|
Thin-layer Chromatography
Thin-layer chromatography (TLC) is a chromatography technique used to separate non-volatile mixtures. Thin-layer chromatography is performed on a sheet of an inert substrate such as glass, plastic, or aluminium foil, which is coated with a thin layer of adsorbent material, usually silica gel, aluminium oxide (alumina), or cellulose. This layer of adsorbent is known as the stationary phase. After the sample has been applied on the plate, a solvent or solvent mixture (known as the mobile phase) is drawn up the plate via capillary action. Because different analytes ascend the TLC plate at different rates, separation is achieved. It may be performed on the analytical scale as a means of monitoring the progress of a reaction, or on the preparative scale to purify small amounts of a compound. TLC is an analytical tool widely used because of its simplicity, relative low cost, high sensitivity, and speed of separation. TLC functions on the same principle as all chromatography: a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromatography
In chemical analysis, chromatography is a laboratory technique for the separation of a mixture into its components. The mixture is dissolved in a fluid solvent (gas or liquid) called the ''mobile phase'', which carries it through a system (a column, a capillary tube, a plate, or a sheet) on which a material called the ''stationary phase'' is fixed. Because the different constituents of the mixture tend to have different affinities for the stationary phase and are retained for different lengths of time depending on their interactions with its surface sites, the constituents travel at different apparent velocities in the mobile fluid, causing them to separate. The separation is based on the differential partitioning between the mobile and the stationary phases. Subtle differences in a compound's partition coefficient result in differential retention on the stationary phase and thus affect the separation. Chromatography may be preparative or analytical. The purpose of preparat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
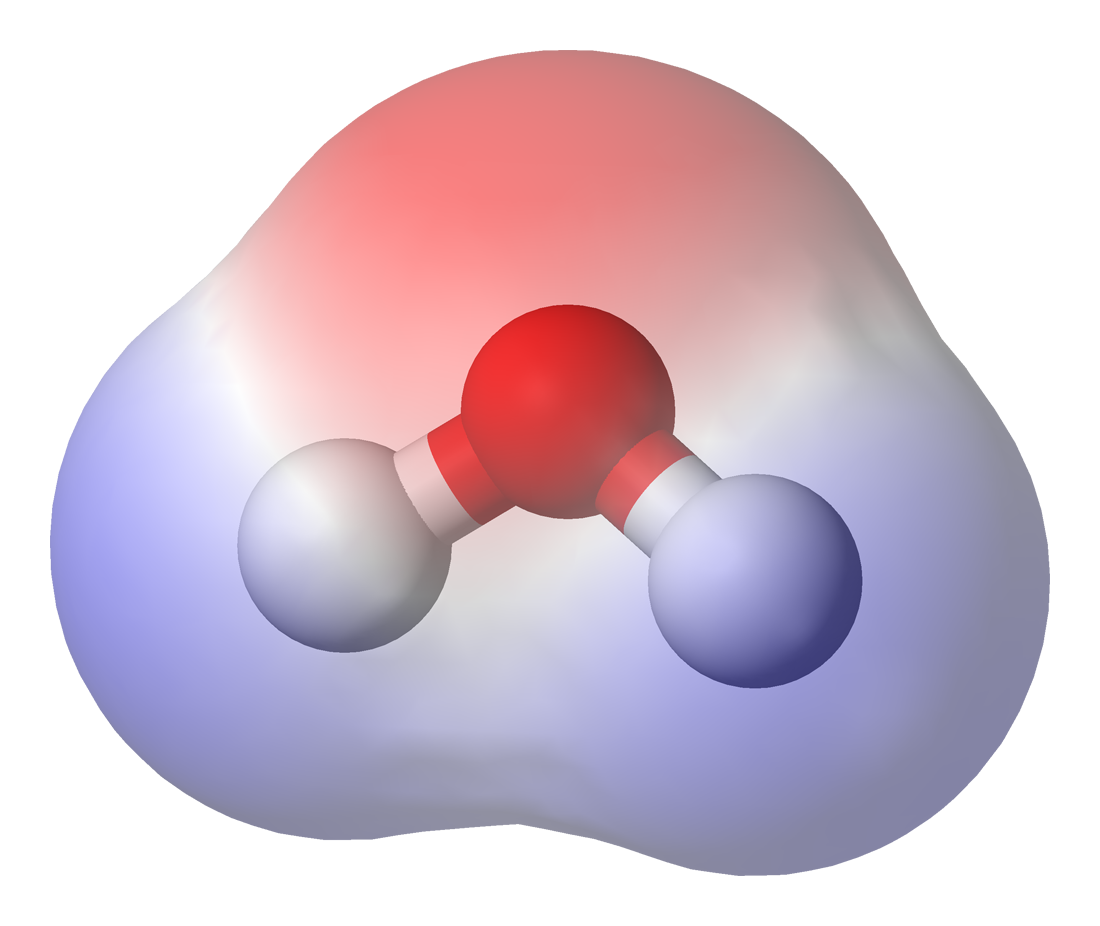
Polarity (chemistry)
In chemistry, polarity is a separation of electric charge leading to a molecule or its chemical groups having an electric dipole moment, with a negatively charged end and a positively charged end. Polar molecules must contain one or more polar bonds due to a difference in electronegativity between the bonded atoms. Molecules containing polar bonds have no molecular polarity if the bond dipoles cancel each other out by symmetry. Polar molecules interact through dipole–dipole intermolecular forces and hydrogen bonds. Polarity underlies a number of physical properties including surface tension, solubility, and melting and boiling points. Polarity of bonds Not all atoms attract electrons with the same force. The amount of "pull" an atom exerts on its electrons is called its electronegativity. Atoms with high electronegativitiessuch as fluorine, oxygen, and nitrogenexert a greater pull on electrons than atoms with lower electronegativities such as alkali metals and alka ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiopharmaceutical
Radiopharmaceuticals, or medicinal radiocompounds, are a group of pharmaceutical drugs containing radioactive isotopes. Radiopharmaceuticals can be used as diagnostic and therapeutic agents. Radiopharmaceuticals emit radiation themselves, which is different from contrast media which absorb or alter external electromagnetism or ultrasound. Radiopharmacology is the branch of pharmacology that specializes in these agents. The main group of these compounds are the radiotracers used to diagnose dysfunction in body tissues. While not all medical isotopes are radioactive, radiopharmaceuticals are the oldest and still most common such drugs. Drug nomenclature As with other pharmaceutical drugs, there is standardization of the drug nomenclature for radiopharmaceuticals, although various standards coexist. The International Nonproprietary Names (INNs), United States Pharmacopeia (USP) names, and IUPAC names for these agents are usually similar other than trivial style differences. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forensic
Forensic science, also known as criminalistics, is the application of science to criminal and civil laws, mainly—on the criminal side—during criminal investigation, as governed by the legal standards of admissible evidence and criminal procedure. Forensic science is a broad field that includes; DNA analysis, fingerprint analysis, blood stain pattern analysis, firearms examination and ballistics, tool mark analysis, serology, toxicology, hair and fiber analysis, entomology, questioned documents, anthropology, odontology, pathology, epidemiology, footwear and tire tread analysis, drug chemistry, paint and glass analysis, digital audio video and photo analysis. Forensic scientists collect, preserve, and analyze scientific evidence during the course of an investigation. While some forensic scientists travel to the scene of the crime to collect the evidence themselves, others occupy a laboratory role, performing analysis on objects brought to them by other individuals. St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insecticide
Insecticides are substances used to kill insects. They include ovicides and larvicides used against insect eggs and larvae, respectively. Insecticides are used in agriculture, medicine, industry and by consumers. Insecticides are claimed to be a major factor behind the increase in the 20th-century's agricultural productivity. Nearly all insecticides have the potential to significantly alter ecosystems; many are toxic to humans and/or animals; some become concentrated as they spread along the food chain. Insecticides can be classified into two major groups: systemic insecticides, which have residual or long term activity; and contact insecticides, which have no residual activity. The mode of action describes how the pesticide kills or inactivates a pest. It provides another way of classifying insecticides. Mode of action can be important in understanding whether an insecticide will be toxic to unrelated species, such as fish, birds and mammals. Insecticides may be repe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pesticide
Pesticides are substances that are meant to control pests. This includes herbicide, insecticide, nematicide, molluscicide, piscicide, avicide, rodenticide, bactericide, insect repellent, animal repellent, microbicide, fungicide, and lampricide. The most common of these are herbicides which account for approximately 80% of all pesticide use. Most pesticides are intended to serve as plant protection products (also known as crop protection products), which in general, protect plants from weeds, fungi, or insects. As an example, the fungus '' Alternaria solani'' is used to combat the aquatic weed '' Salvinia''. In general, a pesticide is a chemical (such as carbamate) or biological agent (such as a virus, bacterium, or fungus) that deters, incapacitates, kills, or otherwise discourages pests. Target pests can include insects, plant pathogens, weeds, molluscs, birds, mammals, fish, nematodes (roundworms), and microbes that destroy property, cause nuisance, or spr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fatty Acid
In chemistry, particularly in biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with an aliphatic chain, which is either saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an unbranched chain of an even number of carbon atoms, from 4 to 28. Fatty acids are a major component of the lipids (up to 70% by weight) in some species such as microalgae but in some other organisms are not found in their standalone form, but instead exist as three main classes of esters: triglycerides, phospholipids, and cholesteryl esters. In any of these forms, fatty acids are both important dietary sources of fuel for animals and important structural components for cells. History The concept of fatty acid (''acide gras'') was introduced in 1813 by Michel Eugène Chevreul, though he initially used some variant terms: ''graisse acide'' and ''acide huileux'' ("acid fat" and "oily acid"). Types of fatty acids Fatty acids are classified in many ways: by length, by saturation vs unsat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceramide
Ceramides are a family of waxy lipid molecules. A ceramide is composed of N-acetyl sphingosine and a fatty acid. Ceramides are found in high concentrations within the cell membrane The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane (PM) or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment (the ... of Eukaryote, eukaryotic cells, since they are component lipids that make up sphingomyelin, one of the major lipids in the lipid bilayer. Contrary to previous assumptions that ceramides and other sphingolipids found in cell membrane were purely supporting structural elements, ceramide can participate in a variety of cellular lipid signaling, signaling: examples include regulating cell differentiation, differentiation, cell proliferation, proliferation, and programmed cell death (PCD) of Cell (biology), cells. The word ''ceramide'' comes from the Latin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retardation Factor
In chromatography, the retardation factor (''R'') is the fraction of an analyte in the mobile phase of a chromatographic system. In planar chromatography in particular, the retardation factor ''R''F is defined as the ratio of the distance traveled by the center of a spot to the distance traveled by the solvent front. Ideally, the values for ''RF'' are equivalent to the R values used in column chromatography. Although the term retention factor is sometimes used synonymously with retardation factor in regard to planar chromatography the term is not defined in this context. However, in column chromatography, the retention factor or capacity factor (''k'') is defined as the ratio of time an analyte is retained in the stationary phase to the time it is retained in the mobile phase, which is inversely proportional to the retardation factor. General definition In chromatography, the retardation factor, ''R'', is the fraction of the sample in the mobile phase at equilibrium, defined as: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfuric Acid
Sulfuric acid ( American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphuric acid ( Commonwealth spelling), known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen and hydrogen, with the molecular formula . It is a colorless, odorless and viscous liquid that is miscible with water. Pure sulfuric acid does not exist naturally on Earth due to its strong affinity to water vapor; it is hygroscopic and readily absorbs water vapor from the air. Concentrated sulfuric acid is highly corrosive towards other materials, from rocks to metals, since it is an oxidant with powerful dehydrating properties. Phosphorus pentoxide is a notable exception in that it is not dehydrated by sulfuric acid, but to the contrary dehydrates sulfuric acid to sulfur trioxide. Upon addition of sulfuric acid to water, a considerable amount of heat is released; thus the reverse procedure of adding water to the acid should not be performed since the heat released ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anisaldehyde
4-Anisaldehyde, or ''p''-Anisaldehyde, is an organic compound with the formula CH3OC6H4CHO. The molecule consists of a benzene ring with an formyl and a methoxy group. It is a colorless liquid with a strong aroma. It provides sweet, floral and strong aniseed odor. Two isomers of 4-anisaldehyde are known, ''ortho''-anisaldehyde and ''meta''-anisaldehyde. They are less commonly encountered. Production Anisaldehyde is prepared commercially by oxidation of 4- methoxytoluene (''p''-cresyl methyl ether) using manganese dioxide to convert a methyl group to the aldehyde group. It can also be produced by oxidation of anethole, a related fragrance that is found in some alcoholic beverages, by oxidative cleavage of an alkene. Uses Being structurally related to vanillin Vanillin is an organic compound with the molecular formula . It is a phenolic aldehyde. Its functional groups include aldehyde, hydroxyl, and ether. It is the primary component of the extract of the vanilla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |