|
Sulfoxylic Acid
Sulfoxylic acid (H2SO2) (also known as hyposulfurous acid or sulfur dihydroxide) is an unstable oxoacid of sulfur in an intermediate oxidation state between hydrogen sulfide and dithionous acid. It consists of two hydroxy groups attached to a sulfur atom. Sulfoxylic acid contains sulfur in an oxidation state of +2. Sulfur monoxide (SO) can be considered as a theoretical anhydride for sulfoxylic acid, but it is not actually known to react with water. The complementary base is the sulfoxylate anion which is much more stable. In between these states is the ion, also somewhat stable. Sulfoxylate ions can be made by decomposing thiourea dioxide in an alkaline solution. To do this, thiourea dioxide first forms a tautomer, aminoiminomethanesulfinic acid (H2NC(=NH)SO2H, abbreviated AIMS) which breaks apart. Sulfoxylate reacts with formaldehyde to yield a hydroxymethanesulfinate called rongalite: : + H2CO → which is an important chemical for dyeing. Formation Sulfoxylic acid has been d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
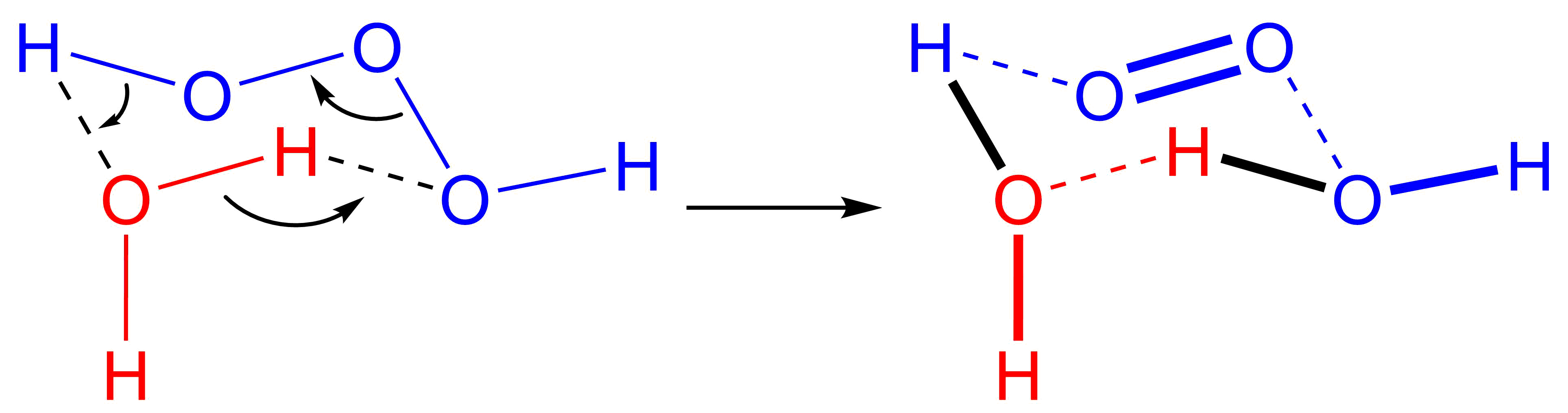
Trioxidane
Trioxidane (systematically named μ-trioxidanediidodihydrogen), also called dihydrogen trioxide, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula (can be written as or ). It is one of the unstable hydrogen polyoxides. In aqueous solutions, trioxidane decomposes to form water and singlet oxygen: The reverse reaction, the addition of singlet oxygen to water, typically does not occur in part due to the scarcity of singlet oxygen. In biological systems, however, ozone is known to be generated from singlet oxygen, and the presumed mechanism is an antibody-catalyzed production of trioxidane from singlet oxygen. Preparation Trioxidane can be obtained in small, but detectable, amounts in reactions of ozone and hydrogen peroxide, or by the electrolysis of water. Larger quantities have been prepared by the reaction of ozone with organic reducing agents at low temperatures in a variety of organic solvents, such as the anthraquinone process. It is also formed during the decomposition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polysulfide
Polysulfides are a class of chemical compounds containing chains of sulfur atoms. There are two main classes of polysulfides: inorganic and organic. Among the inorganic polysulfides, there are ones which contain anions, which have the general formula . These anions are the conjugate bases of the hydrogen polysulfides . Organic polysulfides generally have the formulae , where R = alkyl or aryl. Polysulfide salts and complexes The alkali metal polysulfides arise by treatment of a solution of sulfide, e.g. sodium sulfide, with elemental sulfur: : In some cases, these anions have been obtained as organic salts, which are soluble in organic solvents. The energy released in the reaction of sodium and elemental sulfur is the basis of battery technology. The sodium–sulfur battery and the lithium–sulfur battery require high temperatures to maintain liquid polysulfide and -conductive membranes that are unreactive toward sodium, sulfur, and sodium sulfide. Polysulfides are ligands i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
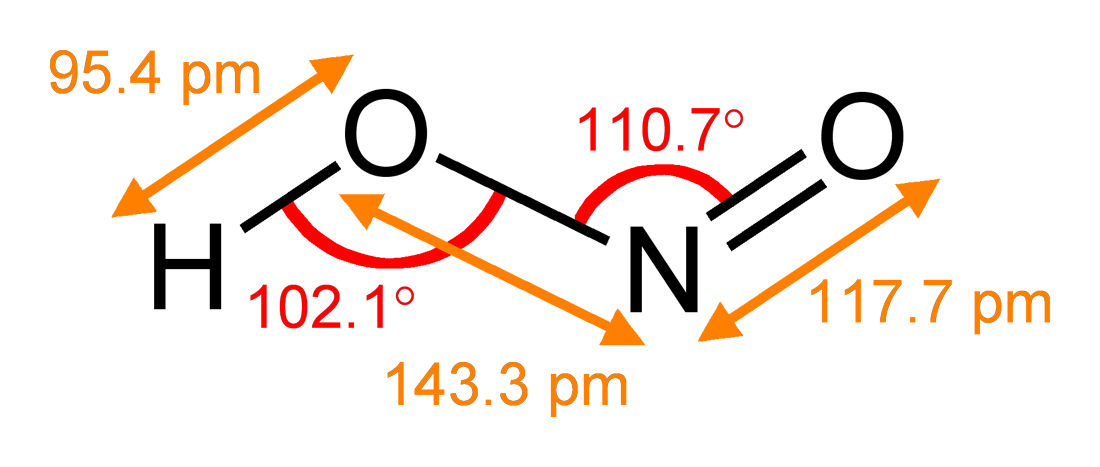
Nitrite
The nitrite polyatomic ion, ion has the chemical formula . Nitrite (mostly sodium nitrite) is widely used throughout chemical and pharmaceutical industries. The nitrite anion is a pervasive intermediate in the nitrogen cycle in nature. The name nitrite also refers to organic compounds having the –ONO group, which are esters of nitrous acid. Production Sodium nitrite is made industrially by passing a mixture of nitrogen oxides into aqueous sodium hydroxide or sodium carbonate solution: : The product is purified by recrystallization. Alkali metal nitrites are thermally stable up to and beyond their melting point (441 °C for KNO2). Ammonium nitrite can be made from dinitrogen trioxide, N2O3, which is formally the anhydride of nitrous acid: :2 NH3 + H2O + N2O3 → 2 NH4NO2 Structure The nitrite ion has a symmetrical structure (C2v molecular point group, symmetry), with both N–O bonds having equal length and a bond angle of about 115°. In valence bond theory, it is des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dithionite
The dithionite is the oxyanion with the formula 2O4sup>2−. It is commonly encountered as the salt sodium dithionite. For historical reasons, it is sometimes called hydrosulfite, but it contains no hydrogen and is not a sulfite. The dianion has a steric number of 4 and trigonal pyramidal geometry. Production and reactions In its main applications, dithionite is generally prepared in situ by reduction of sulfur dioxide by sodium borohydride, described by the following idealized equation:. : Dithionite is a reducing agent. At pH 7, the potential is −0.66 V vs NHE. Redox occurs with formation of sulfite: : + 2 H2O → 2 + 2 e− + 2 H+ Dithionite undergoes acid hydrolytic disproportionation to thiosulfate and bisulfite: :2 + H2O → + 2 It also undergoes alkaline hydrolytic disproportionation to sulfite and sulfide: :3 Na2S2O4 + 6 NaOH → 5 Na2SO3 + Na2S + 3 H2O It is formally derived from dithionous acid (H2S2O4), but this acid does not exist i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfur Dioxide Radical Anion
Sulfur (or sulphur in British English) is a chemical element with the symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with a chemical formula S8. Elemental sulfur is a bright yellow, crystalline solid at room temperature. Sulfur is the tenth most abundant element by mass in the universe and the fifth most on Earth. Though sometimes found in pure, native form, sulfur on Earth usually occurs as sulfide and sulfate minerals. Being abundant in native form, sulfur was known in ancient times, being mentioned for its uses in ancient India, ancient Greece, China, and ancient Egypt. Historically and in literature sulfur is also called brimstone, which means "burning stone". Today, almost all elemental sulfur is produced as a byproduct of removing sulfur-containing contaminants from natural gas and petroleum.. Downloahere The greatest commercial use of the element is the production of su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfite
Sulfites or sulphites are compounds that contain the sulfite ion (or the sulfate(IV) ion, from its correct systematic name), . The sulfite ion is the conjugate base of bisulfite. Although its acid ( sulfurous acid) is elusive, its salts are widely used. Sulfites are substances that naturally occur in some foods and the human body. They are also used as regulated food additives. When in food or drink, sulfites are often lumped together with sulfur dioxide.SeREGULATION (EU) No 1169/2011 OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND OF THE COUNCIL/ref> Structure The structure of the sulfite anion can be described with three equivalent resonance structures. In each resonance structure, the sulfur atom is double-bonded to one oxygen atom with a formal charge of zero (neutral), and sulfur is singly bonded to the other two oxygen atoms, which each carry a formal charge of −1, together accounting for the −2 charge on the anion. There is also a non-bonded lone pair on the sulfur, so the structu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-ray Absorption Near Edge Structure
X-ray absorption near edge structure (XANES), also known as near edge X-ray absorption fine structure (NEXAFS), is a type of absorption spectroscopy that indicates the features in the X-ray absorption spectra ( XAS) of condensed matter due to the photoabsorption cross section for electronic transitions from an atomic core level to final states in the energy region of 50–100 eV above the selected atomic core level ionization energy, where the wavelength of the photoelectron is larger than the interatomic distance between the absorbing atom and its first neighbour atoms. Terminology Both XANES and NEXAFS are acceptable terms for the same technique. XANES name was invented in 1980 by Antonio Bianconi to indicate strong absorption peaks in X-ray absorption spectra in condensed matter due to multiple scattering resonances above the ionization energy. The name NEXAFS was introduced in 1983 by Jo Stohr and is synonymous with XANES, but is generally used when applied to surface and mol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dihydrogen Sulfone
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, and highly combustible. Hydrogen is the most abundant chemical substance in the universe, constituting roughly 75% of all normal matter.However, most of the universe's mass is not in the form of baryons or chemical elements. See dark matter and dark energy. Stars such as the Sun are mainly composed of hydrogen in the plasma state. Most of the hydrogen on Earth exists in molecular forms such as water and organic compounds. For the most common isotope of hydrogen (symbol 1H) each atom has one proton, one electron, and no neutrons. In the early universe, the formation of protons, the nuclei of hydrogen, occurred during the first second after the Big Bang. The emergence of neutral hydrogen atoms throughout the universe occurred about 370,00 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, and highly combustible. Hydrogen is the most abundant chemical substance in the universe, constituting roughly 75% of all normal matter.However, most of the universe's mass is not in the form of baryons or chemical elements. See dark matter and dark energy. Stars such as the Sun are mainly composed of hydrogen in the plasma state. Most of the hydrogen on Earth exists in molecular forms such as water and organic compounds. For the most common isotope of hydrogen (symbol 1H) each atom has one proton, one electron, and no neutrons. In the early universe, the formation of protons, the nuclei of hydrogen, occurred during the first second after the Big Bang. The emergence of neutral hydrogen atoms throughout the universe occurred about 370,000 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neon
Neon is a chemical element with the symbol Ne and atomic number 10. It is a noble gas. Neon is a colorless, odorless, inert monatomic gas under standard conditions, with about two-thirds the density of air. It was discovered (along with krypton and xenon) in 1898 as one of the three residual rare inert elements remaining in dry air, after nitrogen, oxygen, argon and carbon dioxide were removed. Neon was the second of these three rare gases to be discovered and was immediately recognized as a new element from its bright red emission spectrum. The name neon is derived from the Greek word, , neuter singular form of (), meaning 'new'. Neon is chemically inert, and no uncharged neon compounds are known. The compounds of neon currently known include ionic molecules, molecules held together by van der Waals forces and clathrates. During cosmic nucleogenesis of the elements, large amounts of neon are built up from the alpha-capture fusion process in stars. Although neon is a very co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |