|
Tax Cut
A tax cut typically represents a decrease in the amount of money taken from taxpayers to go towards government revenue. This decreases the revenue of the government and increases the disposable income of taxpayers. Tax rate cuts usually refer to reductions in the percentage of tax paid on income, goods and services. As they leave consumers with more disposable income, tax cuts are an example of an expansionary fiscal policy. Tax cuts also include reduction in tax in other ways, such as tax credit, deductions and loopholes. However, sometimes a tax cut can increase tax revenue, as economist Thomas Sowell explains: :"What actually followed the cuts in tax rates in the 1920s were rising output, rising employment to produce that output, rising incomes as a result and rising tax revenues for the government because of the rising incomes, even though the tax rates had been lowered." How a tax cut affects the economy depends on which tax is cut. Policies that increase disposable inco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government Revenue
Government revenue or national revenue is money received by a government from Tax revenue, taxes and Non-tax revenue, non-tax sources to enable it, assuming full resource employment, to undertake non-inflationary public expenditure. Government revenue as well as government spending are components of the government budget and important tools of the government's fiscal policy. The collection of revenue is the most basic task of a government, as the resources released via the collection of revenue are necessary for the operation of government, provision of the common good (through the social contract in order to fulfill the public interest) and enforcement of its Law, laws; this necessity of revenue was a major factor in the development of the modern Bureaucracy, bureaucratic state. Government revenue is distinct from government debt and money creation, which both serve as temporary measures of increasing a government's money supply without increasing its revenue. Sources There are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economic Growth And Tax Relief Reconciliation Act Of 2001
An economy is an area of the production, distribution and trade, as well as consumption of goods and services. In general, it is defined as a social domain that emphasize the practices, discourses, and material expressions associated with the production, use, and management of resources. A given economy is a set of processes that involves its culture, values, education, technological evolution, history, social organization, political structure, legal systems, and natural resources as main factors. These factors give context, content, and set the conditions and parameters in which an economy functions. In other words, the economic domain is a social domain of interrelated human practices and transactions that does not stand alone. Economic agents can be individuals, businesses, organizations, or governments. Economic transactions occur when two groups or parties agree to the value or price of the transacted good or service, commonly expressed in a certain currency. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tax Cuts And Jobs Act
The Act to provide for reconciliation pursuant to titles II and V of the concurrent resolution on the budget for fiscal year 2018, , is a congressional revenue act of the United States originally introduced in Congress as the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA), that amended the Internal Revenue Code of 1986. The legislation is commonly referred to in media as the Trump Tax Cuts. Major elements of the changes include reducing tax rates for corporations and individuals, increasing the standard deduction and family tax credits, eliminating personal exemptions and making it less beneficial to itemize deductions, limiting deductions for state and local income taxes and property taxes, further limiting the mortgage interest deduction, reducing the alternative minimum tax for individuals and eliminating it for corporations, doubling the estate tax exemption, and reducing the penalty for violating the individual mandate of the Affordable Care Act (ACA) to $0. ''The New York Times'' has de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Donald Trump
Donald John Trump (born June 14, 1946) is an American politician, media personality, and businessman who is the 47th president of the United States. A member of the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party, he served as the 45th president from 2017 to 2021. Born into a wealthy family in the New York City borough of Queens, Trump graduated from the University of Pennsylvania in 1968 with a bachelor's degree in economics. He became the president of his family's real estate business in 1971, renamed it the Trump Organization, and began acquiring and building skyscrapers, hotels, casinos, and golf courses. He launched side ventures, many licensing the Trump name, and filed for six business bankruptcies in the 1990s and 2000s. From 2004 to 2015, he hosted the reality television show ''The Apprentice (American TV series), The Apprentice'', bolstering his fame as a billionaire. Presenting himself as a political outsider, Trump won the 2016 United States presidential e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Taxpayer Relief Act Of 2012
The American Taxpayer Relief Act of 2012 (ATRA) was enacted and passed by the United States Congress on January 1, 2013, and was signed into law by US President Barack Obama the next day. ATRA gave permanence to the lower rates of much of the "Bush tax cuts". The Act centers on a partial resolution to the US fiscal cliff by addressing the expiration of certain provisions of the Economic Growth and Tax Relief Reconciliation Act of 2001 and the Jobs and Growth Tax Relief Reconciliation Act of 2003 (known together as the " Bush tax cuts"), which had been temporarily extended by the Tax Relief, Unemployment Insurance Reauthorization, and Job Creation Act of 2010. The Act also addressed the activation of the Budget Control Act of 2011's budget sequestration provisions. A compromise measure, the Act gives permanence to the lower rate of much of the Bush tax cuts, while retaining the higher tax rate at upper income levels that became effective on January 1 due to the expiration of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
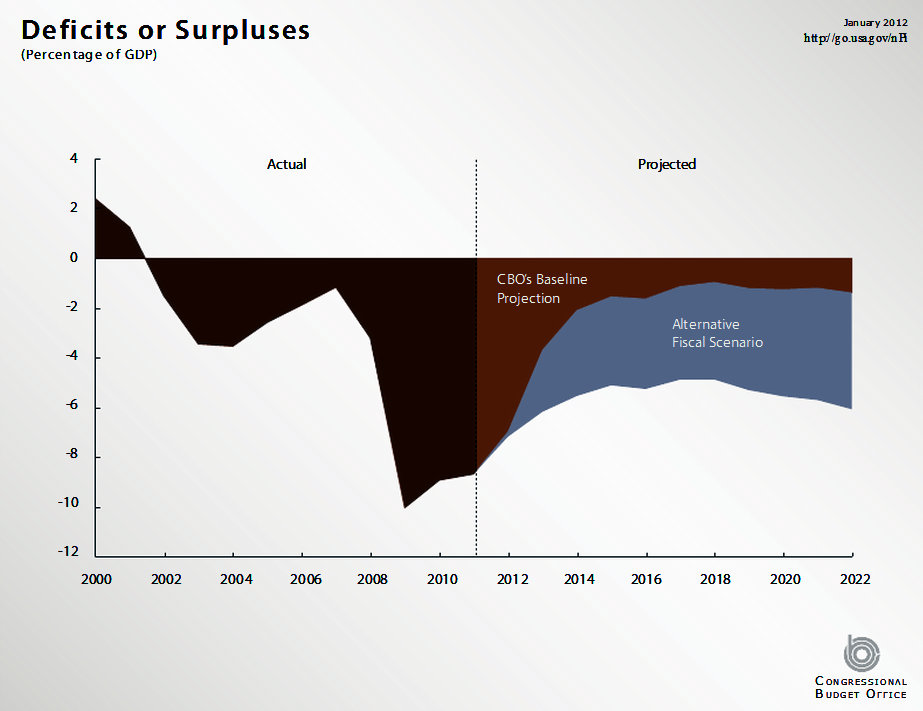
United States Fiscal Cliff
The United States fiscal cliff refers to the combined effect of several previously-enacted laws that came into effect simultaneously in January 2013, increasing taxes and decreasing spending. The Bush tax cuts of 2001 and 2003, which had been extended for two years by the 2010 Tax Relief Act, were scheduled to expire on December 31, 2012. Planned spending cuts under the Budget Control Act of 2011 also came into play. That Act was passed as a compromise to resolve a dispute concerning the US debt ceiling and address the failure of the 111th Congress to pass a federal budget. Discretionary spending for federal agencies and cabinet departments would have been reduced through broad cuts referred to as budget sequestration. Mandatory programs, such as Social Security, Medicaid, federal pay (including military pay and pensions) and veterans' benefits would have been exempted from the spending cuts. The fiscal cliff would have increased tax rates and decreased government spending ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Recession
The Great Recession was a period of market decline in economies around the world that occurred from late 2007 to mid-2009.“US Business Cycle Expansions and Contractions” United States NBER, or National Bureau of Economic Research, updated March 14, 2023. This government agency dates the Great Recession as starting in December 2007 and bottoming-out in June 2009. The scale and timing of the recession varied from country to country (see map). At the time, the International Monetary Fund (IMF) concluded that it was the most severe economic and financial meltdown since the Great Depression. The causes of the Great Recession include a combination of vulnerabilities that developed in the financial system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II (born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who was the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party, he was the first African American president in American history. Obama previously served as a U.S. senator representing Illinois from 2005 to 2008 and as an Illinois state senator from 1997 to 2004. Born in Honolulu, Hawaii, Obama graduated from Columbia University in 1983 with a Bachelor of Arts degree in political science and later worked as a community organizer in Chicago. In 1988, Obama enrolled in Harvard Law School, where he was the first black president of the ''Harvard Law Review''. He became a civil rights attorney and an academic, teaching constitutional law at the University of Chicago Law School from 1992 to 2004. In 1996, Obama was elected to represent the 13th district in the Illinois Senate, a position he held until 2004, when he successfully ran for the U.S. Senate. In the 2008 pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early 2000s Recession
The early 2000s recession was a major decline in economic activity which mainly occurred in developed countries. The recession affected the European Union during 2000 and 2001 and the United States from March to November 2001. The United Kingdom, Canada and Australia avoided the recession, while Russia, a nation that did not experience prosperity during the 1990s, began to recover from it. Japan's Lost Decade (Japan), 1990s recession continued. A combination of the Dot Com Bubble collapse and the September 11 attacks, September 11 attacks lengthed and worsened the recession. This recession was predicted by economists because the boom of the 1990s, accompanied by both low inflation and low unemployment, slowed in some parts of East Asia during the 1997 Asian financial crisis. The recession in industrialized countries was not as significant as either of the two previous worldwide recessions. Some economists in the United States object to characterizing it as a recession since t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George W
George Walker Bush (born July 6, 1946) is an American politician and businessman who was the 43rd president of the United States from 2001 to 2009. A member of the Bush family and the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party, he is the eldest son of the 41st president, George H. W. Bush, and was the 46th governor of Texas from 1995 to 2000. Bush flew warplanes in the Texas Air National Guard in his twenties. After graduating from Harvard Business School in 1975, he worked in the oil industry. He later co-owned the Major League Baseball team Texas Rangers (baseball), Texas Rangers before being elected governor of Texas 1994 Texas gubernatorial election, in 1994. Governorship of George W. Bush, As governor, Bush successfully sponsored legislation for tort reform, increased education funding, set higher standards for schools, and reformed the criminal justice system. He also helped make Texas the Wind power in Texas, leading producer of wind-generated electricity in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tax Reform Act Of 1986
The Tax Reform Act of 1986 (TRA) was passed by the 99th United States Congress and signed into law by President Ronald Reagan on October 22, 1986. The Tax Reform Act of 1986 was the top domestic priority of President Reagan's second term. The act lowered federal income tax rates, decreasing the number of tax brackets and reducing the top tax rate from 50 percent to 28 percent. The act also expanded the earned income tax credit, the standard deduction, and the personal exemption, removing approximately six million lower-income Americans from the tax base. Offsetting these cuts, the act increased the alternative minimum tax and eliminated many tax deductions, including deductions for rental housing, individual retirement accounts, and depreciation. Although the tax reform was projected to be revenue-neutral, it was popularly referred to as the second round of Reagan tax cuts (following the Economic Recovery Tax Act of 1981). The bill passed with majority support in both the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economic Recovery Tax Act Of 1981
The Economic Recovery Tax Act of 1981 (ERTA), or Kemp–Roth Tax Cut, was an Act that introduced a major tax cut, which was designed to encourage economic growth. The Act was enacted by the 97th Congress and signed into law by U.S. President Ronald Reagan. The Accelerated Cost Recovery System (ACRS) was a major component of the Act, and was amended in 1986 to become the Modified Accelerated Cost Recovery System (MACRS). Representative Jack Kemp and Senator William Roth, both Republicans, had nearly won passage of a tax cut during the Carter presidency; however, President Jimmy Carter feared an increase in the deficit and so prevented the bill's passage. Reagan made a major tax cut his top priority once he had taken office. Although Democrats maintained a majority in the U.S. House of Representatives during the 97th Congress, Reagan convinced conservative Democrats like Phil Gramm to support the bill. The Act passed the U.S. Congress on August 4, 1981, and it was signed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |