|
Therapists
A therapy or medical treatment (often abbreviated tx, Tx, or Tx) is the attempted remediation of a health problem, usually following a medical diagnosis. As a rule, each therapy has indications and contraindications. There are many different types of therapy. Not all therapies are effective. Many therapies can produce unwanted adverse effects. ''Medical treatment'' and ''therapy'' are generally considered synonyms. However, in the context of mental health, the term ''therapy'' may refer specifically to psychotherapy. History Before the creating of therapy as a formal procedure, people told stories to one another to inform and assist about the world. The term "healing through words" was used over 3,500 years ago in Greek and Egyptian writing. The term psychotherapy was invented in the 19th century, and psychoanalysis was founded by Sigmund Freud under a decade later. Semantic field The words ''care'', ''therapy'', ''treatment'', and ''intervention'' overlap in a sem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychotherapy
Psychotherapy (also psychological therapy, talk therapy, or talking therapy) is the use of psychological methods, particularly when based on regular personal interaction, to help a person change behavior, increase happiness, and overcome problems. Psychotherapy aims to improve an individual's well-being and mental health, to resolve or mitigate troublesome behaviors, beliefs, compulsions, thoughts, or emotions, and to improve relationships and social skills. Numerous types of psychotherapy have been designed either for individual adults, families, or children and adolescents. Certain types of psychotherapy are considered evidence-based for treating some diagnosed mental disorders; other types have been criticized as pseudoscience. There are hundreds of psychotherapy techniques, some being minor variations; others are based on very different conceptions of psychology. Most involve one-to-one sessions, between the client and therapist, but some are conducted with groups, incl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
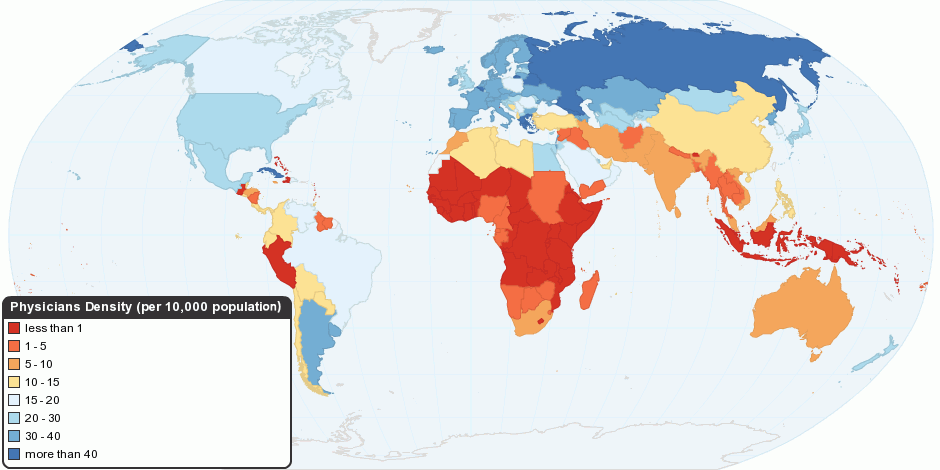
Health Care
Health care or healthcare is the improvement of health via the prevention, diagnosis, treatment, amelioration or cure of disease, illness, injury, and other physical and mental impairments in people. Health care is delivered by health professionals and allied health fields. Medicine, dentistry, pharmacy, midwifery, nursing, optometry, audiology, psychology, occupational therapy, physical therapy, athletic training, and other health professions all constitute health care. It includes work done in providing primary care, secondary care, and tertiary care, as well as in public health. Access to health care may vary across countries, communities, and individuals, influenced by social and economic conditions as well as health policies. Providing health care services means "the timely use of personal health services to achieve the best possible health outcomes". Factors to consider in terms of health care access include financial limitations (such as insurance coverage), geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sigmund Freud
Sigmund Freud ( , ; born Sigismund Schlomo Freud; 6 May 1856 – 23 September 1939) was an Austrian neurologist and the founder of psychoanalysis, a clinical method for evaluating and treating psychopathology, pathologies explained as originating in conflicts in the Psyche (psychology), psyche, through dialogue between a patient and a psychoanalyst. Freud was born to Galician Jews, Galician Jewish parents in the Moravian town of Příbor, Freiberg, in the Austrian Empire. He qualified as a doctor of medicine in 1881 at the University of Vienna. Upon completing his habilitation in 1885, he was appointed a docent in neuropathology and became an affiliated professor in 1902. Freud lived and worked in Vienna, having set up his clinical practice there in 1886. In 1938, Freud left Austria to escape Nazi persecution. He died in exile in the United Kingdom in 1939. In founding psychoanalysis, Freud developed therapeutic techniques such as the use of free association (psychology), free a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mental Health
Mental health encompasses emotional, psychological, and social well-being, influencing cognition, perception, and behavior. It likewise determines how an individual handles stress, interpersonal relationships, and decision-making. Mental health includes subjective well-being, perceived self-efficacy, autonomy, competence, intergenerational dependence, and self-actualization of one's intellectual and emotional potential, among others. From the perspectives of positive psychology or holism, mental health may include an individual's ability to enjoy life and to create a balance between life activities and efforts to achieve psychological resilience. Cultural differences, subjective assessments, and competing professional theories all affect how one defines "mental health". Some early signs related to mental health problems are sleep irritation, lack of energy, lack of appetite and thinking of harming yourself or others. Mental disorders Mental health, as defined by the Public Heal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chronic Kidney Disease
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a type of kidney disease in which a gradual loss of kidney function occurs over a period of months to years. Initially generally no symptoms are seen, but later symptoms may include leg swelling, feeling tired, vomiting, loss of appetite, and confusion. Complications can relate to hormonal dysfunction of the kidneys and include (in chronological order) high blood pressure (often related to activation of the renin–angiotensin system system), bone disease, and anemia. Additionally CKD patients have markedly increased cardiovascular complications with increased risks of death and hospitalization. Causes of chronic kidney disease include diabetes, high blood pressure, glomerulonephritis, and polycystic kidney disease. Risk factors include a family history of chronic kidney disease. Diagnosis is by blood tests to measure the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), and a urine test to measure albumin. Ultrasound or kidney biopsy may be performe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Discrete
Discrete may refer to: *Discrete particle or quantum in physics, for example in quantum theory * Discrete device, an electronic component with just one circuit element, either passive or active, other than an integrated circuit *Discrete group, a group with the discrete topology *Discrete category, category whose only arrows are identity arrows *Discrete mathematics, the study of structures without continuity *Discrete optimization, a branch of optimization in applied mathematics and computer science *Discrete probability distribution, a random variable that can be counted *Discrete space, a simple example of a topological space *Discrete spline interpolation, the discrete analog of ordinary spline interpolation *Discrete time, non-continuous time, which results in discrete-time samples *Discrete variable In mathematics and statistics, a quantitative variable may be continuous or discrete if they are typically obtained by ''measuring'' or '' counting'', respectively. If it can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interventionism (medicine)
Interventionism, when discussing the practice of medicine, is generally a derogatory term used by critics of a medical model in which patients are viewed as passive recipients receiving external treatments provided by the physician that have the effect of prolonging life, or at least of providing a subjective sense of doing everything possible. Interventionism is commonly encouraged by terminally ill patients and their family members when they are emotionally unprepared to acknowledge that the patient is going to die. Most healthcare providers are uncomfortable telling people that further cure-oriented or life-extending treatment is futile medical care, and patients and families are frequently angry with the provider or feel rejected by the provider when they are given accurate, but negative, information about the patient's prospects. In nearly all cases, "something" can be done for the patient, and families often reward and encourage a provider who proposes a string of useless and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coronary Care Unit
A coronary care unit (CCU) or cardiac intensive care unit (CICU) is a hospital ward specialized in the care of patients with heart attacks, unstable angina, cardiac dysrhythmia and (in practice) various other cardiac conditions that require continuous monitoring and treatment. Characteristics The main feature of coronary care is the availability of telemetry or the continuous monitoring of the cardiac rhythm by electrocardiography. This allows early intervention with medication, cardioversion or defibrillation, improving the prognosis. As arrhythmias are relatively common in this group, patients with myocardial infarction or unstable angina are routinely admitted to the coronary care unit. For other indications, such as atrial fibrillation, a specific indication is generally necessary, while for others, such as heart block, coronary care unit admission is standard. Utilization In the United States, cardiac conditions accounted for eight of the eighteen conditions and procedures ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass Noun
In linguistics, a mass noun, uncountable noun, non-count noun, uncount noun, or just uncountable, is a noun with the syntactic property that any quantity of it is treated as an undifferentiated unit, rather than as something with discrete elements. Non-count nouns are distinguished from count nouns. Given that different languages have different grammatical features, the actual test for which nouns are mass nouns may vary between languages. In English, mass nouns are characterized by the impossibility of being directly modified by a numeral without specifying a unit of measurement and by the impossibility of being combined with an indefinite article (''a'' or ''an''). Thus, the mass noun "water" is quantified as "20 litres of water" while the count noun "chair" is quantified as "20 chairs". However, both mass and count nouns can be quantified in relative terms without unit specification (e.g., "so much water", "so many chairs"). Mass nouns have no concept of singular and plural ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Procedure
A medical procedure is a course of action intended to achieve a result in the delivery of healthcare. A medical procedure with the intention of determining, measuring, or diagnosing a patient condition or parameter is also called a medical test. Other common kinds of procedures are therapeutic (i.e., intended to treat, cure, or restore function or structure), such as surgical and physical rehabilitation procedures. Definition *"An activity directed at or performed on an individual with the object of improving health, treating disease or injury, or making a diagnosis."''International Dictionary of Medicine and Biology'', Page 2297. *"The act or conduct of diagnosis, treatment, or operation."''Stedman's Medical Dictionary'', 27th ed. Page 1446. *"A series of steps by which a desired result is accomplished."''Dorland's Illustrated Medical Dictionary'', 28th ed. Page 1353. *"The sequence of steps to be followed in establishing some course of action."''Mosby's Medical, Nursing, & Al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiac Catheterization
Cardiac catheterization (heart cath) is the insertion of a catheter into a chamber or vessel of the heart. This is done both for diagnostic and interventional purposes. A common example of cardiac catheterization is coronary catheterization that involves catheterization of the coronary arteries for coronary artery disease and myocardial infarctions ("heart attacks"). Catheterization is most often performed in special laboratories with fluoroscopy and highly maneuverable tables. These "cath labs" are often equipped with cabinets of catheters, stents, balloons, etc. of various sizes to increase efficiency. Monitors show the fluoroscopy imaging, electrocardiogram (ECG), pressure waves, and more. Uses Coronary angiography is a diagnostic procedure that allows visualization of the coronary vessels. Fluoroscopy is used to visualize the lumens of the arteries as a 2-D projection. Should these arteries show narrowing or blockage, then techniques exist to open these arteries. Percutane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |