|
Suprema
In mathematics, the infimum (abbreviated inf; plural infima) of a subset S of a partially ordered set P is a greatest element in P that is less than or equal to each element of S, if such an element exists. Consequently, the term ''greatest lower bound'' (abbreviated as ) is also commonly used. The supremum (abbreviated sup; plural suprema) of a subset S of a partially ordered set P is the least element in P that is greater than or equal to each element of S, if such an element exists. Consequently, the supremum is also referred to as the ''least upper bound'' (or ). The infimum is in a precise sense dual to the concept of a supremum. Infima and suprema of real numbers are common special cases that are important in analysis, and especially in Lebesgue integration. However, the general definitions remain valid in the more abstract setting of order theory where arbitrary partially ordered sets are considered. The concepts of infimum and supremum are close to minimum and maximu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infimum Illustration
In mathematics, the infimum (abbreviated inf; plural infima) of a subset S of a partially ordered set P is a greatest element in P that is less than or equal to each element of S, if such an element exists. Consequently, the term ''greatest lower bound'' (abbreviated as ) is also commonly used. The supremum (abbreviated sup; plural suprema) of a subset S of a partially ordered set P is the least element in P that is greater than or equal to each element of S, if such an element exists. Consequently, the supremum is also referred to as the ''least upper bound'' (or ). The infimum is in a precise sense dual to the concept of a supremum. Infima and suprema of real numbers are common special cases that are important in analysis, and especially in Lebesgue integration. However, the general definitions remain valid in the more abstract setting of order theory where arbitrary partially ordered sets are considered. The concepts of infimum and supremum are close to minimum and maxi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supremum Illustration
In mathematics, the infimum (abbreviated inf; plural infima) of a subset S of a partially ordered set P is a greatest element in P that is less than or equal to each element of S, if such an element exists. Consequently, the term ''greatest lower bound'' (abbreviated as ) is also commonly used. The supremum (abbreviated sup; plural suprema) of a subset S of a partially ordered set P is the least element in P that is greater than or equal to each element of S, if such an element exists. Consequently, the supremum is also referred to as the ''least upper bound'' (or ). The infimum is in a precise sense dual to the concept of a supremum. Infima and suprema of real numbers are common special cases that are important in analysis, and especially in Lebesgue integration. However, the general definitions remain valid in the more abstract setting of order theory where arbitrary partially ordered sets are considered. The concepts of infimum and supremum are close to minimum and maxim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Empty Set
In mathematics, the empty set is the unique set having no elements; its size or cardinality (count of elements in a set) is zero. Some axiomatic set theories ensure that the empty set exists by including an axiom of empty set, while in other theories, its existence can be deduced. Many possible properties of sets are vacuously true for the empty set. Any set other than the empty set is called non-empty. In some textbooks and popularizations, the empty set is referred to as the "null set". However, null set is a distinct notion within the context of measure theory, in which it describes a set of measure zero (which is not necessarily empty). The empty set may also be called the void set. Notation Common notations for the empty set include "", "\emptyset", and "∅". The latter two symbols were introduced by the Bourbaki group (specifically André Weil) in 1939, inspired by the letter Ø in the Danish and Norwegian alphabets. In the past, "0" was occasionally used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Completeness Of The Real Numbers
Completeness is a property of the real numbers that, intuitively, implies that there are no "gaps" (in Dedekind's terminology) or "missing points" in the real number line. This contrasts with the rational numbers, whose corresponding number line has a "gap" at each irrational value. In the decimal number system, completeness is equivalent to the statement that any infinite string of decimal digits is actually a decimal representation for some real number. Depending on the construction of the real numbers used, completeness may take the form of an axiom (the completeness axiom), or may be a theorem proven from the construction. There are many equivalent forms of completeness, the most prominent being Dedekind completeness and Cauchy completeness ( completeness as a metric space). Forms of completeness The real numbers can be defined synthetically as an ordered field satisfying some version of the ''completeness axiom''. Different versions of this axiom are all equiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Real Numbers
In mathematics, a real number is a number that can be used to measure a ''continuous'' one-dimensional quantity such as a distance, duration or temperature. Here, ''continuous'' means that values can have arbitrarily small variations. Every real number can be almost uniquely represented by an infinite decimal expansion. The real numbers are fundamental in calculus (and more generally in all mathematics), in particular by their role in the classical definitions of limits, continuity and derivatives. The set of real numbers is denoted or \mathbb and is sometimes called "the reals". The adjective ''real'' in this context was introduced in the 17th century by René Descartes to distinguish real numbers, associated with physical reality, from imaginary numbers (such as the square roots of ), which seemed like a theoretical contrivance unrelated to physical reality. The real numbers include the rational numbers, such as the integer and the fraction . The rest of the rea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Least-upper-bound Property
In mathematics, the least-upper-bound property (sometimes called completeness or supremum property or l.u.b. property) is a fundamental property of the real numbers. More generally, a partially ordered set has the least-upper-bound property if every non-empty subset of with an upper bound has a ''least'' upper bound (supremum) in . Not every (partially) ordered set has the least upper bound property. For example, the set \mathbb of all rational numbers with its natural order does ''not'' have the least upper bound property. The least-upper-bound property is one form of the completeness axiom for the real numbers, and is sometimes referred to as Dedekind completeness.Willard says that an ordered space "X is Dedekind complete if every subset of X having an upper bound has a least upper bound." (pp. 124-5, Problem 17E.) It can be used to prove many of the fundamental results of real analysis, such as the intermediate value theorem, the Bolzano–Weierstrass theorem, the extreme v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperreals
In mathematics, the system of hyperreal numbers is a way of treating infinite and infinitesimal (infinitely small but non-zero) quantities. The hyperreals, or nonstandard reals, *R, are an extension of the real numbers R that contains numbers greater than anything of the form :1 + 1 + \cdots + 1 (for any finite number of terms). Such numbers are infinite, and their reciprocals are infinitesimals. The term "hyper-real" was introduced by Edwin Hewitt in 1948. The hyperreal numbers satisfy the transfer principle, a rigorous version of Leibniz's heuristic law of continuity. The transfer principle states that true first-order statements about R are also valid in *R. For example, the commutative law of addition, , holds for the hyperreals just as it does for the reals; since R is a real closed field, so is *R. Since \sin()=0 for all integers ''n'', one also has \sin()=0 for all hyperintegers H. The transfer principle for ultrapowers is a consequence of Łoś' theo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
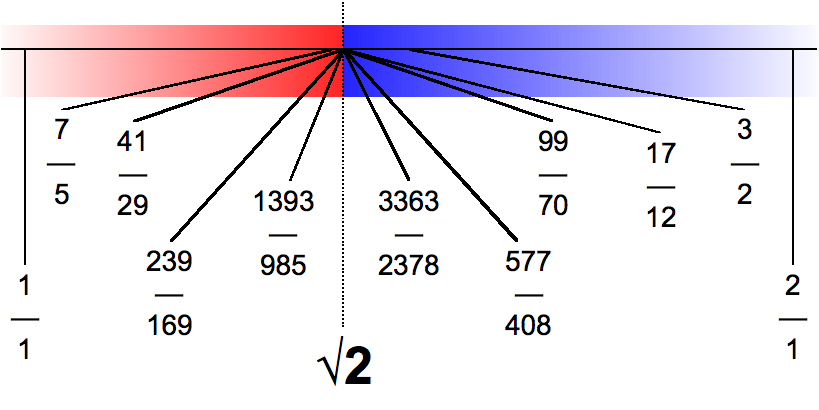
Square Root Of 2
The square root of 2 (approximately 1.4142) is a positive real number that, when multiplied by itself, equals the number 2. It may be written in mathematics as \sqrt or 2^, and is an algebraic number. Technically, it should be called the principal square root of 2, to distinguish it from the negative number with the same property. Geometrically, the square root of 2 is the length of a diagonal across a square with sides of one unit of length; this follows from the Pythagorean theorem. It was probably the first number known to be irrational. The fraction (≈ 1.4142857) is sometimes used as a good rational approximation with a reasonably small denominator. Sequence in the On-Line Encyclopedia of Integer Sequences consists of the digits in the decimal expansion of the square root of 2, here truncated to 65 decimal places: : History The Babylonian clay tablet YBC 7289 (c. 1800–1600 BC) gives an approximation of in four sexagesimal figures, , which is accurate to a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Well-order
In mathematics, a well-order (or well-ordering or well-order relation) on a set ''S'' is a total order on ''S'' with the property that every non-empty subset of ''S'' has a least element in this ordering. The set ''S'' together with the well-order relation is then called a well-ordered set. In some academic articles and textbooks these terms are instead written as wellorder, wellordered, and wellordering or well order, well ordered, and well ordering. Every non-empty well-ordered set has a least element. Every element ''s'' of a well-ordered set, except a possible greatest element, has a unique successor (next element), namely the least element of the subset of all elements greater than ''s''. There may be elements besides the least element which have no predecessor (see below for an example). A well-ordered set ''S'' contains for every subset ''T'' with an upper bound a least upper bound, namely the least element of the subset of all upper bounds of ''T'' in ''S''. If ≤ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integer
An integer is the number zero (), a positive natural number (, , , etc.) or a negative integer with a minus sign ( −1, −2, −3, etc.). The negative numbers are the additive inverses of the corresponding positive numbers. In the language of mathematics, the set of integers is often denoted by the boldface or blackboard bold \mathbb. The set of natural numbers \mathbb is a subset of \mathbb, which in turn is a subset of the set of all rational numbers \mathbb, itself a subset of the real numbers \mathbb. Like the natural numbers, \mathbb is countably infinite. An integer may be regarded as a real number that can be written without a fractional component. For example, 21, 4, 0, and −2048 are integers, while 9.75, , and are not. The integers form the smallest group and the smallest ring containing the natural numbers. In algebraic number theory, the integers are sometimes qualified as rational integers to distinguish them from the more general algebraic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Totally Ordered Set
In mathematics, a total or linear order is a partial order in which any two elements are comparable. That is, a total order is a binary relation \leq on some set X, which satisfies the following for all a, b and c in X: # a \leq a ( reflexive). # If a \leq b and b \leq c then a \leq c ( transitive). # If a \leq b and b \leq a then a = b ( antisymmetric). # a \leq b or b \leq a (strongly connected, formerly called total). Total orders are sometimes also called simple, connex, or full orders. A set equipped with a total order is a totally ordered set; the terms simply ordered set, linearly ordered set, and loset are also used. The term ''chain'' is sometimes defined as a synonym of ''totally ordered set'', but refers generally to some sort of totally ordered subsets of a given partially ordered set. An extension of a given partial order to a total order is called a linear extension of that partial order. Strict and non-strict total orders A on a set X is a strict partial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maximal Element
In mathematics, especially in order theory, a maximal element of a subset ''S'' of some preordered set is an element of ''S'' that is not smaller than any other element in ''S''. A minimal element of a subset ''S'' of some preordered set is defined dually as an element of ''S'' that is not greater than any other element in ''S''. The notions of maximal and minimal elements are weaker than those of greatest element and least element which are also known, respectively, as maximum and minimum. The maximum of a subset S of a preordered set is an element of S which is greater than or equal to any other element of S, and the minimum of S is again defined dually. In the particular case of a partially ordered set, while there can be at most one maximum and at most one minimum there may be multiple maximal or minimal elements. Specializing further to totally ordered sets, the notions of maximal element and maximum coincide, and the notions of minimal element and minimum coincide. As ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |