|
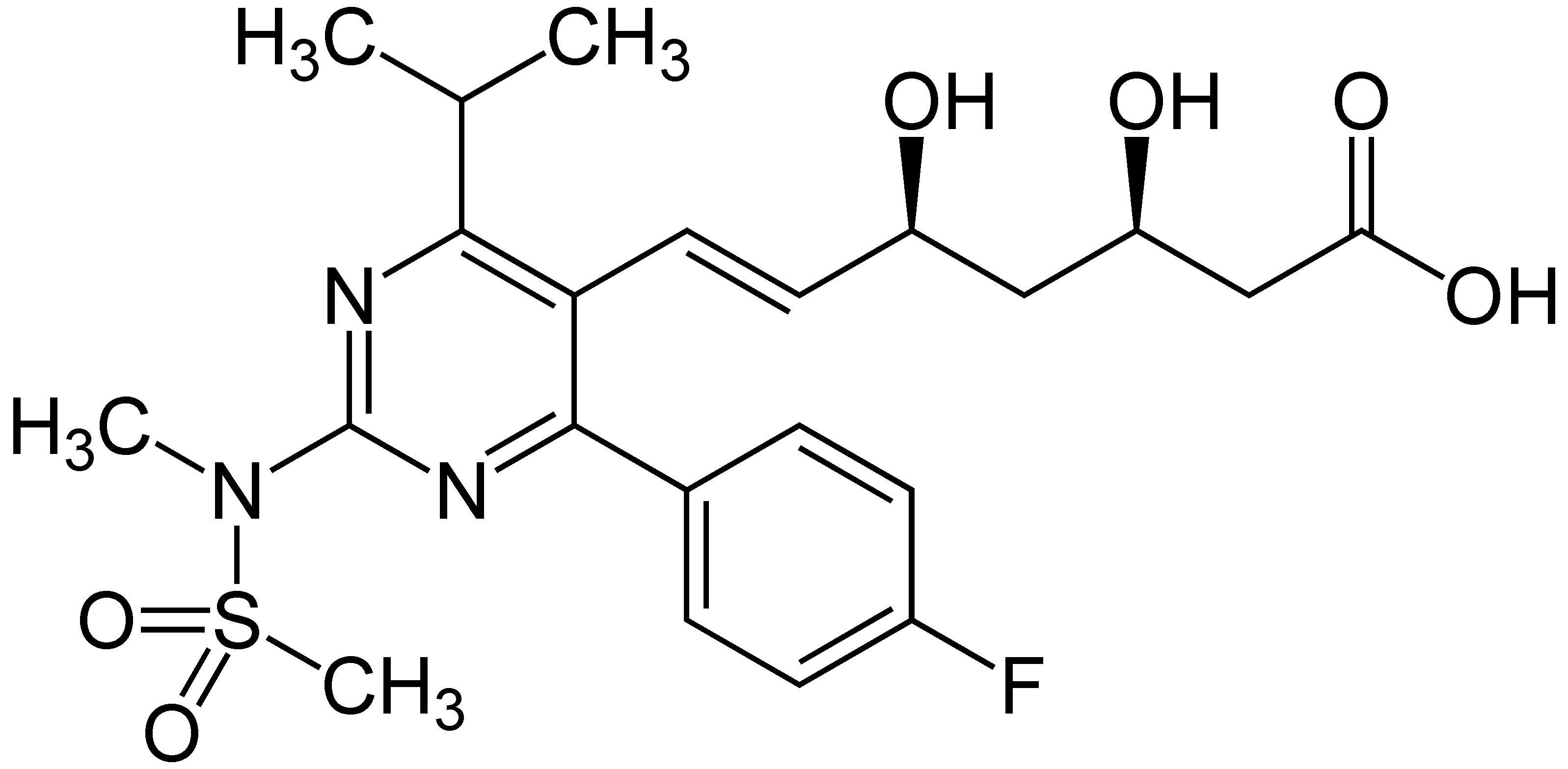
Tazemetostat
Tazemetostat, sold under the brand name Tazverik, is a medication used for the treatment of adults and adolescents aged 16 years and older with metastatic (when cancer cells spread to other parts of the body) or locally advanced (when cancer has grown outside the organ it started in, but has not yet spread to distant parts of the body) epithelioid sarcoma not eligible for complete resection (surgically removing all of a tissue, structure, or organ). The most common side effects are pain, fatigue, nausea, decreased appetite, vomiting and constipation. People taking tazemetostat are at increased risk of developing secondary malignancies including: T-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma (a type of blood cancer that affects the lymphatic system usually found in the lymph nodes), myelodysplastic syndrome (a disorder resulting from poorly formed or dysfunctional blood cells) and acute myeloid leukemia (a cancer of the blood and bone marrow). Tazemetostat is a cancer drug that acts as a pote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EZH2
Enhancer of zeste homolog 2 (EZH2) is a histone-lysine N-methyltransferase enzyme ( EC 2.1.1.43) encoded by gene, that participates in histone methylation and, ultimately, transcriptional repression. EZH2 catalyzes the addition of methyl groups to histone H3 at lysine 27, by using the cofactor S-adenosyl-L-methionine. Methylation activity of EZH2 facilitates heterochromatin formation thereby silences gene function. Remodeling of chromosomal heterochromatin by EZH2 is also required during cell mitosis. EZH2 is the functional enzymatic component of the Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 (PRC2), which is responsible for healthy embryonic development through the epigenetic maintenance of genes responsible for regulating development and differentiation. EZH2 is responsible for the methylation activity of PRC2, and the complex also contains proteins required for optimal function ( EED, SUZ12, JARID2, AEBP2, RbAp46/48, and PCL). Mutation or over-expression of EZH2 has been linked to ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epithelioid Sarcoma
Epithelioid sarcoma is a rare soft tissue sarcoma arising from mesenchymal tissue and characterized by epithelioid-like features. It accounts for less than 1% of all soft tissue sarcomas. It was first clearly characterized by F.M. Enzinger in 1970. It commonly presents itself in the distal limbs (fingers, hands, forearms, or feet) of young adults as a small, soft mass or a series of bumps. A proximal version has also been described, frequently occurring in the upper extremities. Rare cases have been reported in the pelvis, vulva, penis, and spine. Histologically, epithelioid sarcoma forms nodules with central necrosis surrounded by bland, polygonal cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm and peripheral spindling. Epithelioid sarcomas typically express vimentin, cytokeratins, epithelial membrane antigen, and CD34, whereas they are usually negative for S100, desmin, and FLI1 (FLI-1). They typically stain positive for CA125. Epithelioid sarcoma most commonly strikes young adults, yet no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First-in-class Medication
A first-in-class medication is a pharmaceutical that uses a "new and unique mechanism of action" to treat a particular medical condition. While the Food and Drug Administration's Center for Drug Evaluation and Research tracks first-in-class medications and reports on them annually, first-in-class is not considered a regulatory category. Although many first-in-class medications qualify as breakthrough therapies, Regenerative Medicine Advanced Therapies and/or orphan drugs, first-in-class status itself has no regulatory effect. Examples Controversy Safety By definition, a first-in-class drug does not have the safety evidence from analogous products that not-first-in-class drugs would have. However, a study investigating recalls and warnings in relation to first-in-class drugs approved between 1997 and 2012 by Health Canada has found that first-in-class drugs actually have a more favourable benefit-to-harm ratio. Economics First-in-class drugs are often seen as commerci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food And Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a List of United States federal agencies, federal agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food safety, tobacco products, caffeine products, dietary supplements, Prescription drug, prescription and Over-the-counter drug, over-the-counter pharmaceutical drugs (medications), vaccines, biopharmaceuticals, blood transfusions, medical devices, electromagnetic radiation emitting devices (ERED), cosmetics, Animal feed, animal foods & feed and Veterinary medicine, veterinary products. The FDA's primary focus is enforcement of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FD&C), but the agency also enforces other laws, notably Section 361 of the Public Health Service Act, as well as associated regulations. Much of this regulatory-enforcement work is not d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme Inhibitor
An enzyme inhibitor is a molecule that binds to an enzyme and blocks its activity. Enzymes are proteins that speed up chemical reactions necessary for life, in which substrate molecules are converted into products. An enzyme facilitates a specific chemical reaction by binding the substrate to its active site, a specialized area on the enzyme that accelerates the most difficult step of the reaction. An enzyme inhibitor stops ("inhibits") this process, either by binding to the enzyme's active site (thus preventing the substrate itself from binding) or by binding to another site on the enzyme such that the enzyme's catalysis of the reaction is blocked. Enzyme inhibitors may bind reversibly or irreversibly. Irreversible inhibitors form a chemical bond with the enzyme such that the enzyme is inhibited until the chemical bond is broken. By contrast, reversible inhibitors bind non-covalently and may spontaneously leave the enzyme, allowing the enzyme to resume its function. Reve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lysine
Lysine (symbol Lys or K) is an α-amino acid that is a precursor to many proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated form under biological conditions), an α-carboxylic acid group (which is in the deprotonated −COO− form under biological conditions), and a side chain lysyl ((CH2)4NH2), classifying it as a basic, charged (at physiological pH), aliphatic amino acid. It is encoded by the codons AAA and AAG. Like almost all other amino acids, the α-carbon is chiral and lysine may refer to either enantiomer or a racemic mixture of both. For the purpose of this article, lysine will refer to the biologically active enantiomer L-lysine, where the α-carbon is in the ''S'' configuration. The human body cannot synthesize lysine. It is essential in humans and must therefore be obtained from the diet. In organisms that synthesise lysine, two main biosynthetic pathways exist, the diaminopimelate and α-aminoadipate pathways, which employ distinct e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tumor
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists in growing abnormally, even if the original trigger is removed. This abnormal growth usually forms a mass, when it may be called a tumor. ICD-10 classifies neoplasms into four main groups: benign neoplasms, in situ neoplasms, malignant neoplasms, and neoplasms of uncertain or unknown behavior. Malignant neoplasms are also simply known as cancers and are the focus of oncology. Prior to the abnormal growth of tissue, as neoplasia, cells often undergo an abnormal pattern of growth, such as metaplasia or dysplasia. However, metaplasia or dysplasia does not always progress to neoplasia and can occur in other conditions as well. The word is from Ancient Greek 'new' and 'formation, creation'. Types A neoplasm can be benign, potentially m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accelerated Approval (FDA)
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) initiated the FDA Accelerated Approval Program in 1992 to allow faster approval of drugs for serious conditions that fill an unmet medical need. The faster approval relies on use of surrogate endpoints. Drug approval typically requires clinical trials with endpoints that demonstrate a clinical benefit, such as increased survival for cancer patients. Drugs with accelerated approval can initially be tested in clinical trials that use a surrogate endpoint, or something that is thought to predict clinical benefit. Surrogate endpoints typically require less time, and in the case of a cancer patient, it is much faster to measure a reduction in tumor size, for example, than overall patient survival. Drugs approved under the FDA Accelerated Approval Program still need to be tested in clinical trials using endpoints that demonstrate clinical benefit, and those trials are known as phase 4 confirmatory trials. If the drug later proves unabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orphan Drug
An orphan drug is a pharmaceutical agent developed to treat medical conditions which, because they are so rare, would not be profitable to produce without government assistance. The conditions are referred to as orphan diseases. The assignment of orphan status to a disease and to drugs developed to treat it is a matter of public policy in many countries and has yielded medical breakthroughs that might not otherwise have been achieved, due to the economics of drug research and development. In the U.S. and the EU, it is easier to gain marketing approval for an orphan drug. There may be other financial incentives, such as an extended period of exclusivity, during which the producer has sole rights to market the drug. All are intended to encourage development of drugs which would otherwise lack sufficient profit motive to attract corporate research budgets and personnel. Definition According to the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), an orphan drug is defined as one "intended for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antineoplastic Drugs
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated to chemo and sometimes CTX or CTx) is a type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) as part of a standardized chemotherapy regimen. Chemotherapy may be given with a curative intent (which almost always involves combinations of drugs) or it may aim to prolong life or to reduce symptoms ( palliative chemotherapy). Chemotherapy is one of the major categories of the medical discipline specifically devoted to pharmacotherapy for cancer, which is called ''medical oncology''. The term ''chemotherapy'' has come to connote non-specific usage of intracellular poisons to inhibit mitosis (cell division) or induce DNA damage, which is why inhibition of DNA repair can augment chemotherapy. The connotation of the word chemotherapy excludes more selective agents that block extracellular signals ( signal transduction). The development of therapies with specific molecular or genetic targets, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cancer Treatments
Cancer can be treated by surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, hormonal therapy, targeted therapy (including immunotherapy such as monoclonal antibody therapy) and synthetic lethality, most commonly as a series of separate treatments (e.g. chemotherapy before surgery). The choice of therapy depends upon the location and grade of the tumor and the stage of the disease, as well as the general state of the patient (performance status). Cancer genome sequencing helps in determining which cancer the patient exactly has for determining the best therapy for the cancer. A number of experimental cancer treatments are also under development. Under current estimates, two in five people will have cancer at some point in their lifetime. Complete removal of the cancer without damage to the rest of the body (that is, achieving cure with near-zero adverse effects) is the ideal, if rarely achieved, goal of treatment and is often the goal in practice. Sometimes this can be accomplished by sur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated to chemo and sometimes CTX or CTx) is a type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) as part of a standardized chemotherapy regimen. Chemotherapy may be given with a curative intent (which almost always involves combinations of drugs) or it may aim to prolong life or to reduce symptoms ( palliative chemotherapy). Chemotherapy is one of the major categories of the medical discipline specifically devoted to pharmacotherapy for cancer, which is called ''medical oncology''. The term ''chemotherapy'' has come to connote non-specific usage of intracellular poisons to inhibit mitosis (cell division) or induce DNA damage, which is why inhibition of DNA repair can augment chemotherapy. The connotation of the word chemotherapy excludes more selective agents that block extracellular signals (signal transduction). The development of therapies with specific molecular or genetic targets, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)