|
Tetrahydropyran
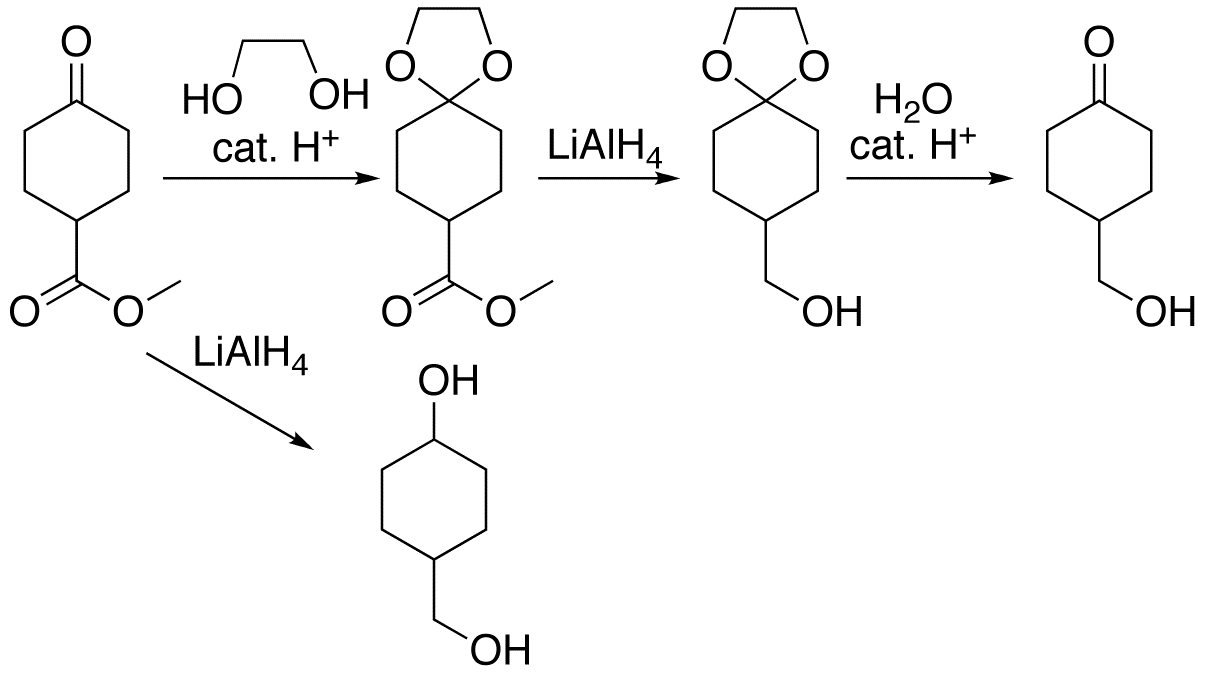
Tetrahydropyran (THP) is the organic compound consisting of a saturated six-membered ring containing five carbon atoms and one oxygen atom. It is named by reference to pyran, which contains two double bonds, and may be produced from it by adding four hydrogens. In 2013, its preferred IUPAC name was established as oxane. The compound is a colourless volatile liquid. Derivatives of tetrahydropyran are, however, more common. 2-Tetrahydropyranyl (THP-) ethers derived from the reaction of alcohols and 3,4-dihydropyran are commonly used as protecting groups in organic synthesis. Furthermore, a tetrahydropyran ''ring system'', i.e., five carbon atoms and an oxygen, is the core of pyranose sugars, such as glucose. Structure and preparation In gas phase, the THP exists in its lowest energy Cs symmetry chair conformation. One classic procedure for the organic synthesis of tetrahydropyran is by hydrogenation of the 3,4-isomer of dihydropyran with Raney nickel. Tetrahydropyranyl deri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyridinium P-toluenesulfonate
Pyridinium ''p''-toluenesulfonate (PPTS) is a colourless solid salt of pyridine and ''p''-toluenesulfonic acid. Uses In organic synthesis, PPTS is used as a weakly acidic catalyst, providing an organic soluble source of pyridinium (C5H5NH+) ions. For example, PPTS is used to deprotect silyl ethers or tetrahydropyranyl ethers when a substrate is unstable to stronger acid catalysts. It is also a commonly used catalyst for the preparation of acetals and ketal In organic chemistry, an acetal is a functional group with the connectivity . Here, the R groups can be organic fragments (a carbon atom, with arbitrary other atoms attached to that) or hydrogen, while the R' groups must be organic fragments n ...s from aldehydes and ketones. References {{Reflist Sulfonates Pyridinium compounds Salts Reagents for organic chemistry P-Tosyl compounds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protecting Group
A protecting group or protective group is introduced into a molecule by chemical modification of a functional group to obtain chemoselectivity in a subsequent chemical reaction. It plays an important role in multistep organic synthesis. In many preparations of delicate organic compounds, specific parts of the molecules cannot survive the required reagents or chemical environments. These parts (functional groups) must be protected. For example, lithium aluminium hydride is a highly reactive reagent that usefully reduces esters to alcohols. It always reacts with carbonyl groups, and cannot be discouraged by any means. When an ester must be reduced in the presence of a carbonyl, hydride attack on the carbonyl must be prevented. One way to do so converts the carbonyl into an acetal, which does not react with hydrides. The acetal is then called a protecting group for the carbonyl. After the hydride step is complete, aqueous acid removes the acetal, restoring the carbonyl. This step ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3,4-dihydropyran
3,4-Dihydropyran (DHP) is a heterocyclic compound with the formula C5H8O. The six-membered C5O ring has the unsaturation adjacent to oxygen. The isomeric 3,6-dihydropyran has a methylene separating the double bond and oxygen. DHP is used for protecting group for alcohols. It is a colorless liquid. Preparation Dihydropyran is prepared by the dehydration of tetrahydrofurfuryl alcohol over alumina at 300–400 °C. THFA is itself prepared from tetrahydro-2-furoic acid. : Reactions In organic synthesis, the 2-tetrahydropyranyl (THP) group is used as a protecting group for alcohols. Reaction of the alcohol with DHP forms a THP ether, protecting the alcohol from a variety of reactions. The alcohol can later be restored by acidic hydrolysis, concomitant with formation of 5-hydroxypentanal. : See also *Pyran *Tetrahydropyran Tetrahydropyran (THP) is the organic compound consisting of a saturated six-membered ring containing five carbon atoms and one oxygen atom. It is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protecting Groups
A protecting group or protective group is introduced into a molecule by chemical modification of a functional group to obtain chemoselectivity in a subsequent chemical reaction. It plays an important role in multistep synthesis, multistep organic synthesis. In many preparations of delicate organic compounds, specific parts of the molecules cannot survive the required reagents or chemical environments. These parts (functional groups) must be protected. For example, lithium aluminium hydride is a highly reactive reagent that usefully reduces esters to Alcohol (chemistry), alcohols. It always reacts with carbonyl groups, and cannot be discouraged by any means. When an ester must be reduced in the presence of a carbonyl, hydride attack on the carbonyl must be prevented. One way to do so converts the carbonyl into an acetal, which does not react with hydrides. The acetal is then called a protecting group for the carbonyl. After the hydride step is complete, aqueous acid removes the ace ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyran
In chemistry, pyran is a six-membered heterocyclic, non-aromatic ring, consisting of five carbon atoms and one oxygen atom and containing two double bonds. The molecular formula is C5H6O. There are two isomers of pyran that differ by the location of the double bonds. In 2''H''-pyran, the saturated carbon is at position 2, whereas, in 4''H''-pyran, the saturated carbon is at position 4. "Oxine” is not used for pyran because it has been used as a trivial name for quinolin-8-ol. 4''H''-Pyran was first isolated and characterized in 1962 via pyrolysis of 2-acetoxy-3,4-dihydro-2''H''-pyran. It was found to be unstable, particularly in the presence of air. 4''H''-pyran easily disproportionates to the corresponding dihydropyran and the pyrylium ion, which is easily hydrolyzed in aqueous medium. Although the pyrans themselves have little significance in chemistry, many of their derivatives are important biological molecules, such as the pyranoflavonoids. The term pyran is also often ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3,4-Dihydropyran
3,4-Dihydropyran (DHP) is a heterocyclic compound with the formula C5H8O. The six-membered C5O ring has the unsaturation adjacent to oxygen. The isomeric 3,6-dihydropyran has a methylene separating the double bond and oxygen. DHP is used for protecting group for alcohols. It is a colorless liquid. Preparation Dihydropyran is prepared by the dehydration of tetrahydrofurfuryl alcohol over alumina at 300–400 °C. THFA is itself prepared from tetrahydro-2-furoic acid. : Reactions In organic synthesis, the 2-tetrahydropyranyl (THP) group is used as a protecting group for alcohols. Reaction of the alcohol with DHP forms a THP ether, protecting the alcohol from a variety of reactions. The alcohol can later be restored by acidic hydrolysis, concomitant with formation of 5-hydroxypentanal. : See also *Pyran *Tetrahydropyran Tetrahydropyran (THP) is the organic compound consisting of a saturated six-membered ring containing five carbon atoms and one oxygen atom. It is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triphenylphosphine
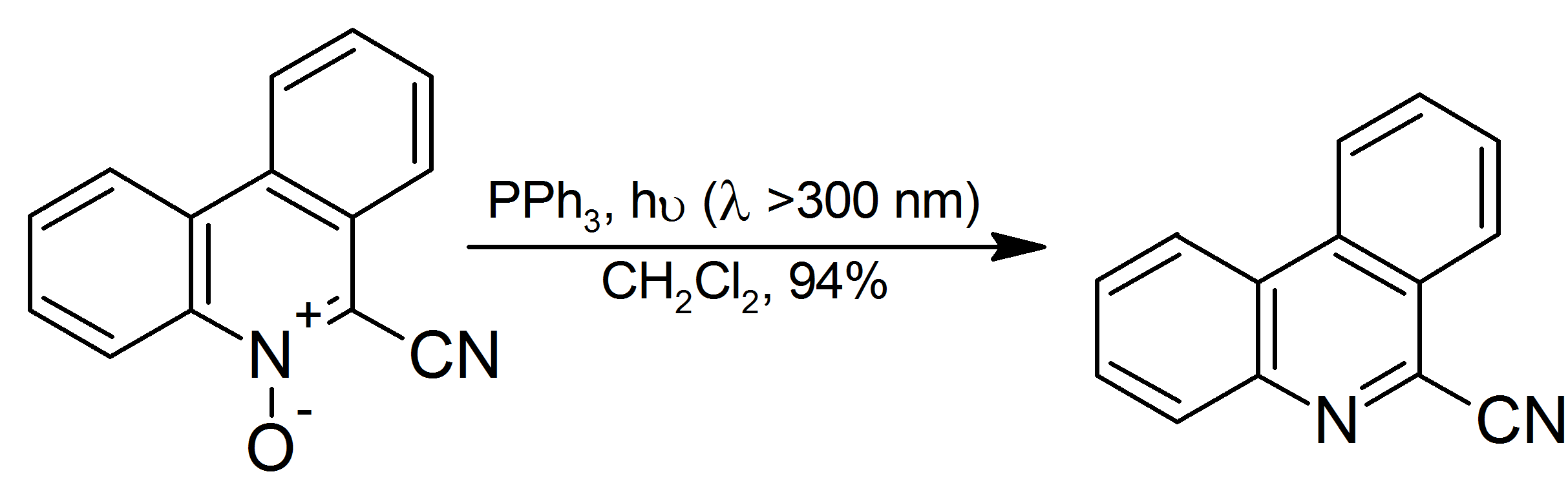
Triphenylphosphine (IUPAC name: triphenylphosphane) is a common organophosphorus compound with the formula P(C6H5)3 and often abbreviated to P Ph3 or Ph3P. It is versatile compound that is widely used as a reagent in organic synthesis and as a ligand for transition metal complexes, including ones that serve as catalysts in organometallic chemistry. PPh3 exists as relatively air stable, colorless crystals at room temperature. It dissolves in non-polar organic solvents such as benzene and diethyl ether. Preparation and structure Triphenylphosphine can be prepared in the laboratory by treatment of phosphorus trichloride with phenylmagnesium bromide or phenyllithium. The industrial synthesis involves the reaction between phosphorus trichloride, chlorobenzene, and sodium: :PCl3 + 3 PhCl + 6 Na → PPh3 + 6 NaCl Triphenylphosphine crystallizes in triclinic and monoclinic modification. In both cases, the molecule adopts a pyramidal structure with propeller-like arrangement of the thre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diethyl Azodicarboxylate
Diethyl azodicarboxylate, conventionally abbreviated as DEAD and sometimes as DEADCAT, is an organic compound with the structural formula . Its molecular structure consists of a central azo compound, azo functional group, RN=NR, flanked by two ethyl ester groups. This orange-red liquid is a valuable reagent but also quite dangerous and explodes upon heating. Therefore, commercial shipment of pure diethyl azodicarboxylate is prohibited in the United States and is carried out either in solution or on polystyrene particles. DEAD is an aza-Diels–Alder reaction, dienophile and an efficient dehydrogenating agent, converting Alcohol (chemistry), alcohols to aldehydes, thiols to disulfides and hydrazo groups to Azo compound, azo groups; it is also a good electron acceptor. While DEAD is used in numerous chemical reactions it is mostly known as a key component of the Mitsunobu reaction, a common strategy for the preparation of an amine, azide, ether, thioether, or ester from the corresp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Compound
Some chemical authorities define an organic compound as a chemical compound that contains a carbon–hydrogen or carbon–carbon bond; others consider an organic compound to be any chemical compound that contains carbon. For example, carbon-containing compounds such as alkanes (e.g. methane ) and its derivatives are universally considered organic, but many others are sometimes considered inorganic, such as certain compounds of carbon with nitrogen and oxygen (e.g. cyanide ion , hydrogen cyanide , chloroformic acid , carbon dioxide , and carbonate ion ). Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. The study of the properties, reactions, and syntheses of organic compounds comprise the discipline known as organic chemistry. For historical reasons, a few classes of carbon-containing compounds (e.g., carbonate salts and cyanide salts), along with a few other exceptions (e.g., carbon dioxide, and even ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrahydrofuran
Tetrahydrofuran (THF), or oxolane, is an organic compound with the formula (CH2)4O. The compound is classified as heterocyclic compound, specifically a cyclic ether. It is a colorless, water- miscible organic liquid with low viscosity. It is mainly used as a precursor to polymers. Being polar and having a wide liquid range, THF is a versatile solvent. It is an isomer of another solvent, butanone. Production About 200,000 tonnes of tetrahydrofuran are produced annually. The most widely used industrial process involves the acid-catalyzed dehydration of 1,4-Butanediol, 1,4-butanediol. Ashland Inc., Ashland/ISP is one of the biggest producers of this chemical route. The method is similar to the production of diethyl ether from ethanol. The butanediol is derived from Condensation reaction, condensation of acetylene with formaldehyde followed by hydrogenation. DuPont developed a process for producing THF by oxidizing Butane#Isomers, ''n''-butane to crude maleic anhydride, follow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetic Acid
Acetic acid , systematically named ethanoic acid , is an acidic, colourless liquid and organic compound with the chemical formula (also written as , , or ). Vinegar is at least 4% acetic acid by volume, making acetic acid the main component of vinegar apart from water. Historically, vinegar was produced from the third century BC and was likely the first acid to be produced in large quantities. Acetic acid is the second simplest carboxylic acid (after formic acid). It is an important Reagent, chemical reagent and industrial chemical across various fields, used primarily in the production of cellulose acetate for photographic film, polyvinyl acetate for wood Adhesive, glue, and synthetic fibres and fabrics. In households, diluted acetic acid is often used in descaling agents. In the food industry, acetic acid is controlled by the E number, food additive code E260 as an acidity regulator and as a condiment. In biochemistry, the acetyl group, derived from acetic acid, is funda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |