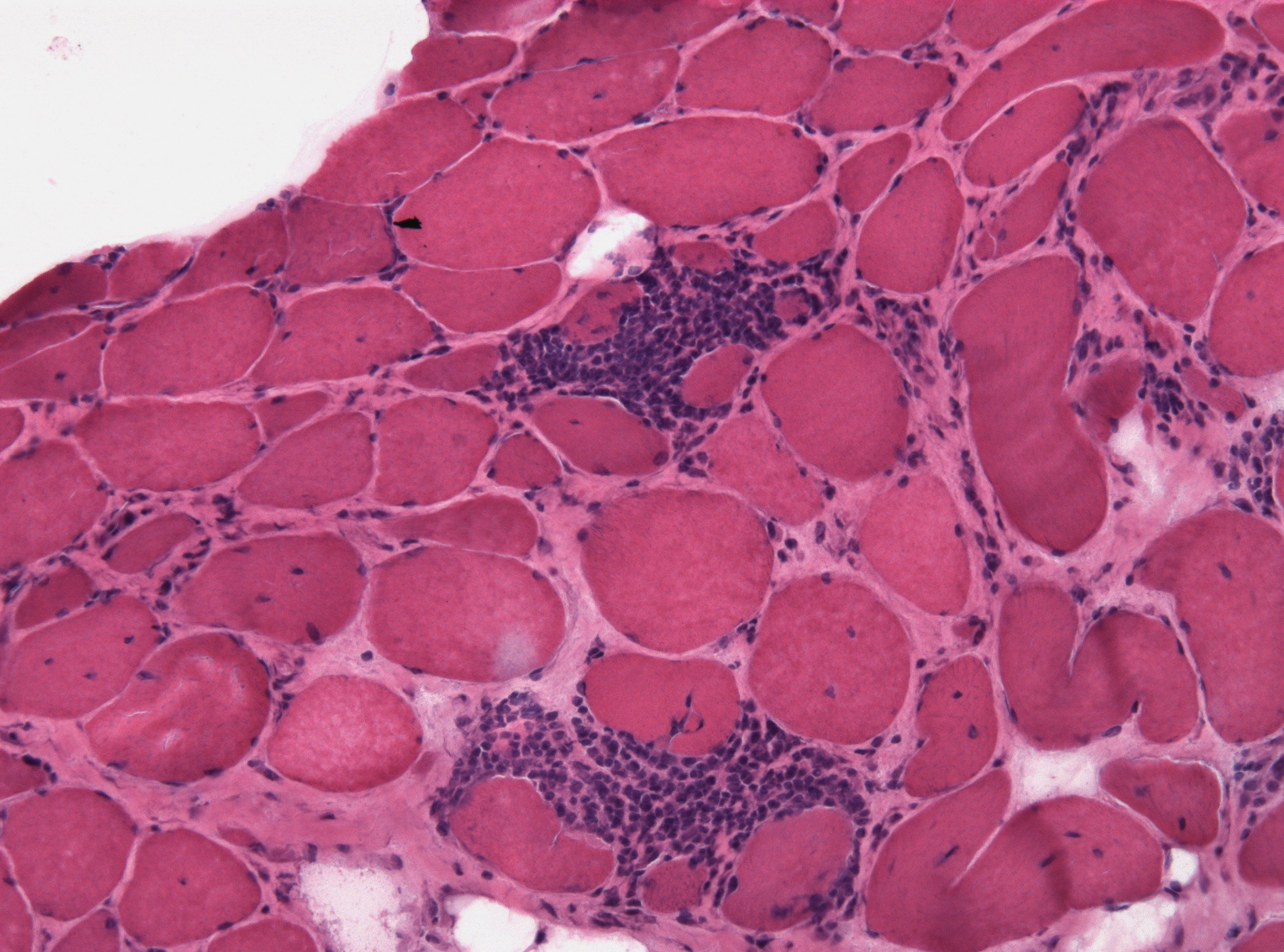
Post-polio Syndrome
Post-polio syndrome (PPS, poliomyelitis sequelae) is a group of latent symptoms of poliomyelitis (polio), occurring at about a 25–40% rate (latest data greater than 80%). These symptoms are caused by the damaging effects of the viral infection on the nervous system. Symptoms typically occur 15 to 30 years after an initial acute paralytic attack. Symptoms include decreasing muscular function or acute weakness with pain and fatigue. The same symptoms may also occur years after a nonparalytic polio (NPP) infection. The precise mechanism that causes PPS is unknown. It shares many features with chronic fatigue syndrome, but unlike that disorder it tends to be progressive and can cause loss of muscle strength. Treatment is primarily limited to adequate rest, conservation of available energy, and supportive measures, such as leg braces and energy-saving devices such as powered wheelchairs, analgesia (pain relief), and sleep aids. Signs and symptoms After a period of prolonged stabi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polio
Poliomyelitis, commonly shortened to polio, is an infectious disease caused by the poliovirus. Approximately 70% of cases are asymptomatic; mild symptoms which can occur include sore throat and fever; in a proportion of cases more severe symptoms develop such as headache, neck stiffness, and paresthesia. These symptoms usually pass within one or two weeks. A less common symptom is permanent paralysis, and possible death in extreme cases.. Years after recovery, post-polio syndrome may occur, with a slow development of muscle weakness similar to that which the person had during the initial infection. Polio occurs naturally only in humans. It is highly infectious, and is spread from person to person either through fecal-oral transmission (e.g. poor hygiene, or by ingestion of food or water contaminated by human feces), or via the oral-oral route. Those who are infected may spread the disease for up to six weeks even if no symptoms are present. The disease may be diagnosed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscular Dystrophy
Muscular dystrophies (MD) are a genetically and clinically heterogeneous group of rare neuromuscular diseases that cause progressive weakness and breakdown of skeletal muscles over time. The disorders differ as to which muscles are primarily affected, the degree of weakness, how fast they worsen, and when symptoms begin. Some types are also associated with problems in other organs. Over 30 different disorders are classified as muscular dystrophies. Of those, Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) accounts for approximately 50% of cases and affects males beginning around the age of four. Other relatively common muscular dystrophies include Becker muscular dystrophy, facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy, and myotonic dystrophy, whereas limb–girdle muscular dystrophy and congenital muscular dystrophy are themselves groups of several – usually ultrarare – genetic disorders. Muscular dystrophies are caused by mutations in genes, usually those involved in making muscle proteins. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lou Gehrig's Disease
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as motor neuron disease (MND) or Lou Gehrig's disease, is a neurodegenerative disease that results in the progressive loss of motor neurons that control voluntary muscles. ALS is the most common type of motor neuron diseases. Early symptoms of ALS include stiff muscles, muscle twitches, and gradual increasing weakness and muscle wasting. ''Limb-onset ALS'' begins with weakness in the arms or legs, while ''bulbar-onset ALS'' begins with difficulty speaking or swallowing. Half of the people with ALS develop at least mild difficulties with thinking and behavior, and about 15% develop frontotemporal dementia. Most people experience pain. The affected muscles are responsible for chewing food, speaking, and walking. Motor neuron loss continues until the ability to eat, speak, move, and finally the ability to breathe is lost. ALS eventually causes paralysis and early death, usually from respiratory failure. Most cases of ALS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuromuscular Disease
A neuromuscular disease is any disease affecting the peripheral nervous system (PNS), the neuromuscular junction, or skeletal muscle, all of which are components of the motor unit. Damage to any of these structures can cause muscle atrophy and weakness. Issues with sensation can also occur. Neuromuscular diseases can be acquired or genetic. Mutations of more than 500 genes have shown to be causes of neuromuscular diseases. Other causes include nerve or muscle degeneration, autoimmunity, toxins, medications, malnutrition, metabolic derangements, hormone imbalances, infection, nerve compression/entrapment, comprised blood supply, and trauma. Signs and symptoms Symptoms of neuromuscular disease may include numbness, paresthesia, muscle weakness, muscle atrophy, myalgia (muscle pain), and fasciculations (muscle twitches). Causes Neuromuscular disease can be caused by autoimmune disorders, genetic/hereditary disorders and some forms of the collagen disorder Ehlers–Dan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |