|
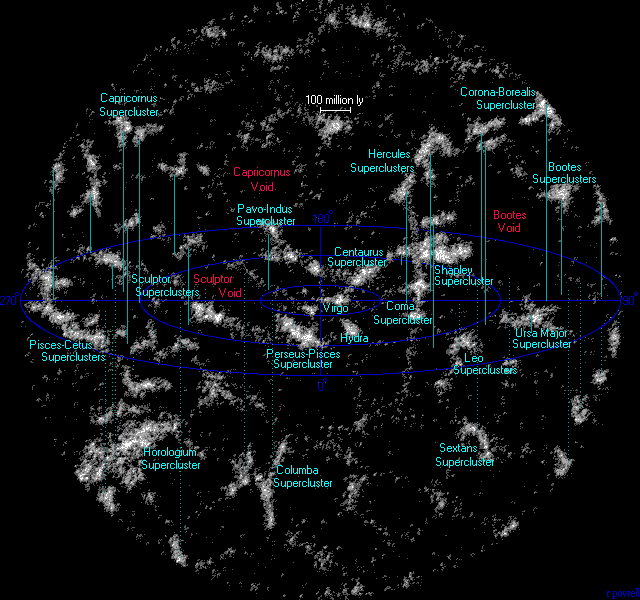
Superclusters
A supercluster is a large group of smaller galaxy clusters or galaxy groups; they are among the largest known structures in the universe. The Milky Way is part of the Local Group galaxy group (which contains more than 54 galaxies), which in turn is part of the Virgo Supercluster, which is part of the Laniakea Supercluster."Earth's new address: 'Solar System, Milky Way, Laniakea '''' The large size and low density of superclusters means that they, unlike clusters, expand with the . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superclusters Atlasoftheuniverse
A supercluster is a large group of smaller galaxy clusters or galaxy groups; they are among the largest known structures in the universe. The Milky Way is part of the Local Group galaxy group (which contains more than 54 galaxies), which in turn is part of the Virgo Supercluster, which is part of the Laniakea Supercluster."Earth's new address: 'Solar System, Milky Way, Laniakea ''Nature (journal), Nature'' The large size and low density of superclusters means that they, unlike clusters, expand with the Hubble expansion. The number of superclusters in the observable universe is estimated to be 10 million. Existence [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
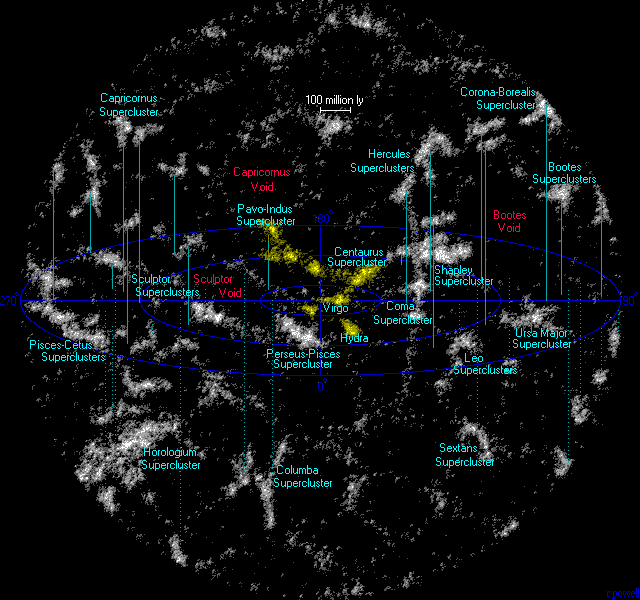
Laniakea Supercluster
The Laniakea Supercluster (; Hawaiian for "open skies" or "immense heaven") is the galaxy supercluster that is home to the Milky Way and approximately 100,000 other nearby galaxies. It was defined in September 2014, when a group of astronomers including R. Brent Tully of the University of Hawaiʻi, Hélène Courtois of the University of Lyon, Yehuda Hoffman of the Hebrew University of Jerusalem, and Daniel Pomarède of CEA Université Paris-Saclay published a new way of defining superclusters according to the relative velocities of galaxies. The new definition of the local supercluster subsumes the prior defined local supercluster, the Virgo Supercluster, as an appendage. Follow-up studies suggest that the Laniakea Supercluster is not gravitationally bound; it will disperse rather than continue to maintain itself as an overdensity relative to surrounding areas. Name The name () means 'immense heaven' in Hawaiian, . The name was suggested by Nawaʻa Napoleon, an assoc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virgo Supercluster
The Virgo Supercluster (Virgo SC) or the Local Supercluster (LSC or LS) is a mass concentration of galaxies containing the Virgo Cluster and Local Group, which itself contains the Milky Way and Andromeda galaxies, as well as others. At least 100 galaxy groups and clusters are located within its diameter of 33 megaparsecs (110 million light-years). The Virgo SC is one of about 10 million superclusters in the observable universe and is in the Pisces–Cetus Supercluster Complex, a galaxy filament. A 2014 study indicates that the Virgo Supercluster is only a lobe of an even greater supercluster, Laniakea, a larger, competing referent of the term Local Supercluster centered on the Great Attractor. Background Beginning with the first large sample of nebulae published by William and John Herschel in 1863, it was known that there is a marked excess of nebular fields in the constellation Virgo (near the north galactic pole). In the 1950s, French–American astronomer Gérard de Vau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pavo–Indus Supercluster
The Pavo-Indus Supercluster is a neighboring supercluster located about away in the constellations of Pavo, Indus, and Telescopium. The supercluster contains three main clusters, Abell 3656, Abell 3698, and Abell 3742. Other groups and clusters in the supercluster include the NGC 6769 Group and Abell S805 (IC 4765 Group, Pavo II, DRCG 1842-63) and the massive Norma Cluster. In 2014 it was announced that the Pavo-Indus Supercluster is a lobe in a greater supercluster, Laniakea, that is centered on the Great Attractor. The Virgo Supercluster would also be part of this greater supercluster, thus becoming the local supercluster. Structure The Pavo-Indus Supercluster exhibits a wall or filamentary structure that extends to a total length of . The supercluster along with the Telescopium−Grus Cloud form parts of a wall bounding the Local Void and the Sculptor Void. Nearby superclusters Centaurus Supercluster In 1983, Winkler. et al suggested based on redshift maps of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Void (astronomy)
Cosmic voids (also known as dark space) are vast spaces between filaments (the largest-scale structures in the universe), which contain very few or no galaxies. The cosmological evolution of the void regions differs drastically from the evolution of the Universe as a whole: there is a long stage when the curvature term dominates, which prevents the formation of galaxy clusters and massive galaxies. Hence, although even the emptiest regions of voids contain more than ~15% of the average matter density of the Universe, the voids look almost empty for an observer. Voids typically have a diameter of 10 to 100 megaparsecs (30 to 300 million light-years); particularly large voids, defined by the absence of rich superclusters, are sometimes called supervoids. They were first discovered in 1978 in a pioneering study by Stephen Gregory and Laird A. Thompson at the Kitt Peak National Observatory. Voids are believed to have been formed by baryon acoustic oscillations in the Big Bang, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Universe
The universe is all of space and time and their contents, including planets, stars, galaxies, and all other forms of matter and energy. The Big Bang theory is the prevailing cosmological description of the development of the universe. According to this theory, space and time emerged together ago, and the universe has been expanding ever since the Big Bang. While the spatial size of the entire universe is unknown, it is possible to measure the size of the observable universe, which is approximately 93 billion light-years in diameter at the present day. Some of the earliest cosmological models of the universe were developed by ancient Greek and Indian philosophers and were geocentric, placing Earth at the center. Over the centuries, more precise astronomical observations led Nicolaus Copernicus to develop the heliocentric model with the Sun at the center of the Solar System. In developing the law of universal gravitation, Isaac Newton built upon Copernicus's work as well ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Observable Universe
The observable universe is a ball-shaped region of the universe comprising all matter that can be observed from Earth or its space-based telescopes and exploratory probes at the present time, because the electromagnetic radiation from these objects has had time to reach the Solar System and Earth since the beginning of the cosmological expansion. There may be 2 trillion galaxies in the observable universe, although that number was reduced in 2021 to only several hundred billion based on data from '' New Horizons''. Assuming the universe is isotropic, the distance to the edge of the observable universe is roughly the same in every direction. That is, the observable universe is a spherical region centered on the observer and is unique for every unique observational position. The word ''observable'' in this sense does not refer to the capability of modern technology to detect light or other information from an object, or whether there is anything to be detected. It refers to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galaxy Filament
In cosmology, galaxy filaments (subtypes: supercluster complexes, galaxy walls, and galaxy sheets) Boris V. Komberg, Andrey V. Kravtsov, Vladimir N. Lukash; "The search and investigation of the Large Groups of Quasars" ; ;R.G. Clowes; "Large Quasar Groups - A Short Review"; ''The New Era of Wide Field Astronomy'', ASP Conference Series, vol. 232.; 2001; Astronomical Society of the Pacific; ; are the largest known structures in the universe, consisting of walls of gravitationally bound galaxy superclusters. These massive, thread-like formations can reach 80 parsec#Megaparsecs and gigaparsecs, megaparsecs ''h''−1 (or of the order of 160 to 260 million light-years) and form the boundaries between large void (astronomy), voids. Formation In the Lambda-CDM model, standard model of the evolution of the universe, galactic filaments form along and follow web-like strings of dark matter—also referred to as the galactic web or cosmic web. It is thought that this dark matter dictates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galaxy Cluster
A galaxy cluster, or a cluster of galaxies, is a structure that consists of anywhere from hundreds to thousands of galaxies that are bound together by gravity, with typical masses ranging from 1014 to 1015 solar masses. They are the second-largest known gravitationally bound structures in the universe after galaxy filaments and were believed to be the largest known structures in the universe until the 1980s, when superclusters were discovered. One of the key features of clusters is the intracluster medium (ICM). The ICM consists of heated gas between the galaxies and has a peak temperature between 2–15 keV that is dependent on the total mass of the cluster. Galaxy clusters should not be confused with ''galactic clusters'' (also known as open clusters), which are star clusters ''within'' galaxies, or with globular clusters, which typically orbit galaxies. Small aggregates of galaxies are referred to as galaxy groups rather than clusters of galaxies. The galaxy groups and c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydra–Centaurus Supercluster
The Hydra-Centaurus Supercluster (SCl 128), or the Hydra and Centaurus Superclusters, is a supercluster in two parts, the closest neighbour of Virgo Supercluster. Hydra-Centaurus The cluster includes four large galaxy clusters in the Centaurus part * Abell 3526 (Centaurus Cluster) * Abell 3565 * Abell 3574 * Abell 3581 and the proximate * Hydra Cluster (A1060) * Antlia Cluster (AS0636) Apart from the central clusters, which are 150 to 200 million light years away, several smaller clusters belong to the group. Within the proximity of this supercluster lies the Great Attractor, dominated by the Norma Cluster (Abell 3627). This massive cluster of galaxies exerts a large gravitational force, causing all matter within 50 Mpc to experience a bulk flow of 600 km/s toward the Norma Cluster Laniakea A 2014 announcement says that the Centaurus Supercluster (Hydra–Centaurus) is just a lobe in a greater supercluster, Laniakea, that is centered on the Great Attractor. That superc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
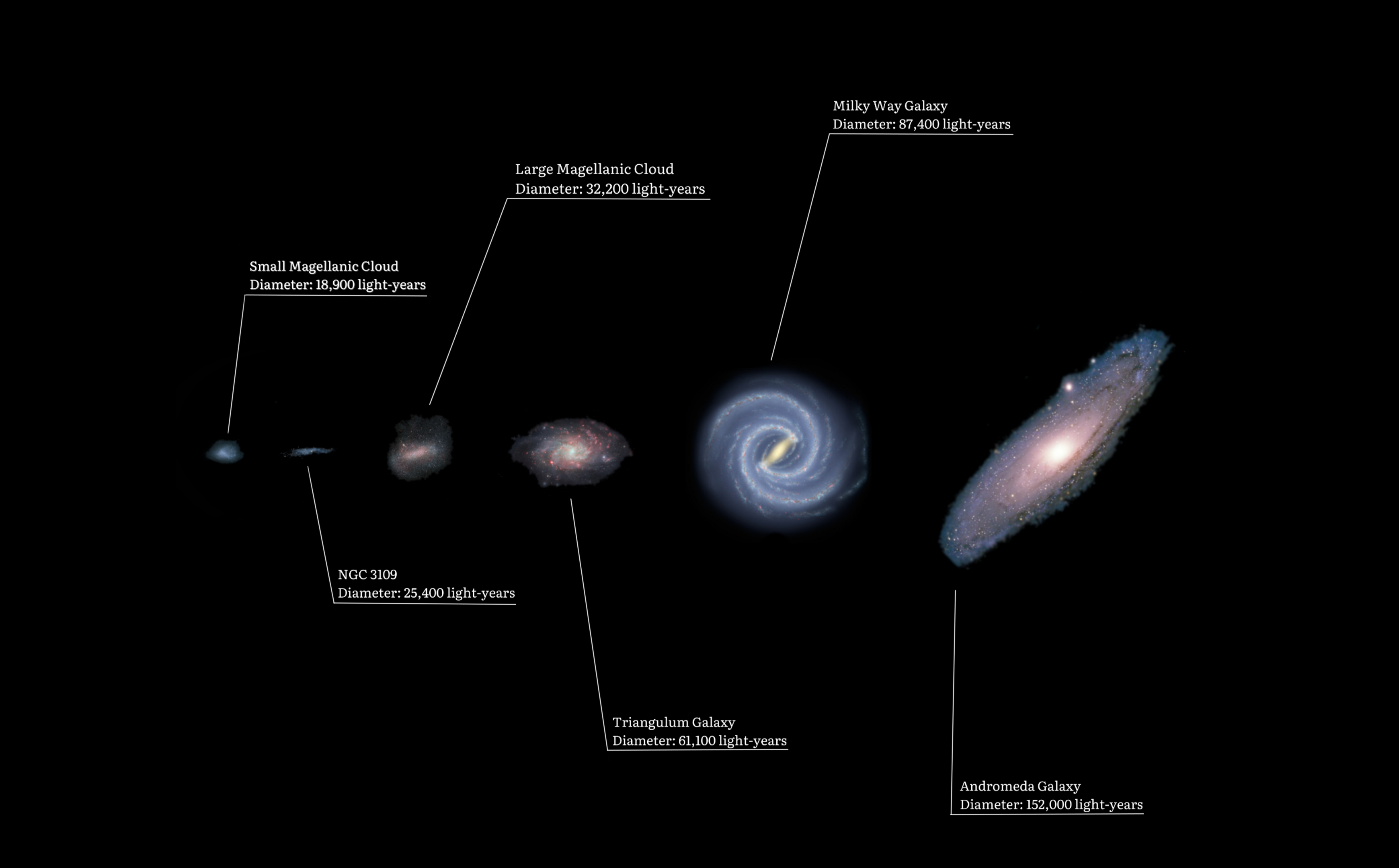
Local Group
The Local Group is the galaxy group that includes the Milky Way. It has a total diameter of roughly , and a total mass of the order of . It consists of two collections of galaxies in a "dumbbell" shape: the Milky Way and its satellites form one lobe, and the Andromeda Galaxy and its satellites constitute the other. The two collections are separated by about and are moving toward one another with a velocity of . The group itself is a part of the larger Virgo Supercluster, which may be a part of the Laniakea Supercluster. The exact number of galaxies in the Local Group is unknown as some are occluded by the Milky Way; however, at least 80 members are known, most of which are dwarf galaxies. The two largest members, the Andromeda Galaxy and the Milky Way, are both spiral galaxies with masses of about solar masses each. Each has its own system of satellite galaxies: * The Andromeda Galaxy's satellite system consists of Messier 32 (M32), Messier 110 (M110), NGC 147, NGC 185, A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sloan Great Wall
The Sloan Great Wall (SGW) is a cosmic structure formed by a giant wall of galaxies (a galaxy filament). Its discovery was announced from Princeton University on October 20, 2003, by J. Richard Gott III, Mario Jurić, and their colleagues, based on data from the Sloan Digital Sky Survey. Size The wall measures in length, located approximately one billion light-years away. In the sky, it is located within the region of the constellations Corvus, Hydra and Centaurus. It is approximately 1/60 of the diameter of the observable universe, making it the sixth largest known object after the large quasar groups Clowes-Campusano LQG, U1.11, Huge-LQG, the Giant GRB Ring and the galaxy filament Hercules–Corona Borealis Great Wall (Her-CrB GW), respectively. The Sloan Great Wall is between 1.8–2.7 times longer than the CfA2 Great Wall of galaxies (discovered by Margaret Geller and John Huchra of Harvard in 1989). It also contains several galactic supercluster A superclus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |