|
Tetramethylethylenediamine(dimethyl)nickel(II)
Tetramethylethylenediamine(dimethyl)nickel(II) is the organonickel complex with the formula (Me = CH3). This yellow-brown, air-sensitive compound is popular precursor to diverse organonickel complexes. It is prepared from the tmeda adduct of nickel(II) acetylacetonate by reaction with methyl lithium.{{cite journal , doi=10.1016/0022-328X(88)89050-8, title=Tmeda-Nickel-Komplexe , year=1988 , last1=Kaschube , first1=Wilfried , last2=Pörschke , first2=Klaus R. , last3=Wilke , first3=Günther , journal=Journal of Organometallic Chemistry , volume=355 , issue=1–3 , pages=525–532 The tmeda ligand is easily displaced by bases such as bipyridine and diphosphines. Treatment of the complex with electrophilic alkenes results in elimination of ethylene, giving alkene complexes. References Organonickel compounds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organonickel Complex
Organonickel chemistry is a branch of organometallic chemistry that deals with organic compounds featuring nickel-carbon bonds. They are used as a catalyst, as a building block in organic chemistry and in chemical vapor deposition. Organonickel compounds are also short-lived intermediates in organic reactions. The first organonickel compound was nickel tetracarbonyl Ni(CO)4, reported in 1890 and quickly applied in the Mond process for nickel purification. Organonickel complexes are prominent in numerous industrial processes including carbonylations, hydrocyanation, and the Shell higher olefin process. Classes of compounds : Alkyl and aryl complexes A popular reagent is Ni(CH3)2(tetramethylethylenediamine). Many alkyl and aryl complexes are known with the formula NiR(X)L2. Examples include dppf)Ni(cinnamyl)Cl) ''trans''-(PCy2Ph)2Ni(''o''-tolyl)Cl, (dppf)Ni(''o''-tolyl)Cl, (TMEDA)Ni(''o''-tolyl)Cl, and (TMEDA)NiMe2. Nickel compounds of the type NiR2 also exist with just 12 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tmeda
Tetramethylethylenediamine (TMEDA or TEMED) is a chemical compound with the formula (CH3)2NCH2CH2N(CH3)2. This species is derived from ethylenediamine by replacement of the four amine hydrogens with four methyl groups. It is a colorless liquid, although old samples often appear yellow. Its odor is similar to that of rotting fish. As a reagent in synthesis TMEDA is widely employed as a ligand for metal ions. It forms stable complexes with many metal halides, e.g. zinc chloride and copper(I) iodide, giving complexes that are soluble in organic solvents. In such complexes, TMEDA serves as a bidentate ligand. TMEDA has an affinity for lithium ions. When mixed with ''n''-butyllithium, TMEDA's nitrogen atoms coordinate to the lithium, forming a cluster of higher reactivity than the tetramer or hexamer that ''n''-butyllithium normally adopts. BuLi/TMEDA is able to metallate or even doubly metallate many substrates including benzene, furan, thiophene, ''N''-alkylpyrroles, and ferrocene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methyl
In organic chemistry, a methyl group is an alkyl derived from methane, containing one carbon atom bonded to three hydrogen atoms, having chemical formula . In formulas, the group is often abbreviated as Me. This hydrocarbon group occurs in many organic compounds. It is a very stable group in most molecules. While the methyl group is usually part of a larger molecule, bounded to the rest of the molecule by a single covalent bond (), it can be found on its own in any of three forms: methanide anion (), methylium cation () or methyl radical (). The anion has eight valence electrons, the radical seven and the cation six. All three forms are highly reactive and rarely observed. Methyl cation, anion, and radical Methyl cation The methylium cation () exists in the gas phase, but is otherwise not encountered. Some compounds are considered to be sources of the cation, and this simplification is used pervasively in organic chemistry. For example, protonation of methanol gives an elect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nickel(II) Acetylacetonate
Nickel(II) bis(acetylacetonate) is a coordination complex with the formula i(acac)2sub>3, where acac is the anion C5H7O2− derived from deprotonation of acetylacetone. It is a dark green paramagnetic solid that is soluble in organic solvents such as toluene. It reacts with water to give the blue-green diaquo complex Ni(acac)2(H2O)2. Structure and properties Anhydrous nickel(II) acetylacetonate exists as molecules of Ni3(acac)6. The three nickel atoms are approximately collinear and each pair of them is bridged by two μ2 oxygen atoms. Each nickel atom has tetragonally distorted octahedral geometry, caused by the difference in the length of the Ni-O bonds between the bridging and non-bridging oxygens. Ni3(acac)6 molecules are almost centrosymmetric, despite the non-centrosymmetric point group of the ''cis''-Ni(acac)2 "monomers," which is uncommon. The trimeric structure allows all nickel centers to achieve an octahedral coordination. The trimer is only formed if intramolecular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methyl Lithium
Methyllithium is the simplest organolithium reagent with the empirical formula CH3Li. This s-block organometallic compound adopts an oligomeric structure both in solution and in the solid state. This highly reactive compound, invariably used in solution with an ether as the solvent, is a reagent in organic synthesis as well as organometallic chemistry. Operations involving methyllithium require anhydrous conditions, because the compound is highly reactive toward water. Oxygen and carbon dioxide are also incompatible with MeLi. Methyllithium is usually not prepared, but purchased as a solution in various ethers. Synthesis In the direct synthesis, methyl bromide is treated with a suspension of lithium in diethyl ether. :2 Li + MeBr → LiMe + LiBr The lithium bromide forms a complex with the methyllithium. Most commercially available methyllithium consists of this complex. "Halide-free" methyllithium is prepared from methyl chloride. Lithium chloride precipitates from the dieth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
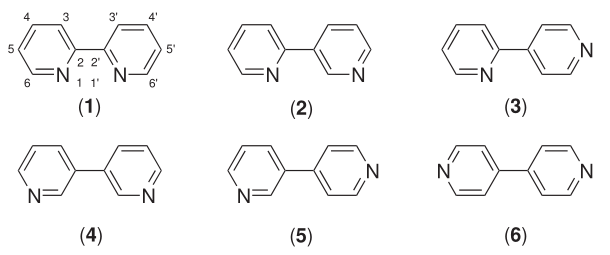
Bipyridine
Bipyridines also known as bipyridyls, dipyridyls, and dipyridines, are a family of chemical compounds with the formula (C5H4N)2, consisting of two pyridyl (C5H4N) rings. Pyridine is an aromatic nitrogen-containing heterocycle. Bipyridines are of significance in pesticides. Six isomers of bipyridine exist, but two are prominent: 2,2′-bipyridine is a popular ligand. 4,4'-Bipyridine is a precursor to the commercial herbicide paraquat. The bipyridines are all colourless solids, which are soluble in organic solvents and slightly soluble in water. 2,2′-Bipyridine 2,2′-Bipyridine (2,2′-bipy) is a chelating ligand that forms complexes with most transition metal ions that are of broad academic interest. Many of these complexes have distinctive optical properties, and some are of interest for analysis. Its complexes are used in studies of electron and energy transfer, supramolecular and materials chemistry, and catalysis. 2,2′-Bipyridine is used in the manufacture of diqua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



2(H2O)2.png)