|
Super-enhancer
In genetics, a super-enhancer is a region of the mammalian genome comprising multiple enhancers that is collectively bound by an array of transcription factor proteins to drive transcription of genes involved in cell identity. Because super-enhancers are frequently identified near genes important for controlling and defining cell identity, they may thus be used to quickly identify key nodes regulating cell identity. Enhancers have several quantifiable traits that have a range of values, and these traits are generally elevated at super-enhancers. Super-enhancers are bound by higher levels of transcription-regulating proteins and are associated with genes that are more highly expressed. Expression of genes associated with super-enhancers is particularly sensitive to perturbations, which may facilitate cell state transitions or explain sensitivity of super-enhancer—associated genes to small molecules that target transcription. History The regulation of transcription by enhancers h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enhancer (genetics)
In genetics, an enhancer is a short (50–1500 bp) region of DNA that can be bound by proteins ( activators) to increase the likelihood that transcription of a particular gene will occur. These proteins are usually referred to as transcription factors. Enhancers are ''cis''-acting. They can be located up to 1 Mbp (1,000,000 bp) away from the gene, upstream or downstream from the start site. There are hundreds of thousands of enhancers in the human genome. They are found in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. The first discovery of a eukaryotic enhancer was in the immunoglobulin heavy chain gene in 1983. This enhancer, located in the large intron, provided an explanation for the transcriptional activation of rearranged Vh gene promoters while unrearranged Vh promoters remained inactive. Locations In eukaryotic cells the structure of the chromatin complex of DNA is folded in a way that functionally mimics the supercoiled state characteristic of prokaryotic DNA, so although the en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mediator (coactivator)
Mediator is a multiprotein complex that functions as a transcriptional coactivator in all eukaryotes. It was discovered in 1990 in the lab of Roger D. Kornberg, recipient of the 2006 Nobel Prize in Chemistry. Mediator complexes interact with transcription factors and RNA polymerase II. The main function of mediator complexes is to transmit signals from the transcription factors to the polymerase. Mediator complexes are variable at the evolutionary, compositional and conformational levels. The first image shows only one "snapshot" of what a particular mediator complex might be composed of, but it certainly does not accurately depict the conformation of the complex ''in vivo''. During evolution, mediator has become more complex. The yeast ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' (a simple eukaryote) is thought to have up to 21 subunits in the core mediator (exclusive of the CDK module), while mammals have up to 26. Individual subunits can be absent or replaced by other subunits under differen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleosome
A nucleosome is the basic structural unit of DNA packaging in eukaryotes. The structure of a nucleosome consists of a segment of DNA wound around eight histone proteins and resembles thread wrapped around a spool. The nucleosome is the fundamental subunit of chromatin. Each nucleosome is composed of a little less than two turns of DNA wrapped around a set of eight proteins called histones, which are known as a histone octamer. Each histone octamer is composed of two copies each of the histone proteins H2A, H2B, H3, and H4. DNA must be compacted into nucleosomes to fit within the cell nucleus. In addition to nucleosome wrapping, eukaryotic chromatin is further compacted by being folded into a series of more complex structures, eventually forming a chromosome. Each human cell contains about 30 million nucleosomes. Nucleosomes are thought to carry epigenetically inherited information in the form of covalent modifications of their core histones. Nucleosome positions in the gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
H3K27ac
H3K27ac is an epigenetic modification to the DNA packaging protein histone H3. It is a mark that indicates acetylation of the lysine residue at N-terminal position 27 of the histone H3 protein. H3K27ac is associated with the higher activation of transcription and therefore defined as an ''active enhancer'' mark. H3K27ac is found at both proximal and distal regions of transcription start site (TSS). Lysine acetylation and deacetylation Proteins are typically acetylated on lysine residues, and the acetylation reaction relies on acetyl-coenzyme A as the acetyl group donor. In histone acetylation and deacetylation, histone proteins are acetylated and deacetylated on lysine residues in the N-terminal tail as part of gene regulation. Typically, these reactions are catalyzed by enzymes with ''histone acetyltransferase'' (HAT) or ''histone deacetylase'' (HDAC) activity, although HATs and HDACs can modify the acetylation status of non-histone proteins as well. The regulation of tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ChIP-sequencing
ChIP-sequencing, also known as ChIP-seq, is a method used to analyze protein interactions with DNA. ChIP-seq combines chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) with massively parallel DNA sequencing to identify the binding sites of DNA-associated proteins. It can be used to map global binding sites precisely for any protein of interest. Previously, ChIP-on-chip was the most common technique utilized to study these protein–DNA relations. Uses ChIP-seq is primarily used to determine how transcription factors and other chromatin-associated proteins influence phenotype-affecting mechanisms. Determining how proteins interact with DNA to regulate gene expression is essential for fully understanding many biological processes and disease states. This epigenetic information is complementary to genotype and expression analysis. ChIP-seq technology is currently seen primarily as an alternative to ChIP-chip which requires a hybridization array. This introduces some bias, as an array is restrict ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biomarker
In biomedical contexts, a biomarker, or biological marker, is a measurable indicator of some biological state or condition. Biomarkers are often measured and evaluated using blood, urine, or soft tissues to examine normal biological processes, pathogenic processes, or pharmacologic responses to a therapeutic intervention. as cited in Biomarkers are used in many scientific fields. Medicine Biomarkers used in the medical field, are a part of a relatively new clinical toolset categorized by their clinical applications. The three main classes are molecular biomarkers, cellular biomarkers or imaging biomarkers. All three types of biomarkers have a clinical role in narrowing or guiding treatment decisions and follow a sub-categorization of being either predictive, prognostic, or diagnostic. Predictive Predictive molecular, cellular, or imaging biomarkers that pass validation can serve as a method of predicting clinical outcomes. Predictive biomarkers are used to help optimize id ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Class Switching
Immunoglobulin class switching, also known as isotype switching, isotypic commutation or class-switch recombination (CSR), is a biological mechanism that changes a B cell's production of immunoglobulin from one type to another, such as from the isotype IgM to the isotype IgG. During this process, the constant-region portion of the antibody heavy chain is changed, but the variable region of the heavy chain stays the same (the terms ''variable'' and ''constant'' refer to changes or lack thereof between antibodies that target different epitopes). Since the variable region does not change, class switching does not affect antigen specificity. Instead, the antibody retains affinity for the same antigens, but can interact with different effector molecules. Mechanism Class switching occurs after activation of a mature B cell via its membrane-bound antibody molecule (or B cell receptor) to generate the different classes of antibody, all with the same variable domains as the origin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
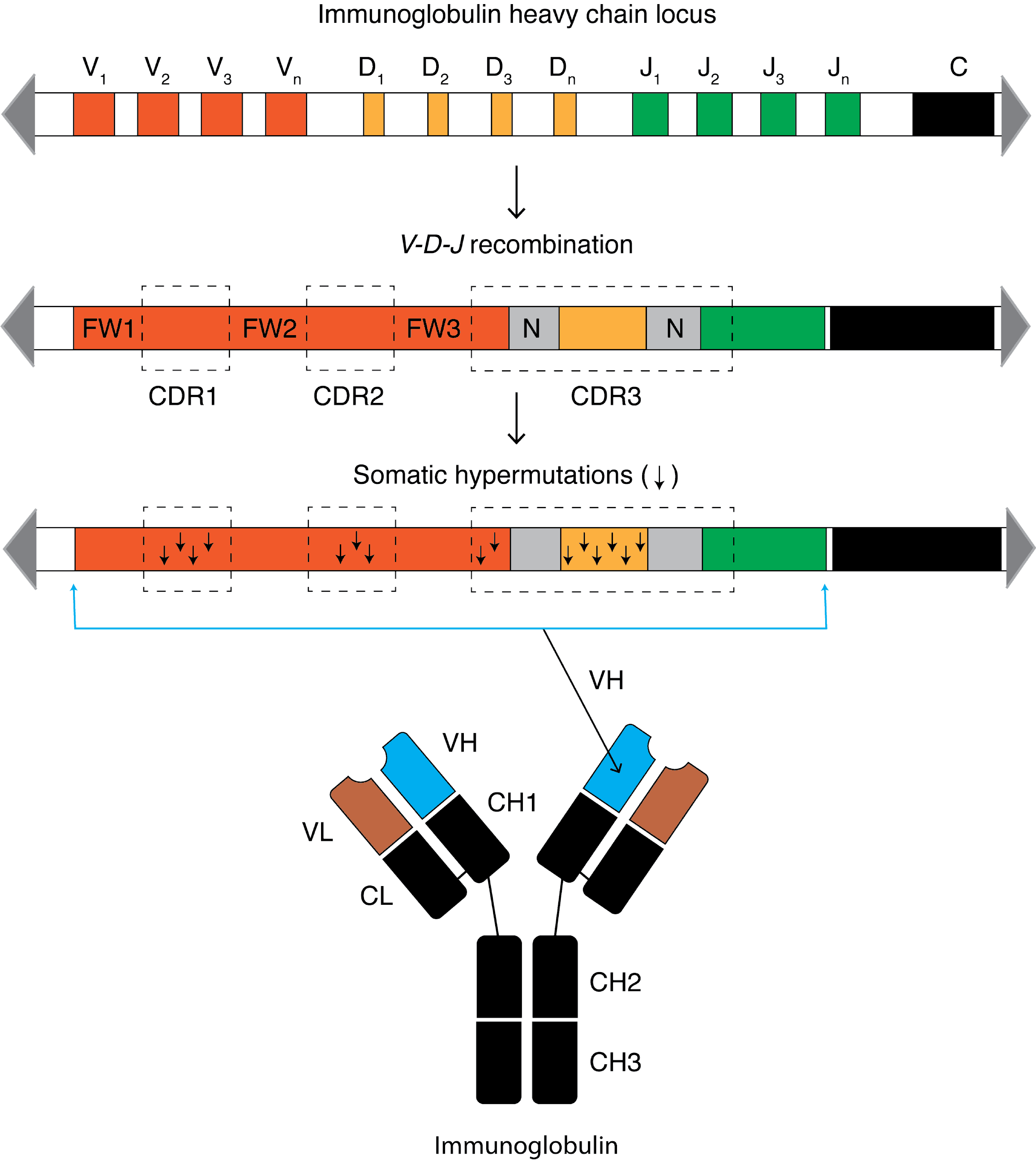
Somatic Hypermutation
Somatic hypermutation (or SHM) is a cellular mechanism by which the immune system adapts to the new foreign elements that confront it (e.g. microbes), as seen during class switching. A major component of the process of affinity maturation, SHM diversifies B cell receptors used to recognize foreign elements (antigens) and allows the immune system to adapt its response to new threats during the lifetime of an organism. Somatic hypermutation involves a programmed process of mutation affecting the variable regions of immunoglobulin genes. Unlike germline mutation, SHM affects only an organism's individual immune cells, and the mutations are not transmitted to the organism's offspring.Oprea, M. (1999''Antibody Repertoires and Pathogen Recognition:'' The Role of Germline Diversity and Somatic Hypermutation'' (Thesis) University of Leeds.'' Because this mechanism is merely selective and not precisely targeted, somatic hypermutation has been strongly implicated in the development of B-cell l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunoglobulins
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique molecule of the pathogen, called an antigen. Each tip of the "Y" of an antibody contains a paratope (analogous to a lock) that is specific for one particular epitope (analogous to a key) on an antigen, allowing these two structures to bind together with precision. Using this binding mechanism, an antibody can ''tag'' a microbe or an infected cell for attack by other parts of the immune system, or can neutralize it directly (for example, by blocking a part of a virus that is essential for its invasion). To allow the immune system to recognize millions of different antigens, the antigen-binding sites at both tips of the antibody come in an equally wide variety. In contrast, the remainder of the antibody is relatively constant. It only occurs in a few varian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Notch Signaling Pathway
The Notch signaling pathway is a highly Conserved sequence, conserved cell signaling system present in most animals. Mammals possess four different Notch proteins, notch receptors, referred to as NOTCH1, NOTCH2, Notch 3, NOTCH3, and NOTCH4. The notch receptor is a single-pass Cell surface receptor, transmembrane receptor protein. It is a hetero-oligomer composed of a large extracellular portion, which associates in a calcium-dependent, non-covalent interaction with a smaller piece of the notch protein composed of a short extracellular region, a single transmembrane-pass, and a small intracellular region. Notch signaling promotes proliferative signaling during neurogenesis, and its activity is inhibited by NUMB (gene), Numb to promote neural differentiation. It plays a major role in the regulation of embryonic development. Notch signaling is dysregulated in many cancers, and faulty notch signaling is implicated in many diseases, including T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (Pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brain-derived Neurotrophic Factor
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), or abrineurin, is a protein found in the and the periphery. that, in humans, is encoded by the ''BDNF'' gene. BDNF is a member of the neurotrophin family of growth factors, which are related to the canonical nerve growth factor (NGF), a family which also includes NT-3 and NT-4/NT-5. Neurotrophic factors are found in the brain and the periphery. BDNF was first isolated from a pig brain in 1982 by Yves-Alain Barde and Hans Thoenen. BDNF activates the TrkB tyrosine kinase receptor. Function BDNF acts on certain neurons of the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system expressing TrkB, helping to support survival of existing neurons, and encouraging growth and differentiation of new neurons and synapses. In the brain it is active in the hippocampus, cortex, and basal forebrain—areas vital to learning, memory, and higher thinking. BDNF is also expressed in the retina, kidneys, prostate, motor neurons, and skeletal musc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leukemia Inhibitory Factor
Leukemia inhibitory factor, or LIF, is an interleukin 6 class cytokine that affects cell growth by inhibiting differentiation. When LIF levels drop, the cells differentiate. Function LIF derives its name from its ability to induce the terminal differentiation of myeloid leukemic cells, thus preventing their continued growth. Other properties attributed to the cytokine include: the growth promotion and cell differentiation of different types of target cells, influence on bone metabolism, cachexia, neural development, embryogenesis and inflammation. p53 regulated LIF has been shown to facilitate implantation in the mouse model and possibly in humans. It has been suggested that recombinant human LIF might help to improve the implantation rate in women with unexplained infertility. Binding/activation LIF binds to the specific LIF receptor ( LIFR-α) which forms a heterodimer with a specific subunit common to all members of that family of receptors, the GP130 signal transducing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |