|
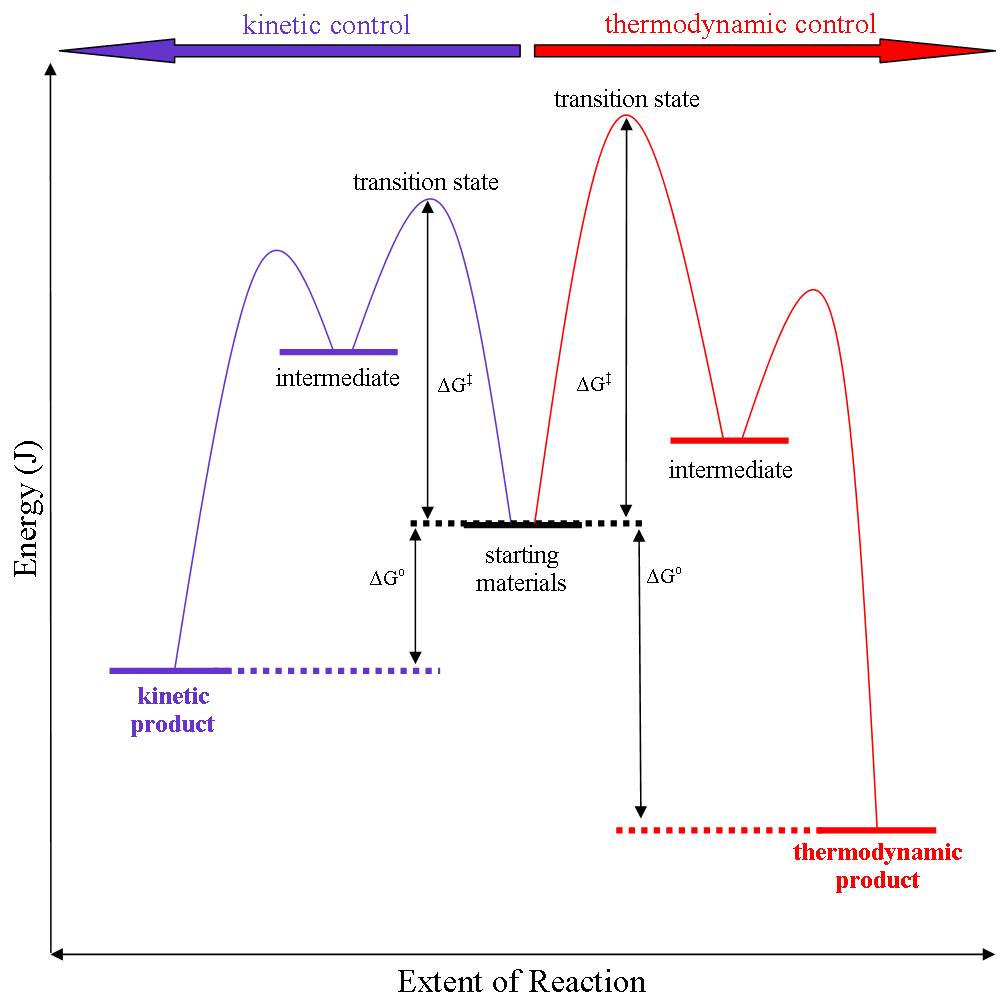
Thermodynamic Control
Thermodynamic reaction control or kinetic reaction control in a chemical reaction can decide the composition in a reaction product mixture when competing pathways lead to different products and the reaction conditions influence the selectivity or stereoselectivity. The distinction is relevant when product A forms faster than product B because the activation energy for product A is lower than that for product B, yet product B is more stable. In such a case A is the kinetic product and is favoured under kinetic control and B is the thermodynamic product and is favoured under thermodynamic control.Introduction to Organic Chemistry I, Seth Robert Elsheimer, Blackwell Publishing, 2000 The conditions of the reaction, such as temperature, pressure, or solvent, affect which reaction pathway may be favored: either the kinetically controlled or the thermodynamically controlled one. Note this is only true if the activation energy of the two pathways differ, with one pathway having a lower '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exo Isomer
In organic chemistry, ''endo''–''exo'' isomerism is a special type of stereoisomerism found in organic compounds with a substituent on a bridged ring system. The prefix ''endo'' is reserved for the isomer with the substituent located closest, or "''syn''", to the longest bridge. The prefix ''exo'' is reserved for the isomer with the substituent located farthest, or "''anti''", to the longest bridge. Here "longest" and "shortest" refer to the number of atoms that comprise the bridge. This type of molecular geometry is found in norbornane systems such as dicyclopentadiene Dicyclopentadiene, abbreviated DCPD, is a chemical compound with formula C10H12. At room temperature, it is a white brittle wax, although lower purity samples can be straw coloured liquids. The pure material smells somewhat of soy wax or camphor .... The terms ''endo'' and ''exo'' are used in a similar sense in discussions of the stereoselectivity in Diels–Alder reactions. References * {{Navbox stereo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protonation
In chemistry, protonation (or hydronation) is the adding of a proton (or hydron, or hydrogen cation), (H+) to an atom, molecule, or ion, forming a conjugate acid. (The complementary process, when a proton is removed from a Brønsted–Lowry acid, is deprotonation.) Some examples include *The protonation of water by sulfuric acid: *:H2SO4 + H2O H3O+ + *The protonation of isobutene in the formation of a carbocation: *:(CH3)2C=CH2 + HBF4 (CH3)3C+ + *The protonation of ammonia in the formation of ammonium chloride from ammonia and hydrogen chloride: *:NH3( g) + HCl( g) → NH4Cl( s) Protonation is a fundamental chemical reaction and is a step in many stoichiometric and catalytic processes. Some ions and molecules can undergo more than one protonation and are labeled polybasic, which is true of many biological macromolecules. Protonation and deprotonation (removal of a proton) occur in most acid–base reactions; they are the core of most acid–base reaction theories. A Brønst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isomerization
In chemistry, isomerization or isomerisation is the process in which a molecule, polyatomic ion or molecular fragment is transformed into an isomer with a different chemical structure. Enolization is an example of isomerization, as is tautomerization. When the isomerization occurs intramolecularly it may be called a rearrangement reaction. When the activation energy for the isomerization reaction is sufficiently small, both isomers will exist in a temperature-dependent equilibrium with each other. Many values of the standard free energy difference, \Delta G^\circ, have been calculated, with good agreement between observed and calculated data. Examples and applications Alkanes Skeletal isomerization occurs in the cracking process, used in the petrochemical industry. As well as reducing the average chain length, straight-chain hydrocarbons are converted to branched isomers in the process, as illustrated the following reaction of ''n''-butane to ''i''-butane. :\overset -> \o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Activation Energy
In chemistry and physics, activation energy is the minimum amount of energy that must be provided for compounds to result in a chemical reaction. The activation energy (''E''a) of a reaction is measured in joules per mole (J/mol), kilojoules per mole (kJ/mol) or kilocalories per mole (kcal/mol). Activation energy can be thought of as the magnitude of the potential barrier (sometimes called the energy barrier) separating minima of the potential energy surface pertaining to the initial and final thermodynamic state. For a chemical reaction to proceed at a reasonable rate, the temperature of the system should be high enough such that there exists an appreciable number of molecules with translational energy equal to or greater than the activation energy. The term "activation energy" was introduced in 1889 by the Swedish scientist Svante Arrhenius. Other uses Although less commonly used, activation energy also applies to nuclear reactions and various other physical phenomena. Te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transition State Theory
In chemistry, transition state theory (TST) explains the reaction rates of elementary chemical reactions. The theory assumes a special type of chemical equilibrium (quasi-equilibrium) between reactants and activated transition state complexes. TST is used primarily to understand qualitatively how chemical reactions take place. TST has been less successful in its original goal of calculating absolute reaction rate constants because the calculation of absolute reaction rates requires precise knowledge of potential energy surfaces, but it has been successful in calculating the standard enthalpy of activation (Δ''H''‡, also written Δ‡''H''ɵ), the standard entropy of activation (Δ''S''‡ or Δ‡''S''ɵ), and the standard Gibbs energy of activation (Δ''G''‡ or Δ‡''G''ɵ) for a particular reaction if its rate constant has been experimentally determined. (The ‡ notation refers to the value of interest ''at the transition state''; Δ''H''‡ is the difference between the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kin Therm Control Diels-alder
__NOTOC__ Kin usually refers to kinship and family. Kin or KIN may also refer to: Culture and religion *Otherkin, people who identify as not entirely human *Kinism, a white supremacist religious movement * Kinh, the majority ethnic group of Vietnam Places * Kin empires and dynasties of China, now romanized as ''Jin'' *Kin, Okinawa, a town in Okinawa, Japan * Kin, Pakistan, a village along the Indus in Pakistan * Kin, Ye, a village in Ye Township, Myanmar * Kin, Mogok, a village in Mogok Township, Myanmar Arts, entertainment, and media Music * ''Kin'' (iamamiwhoami album), 2012 * ''KIN'' (KT Tunstall album), 2016 * ''Kin'' (Pat Metheny album), 2014 * ''Kin'' (Mogwai album), 2018 * ''Kin'' (Xentrix album), 1992 * ''Kin'' (Whitechapel album), 2021 Film * ''Kin'', a 2000 South African-British film by Elaine Proctor * ''Kin'' (film), a 2018 American science fiction film Television * "Kin" (''Justified''), a 2013 episode of the TV series ''Justified'' * ''Kin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemoselectivity
Chemoselectivity is the preferential outcome of a chemical reaction over a set of possible alternative reactions. In another definition, chemoselectivity refers to the selective reactivity of one functional group in the presence of others; often this process in convoluted and protecting groups are on the molecular connectivity alone. Such predictions based on connectivity are generally considered plausible, but the physical outcome of the actual reaction is ultimately dependent on a number of factors that are practically impossible to predict to any useful accuracy (solvent, atomic orbitals, etc.). Chemoselectivity can be difficult to predict, but observing selective outcomes in cases where many reactions are plausible, is common. Examples include the selective organic Redox, reduction of the greater relative chemoselectivity of sodium borohydride Redox, reduction versus lithium aluminium hydride Redox, reduction. In another example, the compound 4-methoxyacetophenone is oxidized ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
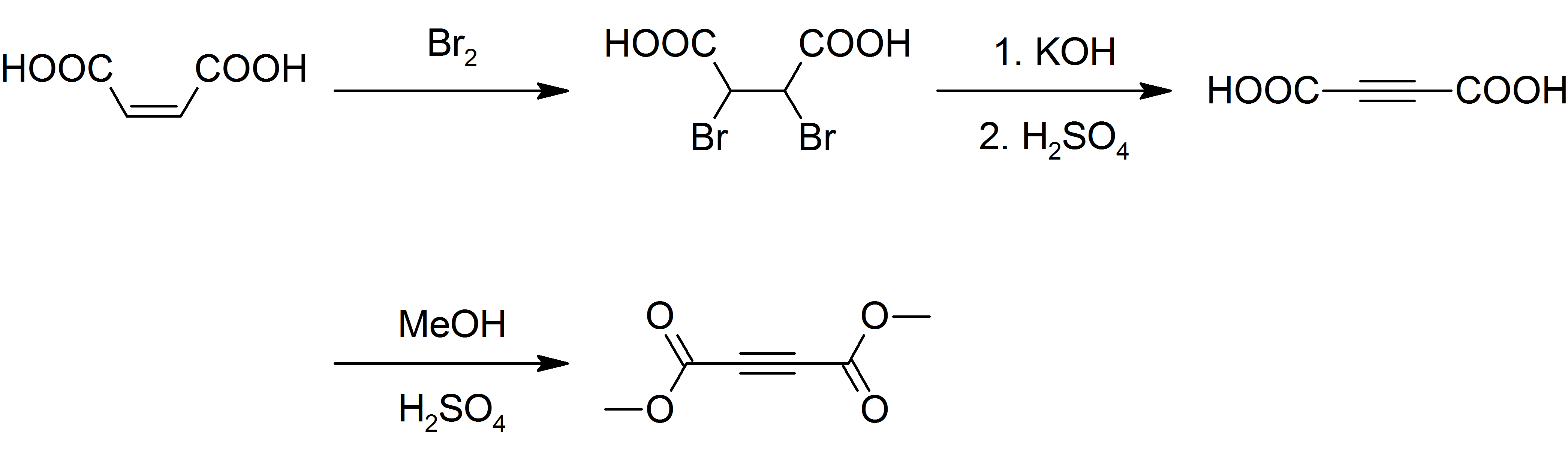
Dimethyl Acetylenedicarboxylate
Dimethyl acetylenedicarboxylate (DMAD) is an organic compound with the formula CH3O2CC2CO2CH3. It is a di-ester in which the ester groups are conjugated with a C-C triple bond. As such, the molecule is highly electrophilic, and is widely employed as a dienophile in cycloaddition reactions, such as the Diels-Alder reaction. It is also a potent Michael acceptor. This compound exists as a colorless liquid at room temperature. This compound was used in the preparation of nedocromil. Preparation Although inexpensively available, DMAD is prepared today as it was originally. Maleic acid is brominated and the resulting dibromosuccinic acid is dehydrohalogenated with potassium hydroxide yielding acetylenedicarboxylic acid. The acid is then esterified with methanol and sulfuric acid as a catalyst: : Safety DMAD is a lachrymator and a vesicant A blister agent (or vesicant), is a chemical compound that causes severe skin, eye and mucosal pain and irritation. They are named for thei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hexafluoro-2-butyne
Hexafluoro-2-butyne (HFB) is a fluorocarbon with the chemical structure CF3C≡CCF3. HFB is a particularly electrophilic acetylene derivative, and hence a potent dienophile for Diels–Alder reactions. HFB is prepared by the action of sulfur tetrafluoride on acetylenedicarboxylic acid or by the reaction of potassium fluoride (KF) with hexachlorobutadiene Hexachlorobutadiene, Cl2C=C(Cl)C(Cl)=CCl2, is a colorless liquid at room temperature that has an odor similar to that of turpentine. It is a chlorinated aliphatic diene with niche applications but is most commonly used as a solvent for other chlo .... References {{Reflist Alkyne derivatives Trifluoromethyl compounds Fluorocarbons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cascade Reaction
A cascade reaction, also known as a domino reaction or tandem reaction, is a chemical process that comprises at least two consecutive reactions such that each subsequent reaction occurs only in virtue of the chemical functionality formed in the previous step.Tietze, L. F.; Beifuss, U. ''Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.'' 1993, ''32'', 131–163. In cascade reactions, isolation of intermediates is not required, as each reaction composing the sequence occurs spontaneously. In the strictest definition of the term, the reaction conditions do not change among the consecutive steps of a cascade and no new reagents are added after the initial step.Padwa, A.; Bur, S. K. ''Tetrahedron'' 2007, ''63'', 5341–5378. By contrast, one-pot procedures similarly allow at least two reactions to be carried out consecutively without any isolation of intermediates, but do not preclude the addition of new reagents or the change of conditions after the first reaction. Thus, any cascade reaction is also a one-pot p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |